| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230747 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 7 Pages |
•Selection of basis sets and relativistic effective core potentials (RECPs) of Te and S atoms.•Computation of MRDCI calculations without and with considering effect of spin–orbit coupling.•Construction of potential energy curves without and with spin–orbit effect.•Computation of spectroscopic constants without and with spin–orbit effect.•Computation of transition probabilities of some transitions and dipole moments.
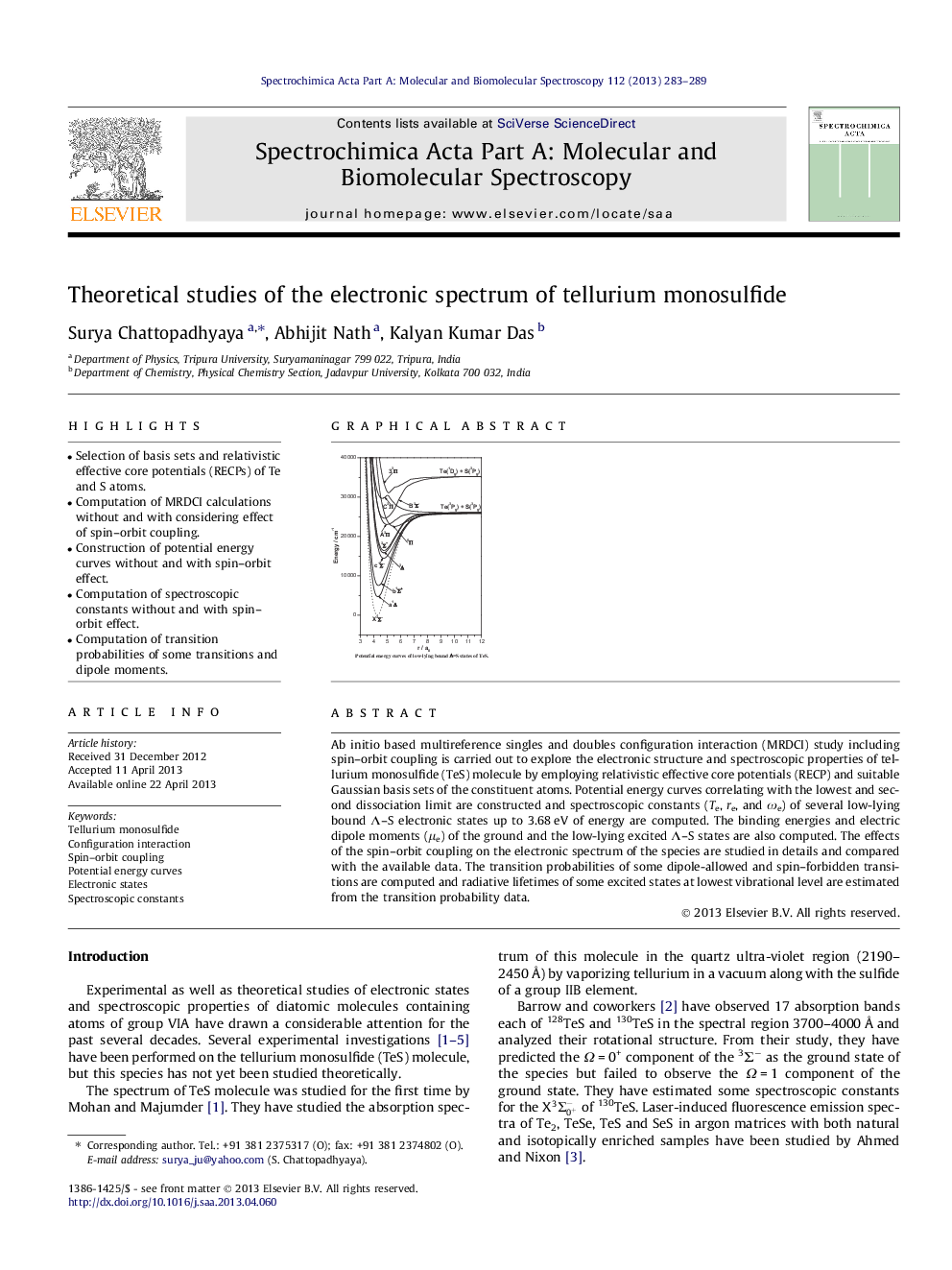
Ab initio based multireference singles and doubles configuration interaction (MRDCI) study including spin–orbit coupling is carried out to explore the electronic structure and spectroscopic properties of tellurium monosulfide (TeS) molecule by employing relativistic effective core potentials (RECP) and suitable Gaussian basis sets of the constituent atoms. Potential energy curves correlating with the lowest and second dissociation limit are constructed and spectroscopic constants (Te, re, and ωe) of several low-lying bound Λ–S electronic states up to 3.68 eV of energy are computed. The binding energies and electric dipole moments (μe) of the ground and the low-lying excited Λ–S states are also computed. The effects of the spin–orbit coupling on the electronic spectrum of the species are studied in details and compared with the available data. The transition probabilities of some dipole-allowed and spin–forbidden transitions are computed and radiative lifetimes of some excited states at lowest vibrational level are estimated from the transition probability data.
Graphical abstractPotential energy curves of low-lying bound Λ–S states of TeS.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide