| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1231119 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2012 | 5 Pages |
TiO2 and Mn-doped TiO2 (1%, 3% and 5%) nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized by a sol-hydrothermal method for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy study. When using the 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4-MBA) as the probing molecule, optimum SERS signals were observed on the Mn–TiO2 (3%) samples. On the 3% Mn doped TiO2 substrate, 4-MBA molecules exhibit a higher SERS intensity by a factor of six as compared with the native enhancement of 4-MBA adsorbed on pure TiO2 NPs. The possible mechanism for the phenomena is also discussed. This study opens up a new dimension for the family of SERS substrates.
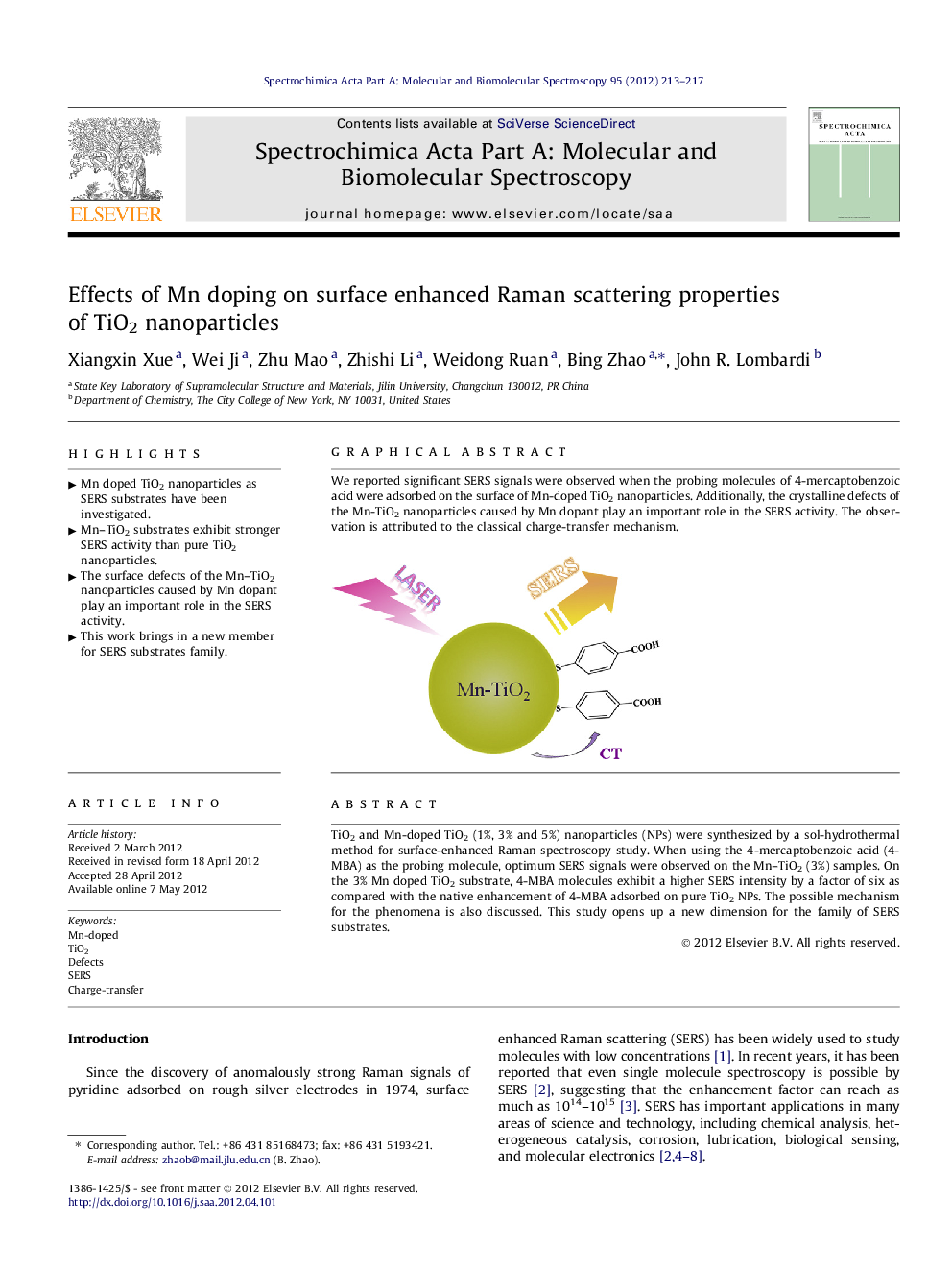
Graphical abstractWe reported significant SERS signals were observed when the probing molecules of 4-mercaptobenzoic acid were adsorbed on the surface of Mn-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Additionally, the crystalline defects of the Mn-TiO2 nanoparticles caused by Mn dopant play an important role in the SERS activity. The observation is attributed to the classical charge-transfer mechanism.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Mn doped TiO2 nanoparticles as SERS substrates have been investigated. ► Mn–TiO2 substrates exhibit stronger SERS activity than pure TiO2 nanoparticles. ► The surface defects of the Mn–TiO2 nanoparticles caused by Mn dopant play an important role in the SERS activity. ► This work brings in a new member for SERS substrates family.