| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230872 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 6 Pages |
•Interactions of clenbuterol with BSA and LYS were studied by fluorescence quenching.•Hydrophobic and electrostatic forces were the major forces in the two systems.•Synchronous fluorescence was performed to analyze the conformational changes.•Energy transfer occurred between clenbuterol and the two proteins.
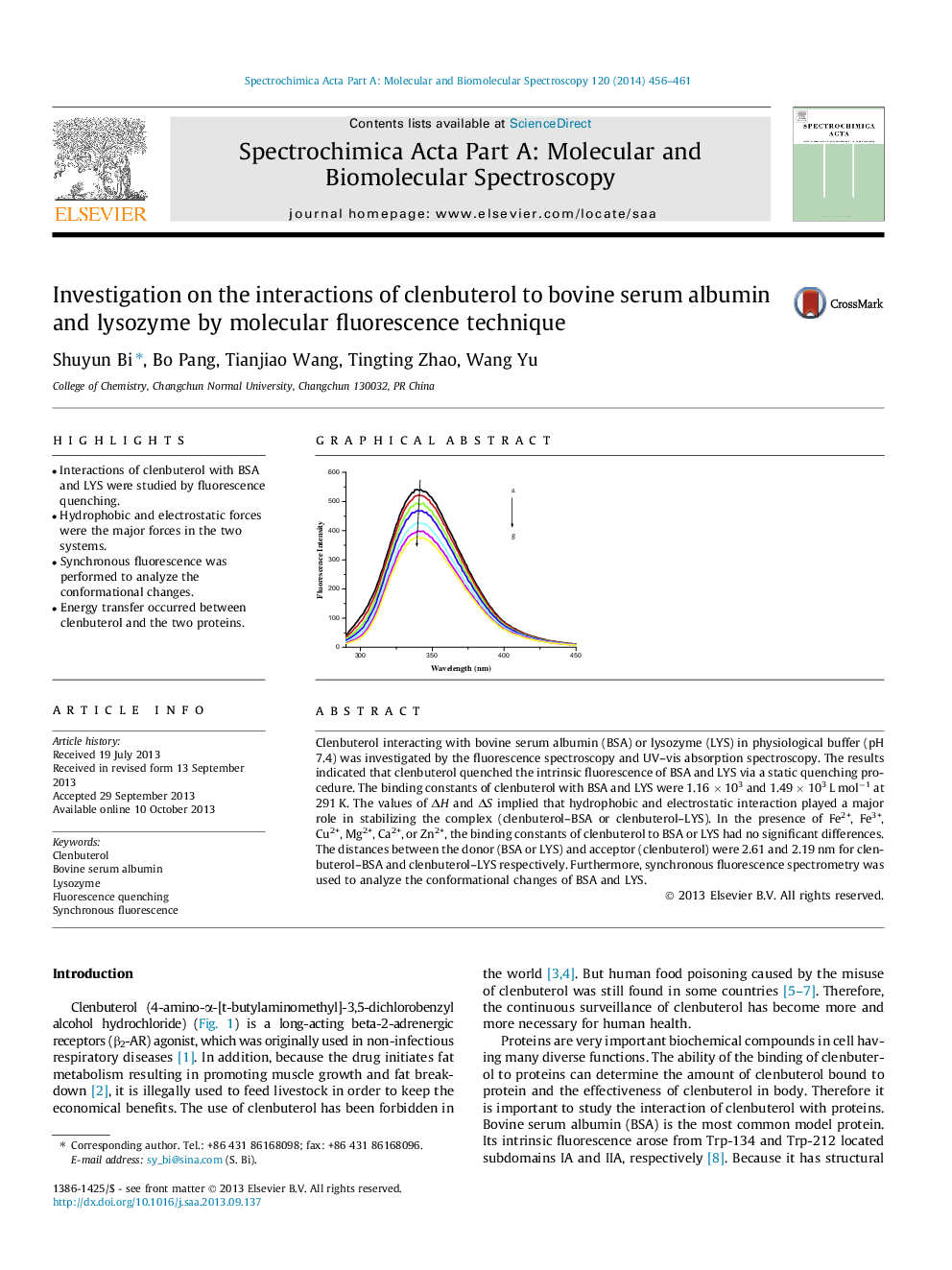
Clenbuterol interacting with bovine serum albumin (BSA) or lysozyme (LYS) in physiological buffer (pH 7.4) was investigated by the fluorescence spectroscopy and UV–vis absorption spectroscopy. The results indicated that clenbuterol quenched the intrinsic fluorescence of BSA and LYS via a static quenching procedure. The binding constants of clenbuterol with BSA and LYS were 1.16 × 103 and 1.49 × 103 L mol−1 at 291 K. The values of ΔH and ΔS implied that hydrophobic and electrostatic interaction played a major role in stabilizing the complex (clenbuterol–BSA or clenbuterol–LYS). In the presence of Fe2+, Fe3+, Cu2+, Mg2+, Ca2+, or Zn2+, the binding constants of clenbuterol to BSA or LYS had no significant differences. The distances between the donor (BSA or LYS) and acceptor (clenbuterol) were 2.61 and 2.19 nm for clenbuterol–BSA and clenbuterol–LYS respectively. Furthermore, synchronous fluorescence spectrometry was used to analyze the conformational changes of BSA and LYS.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide