| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230749 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 8 Pages |
•A novel oxide glass composition based on Bi2O3–GeO2–ZnO system is reported.•This oxide host glass exhibits phonon energy of 707 cm−1.•Optimized Yb3+ and Ho3+ concentration exhibited ηET of 65.92%.•Observed sensitized 2 μm emission is suitable for broad band tunable lasers.•2 μm emission combines with high ηET, moderately high σem and larger Δλeff.
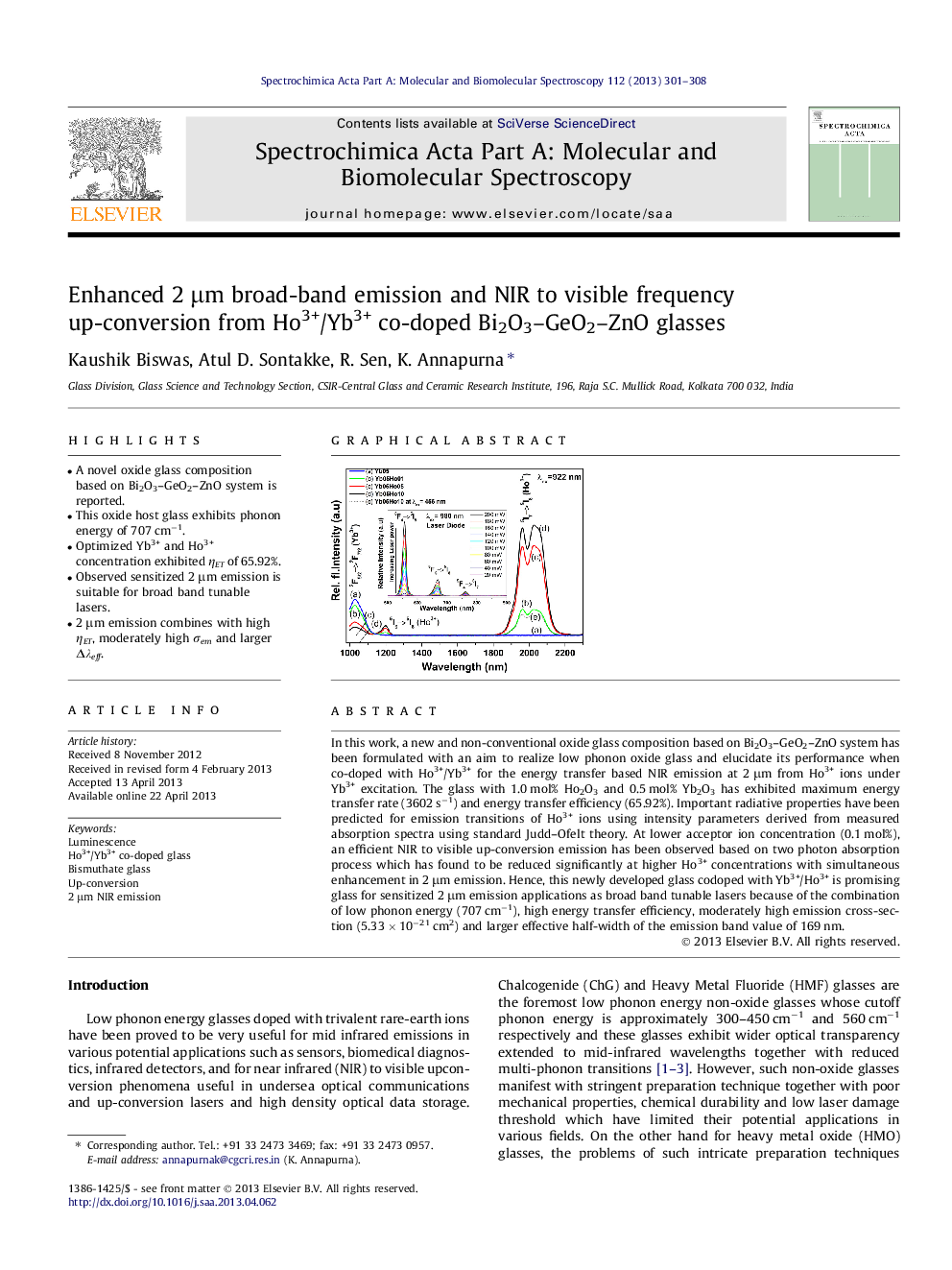
In this work, a new and non-conventional oxide glass composition based on Bi2O3–GeO2–ZnO system has been formulated with an aim to realize low phonon oxide glass and elucidate its performance when co-doped with Ho3+/Yb3+ for the energy transfer based NIR emission at 2 μm from Ho3+ ions under Yb3+ excitation. The glass with 1.0 mol% Ho2O3 and 0.5 mol% Yb2O3 has exhibited maximum energy transfer rate (3602 s−1) and energy transfer efficiency (65.92%). Important radiative properties have been predicted for emission transitions of Ho3+ ions using intensity parameters derived from measured absorption spectra using standard Judd–Ofelt theory. At lower acceptor ion concentration (0.1 mol%), an efficient NIR to visible up-conversion emission has been observed based on two photon absorption process which has found to be reduced significantly at higher Ho3+ concentrations with simultaneous enhancement in 2 μm emission. Hence, this newly developed glass codoped with Yb3+/Ho3+ is promising glass for sensitized 2 μm emission applications as broad band tunable lasers because of the combination of low phonon energy (707 cm−1), high energy transfer efficiency, moderately high emission cross-section (5.33 × 10−21 cm2) and larger effective half-width of the emission band value of 169 nm.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide