| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1230884 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 8 Pages |
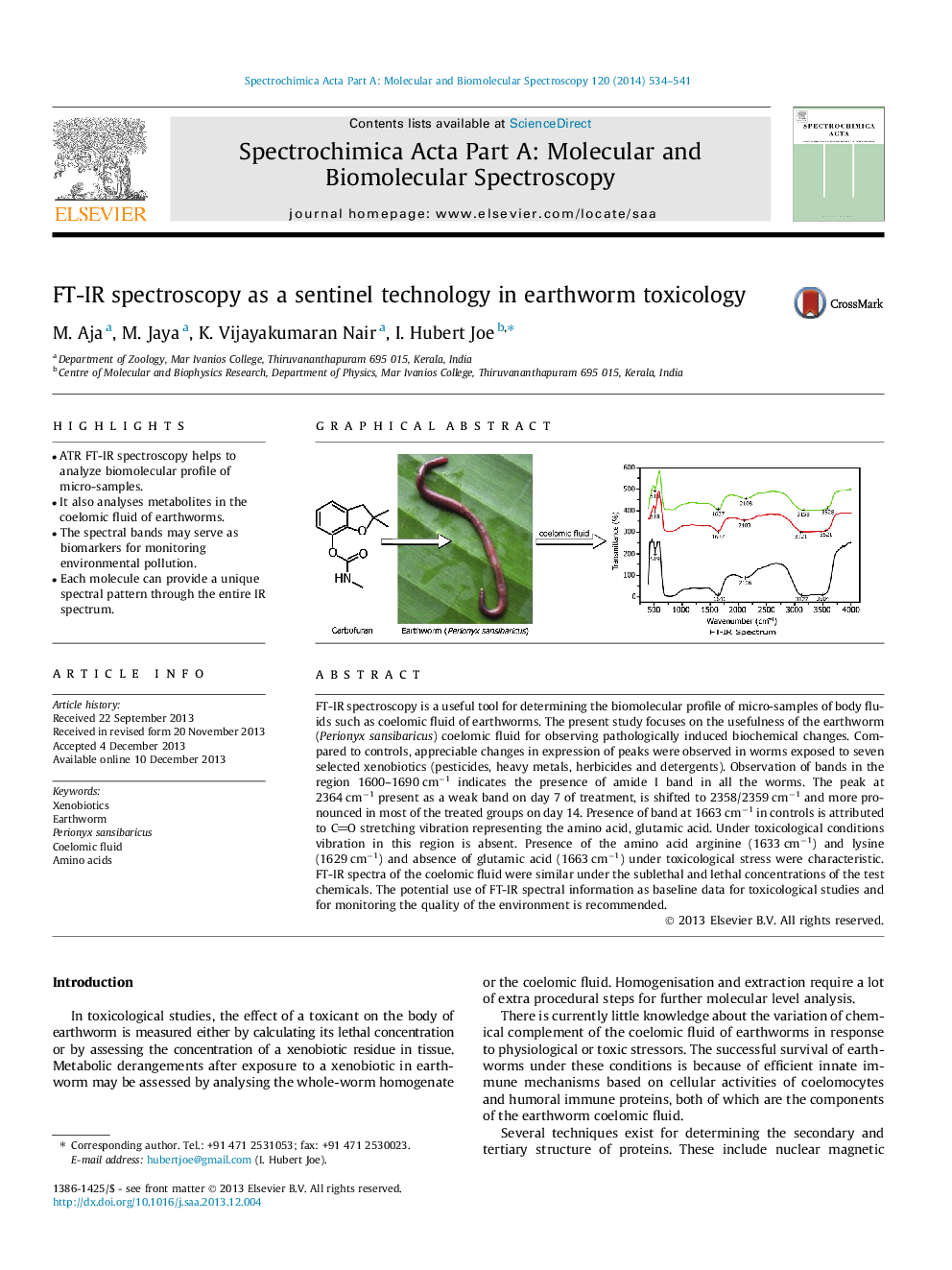
•ATR FT-IR spectroscopy helps to analyze biomolecular profile of micro-samples.•It also analyses metabolites in the coelomic fluid of earthworms.•The spectral bands may serve as biomarkers for monitoring environmental pollution.•Each molecule can provide a unique spectral pattern through the entire IR spectrum.
FT-IR spectroscopy is a useful tool for determining the biomolecular profile of micro-samples of body fluids such as coelomic fluid of earthworms. The present study focuses on the usefulness of the earthworm (Perionyx sansibaricus) coelomic fluid for observing pathologically induced biochemical changes. Compared to controls, appreciable changes in expression of peaks were observed in worms exposed to seven selected xenobiotics (pesticides, heavy metals, herbicides and detergents). Observation of bands in the region 1600–1690 cm−1 indicates the presence of amide I band in all the worms. The peak at 2364 cm−1 present as a weak band on day 7 of treatment, is shifted to 2358/2359 cm−1 and more pronounced in most of the treated groups on day 14. Presence of band at 1663 cm−1 in controls is attributed to CO stretching vibration representing the amino acid, glutamic acid. Under toxicological conditions vibration in this region is absent. Presence of the amino acid arginine (1633 cm−1) and lysine (1629 cm−1) and absence of glutamic acid (1663 cm−1) under toxicological stress were characteristic. FT-IR spectra of the coelomic fluid were similar under the sublethal and lethal concentrations of the test chemicals. The potential use of FT-IR spectral information as baseline data for toxicological studies and for monitoring the quality of the environment is recommended.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide