| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1231103 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2012 | 7 Pages |
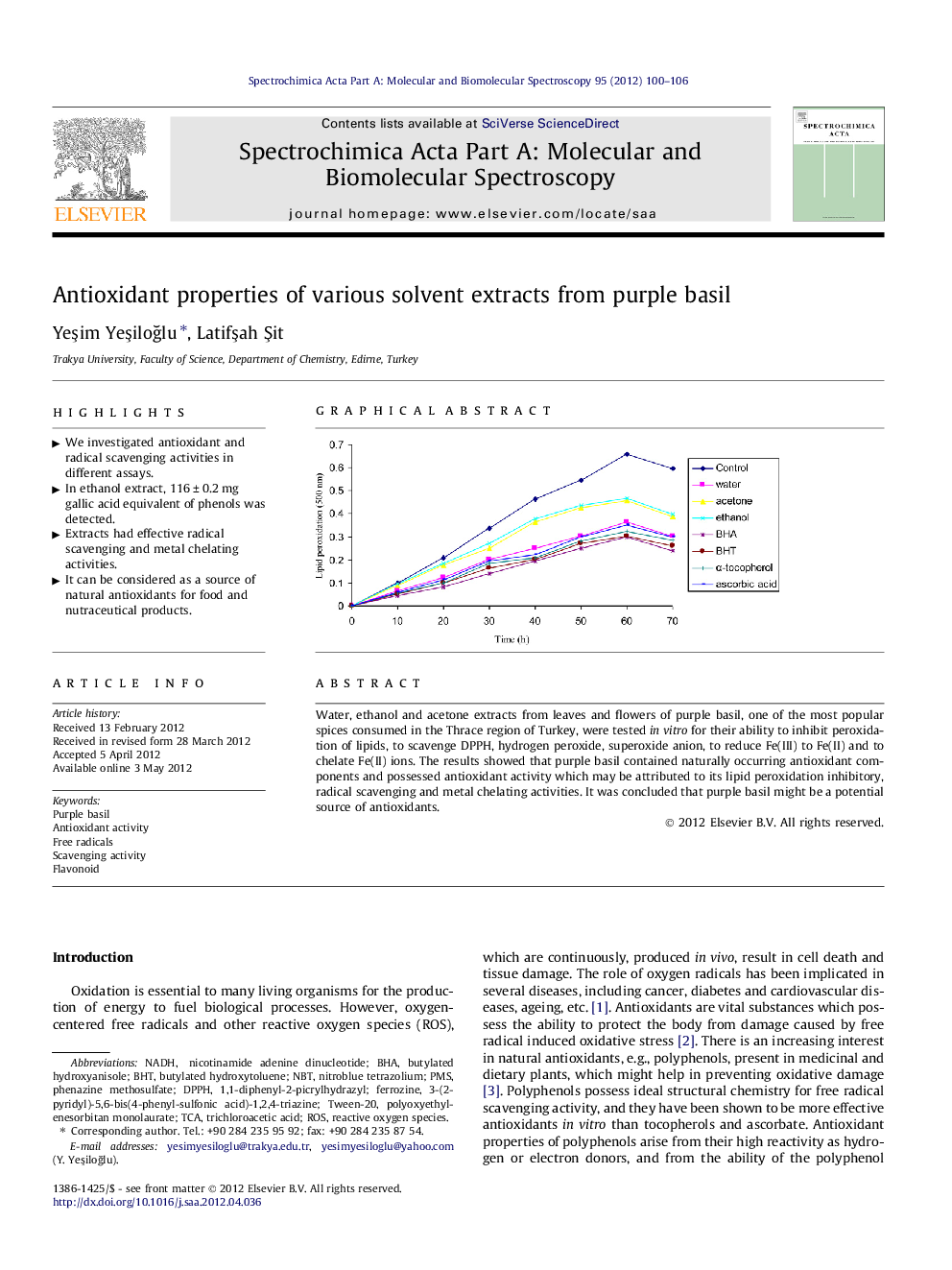
Water, ethanol and acetone extracts from leaves and flowers of purple basil, one of the most popular spices consumed in the Thrace region of Turkey, were tested in vitro for their ability to inhibit peroxidation of lipids, to scavenge DPPH, hydrogen peroxide, superoxide anion, to reduce Fe(III) to Fe(II) and to chelate Fe(II) ions. The results showed that purple basil contained naturally occurring antioxidant components and possessed antioxidant activity which may be attributed to its lipid peroxidation inhibitory, radical scavenging and metal chelating activities. It was concluded that purple basil might be a potential source of antioxidants.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► We investigated antioxidant and radical scavenging activities in different assays. ► In ethanol extract, 116 ± 0.2 mg gallic acid equivalent of phenols was detected. ► Extracts had effective radical scavenging and metal chelating activities. ► It can be considered as a source of natural antioxidants for food and nutraceutical products.