| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1231616 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 12 Pages |
•Sulfamethoxazole and sulfathiazole Schiff bases of substituted salicylaldehydes.•Spectroscopic characterization and single crystal X-ray structure.•DFT computation of the Schiff bases for energy minimized structure.•Antibacterial study against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.•Molecular docking studies of the Schiff bases with DHPS to support experimental results.
New Schiff bases (1, 2) of substituted salicylaldehydes and sulfamethoxazole (SMX)/sulfathiazole (STZ) are synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis and spectroscopic data. Single crystal X-ray structure of one of the compounds (E)-4-((3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-N-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)benzenesulfonamide (1c) has been determined. Antimicrobial activities of the Schiff bases and parent sulfonamides (SMX, STZ) have been examined against several Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and sulfonamide resistant pathogens; the lowest MIC is observed for (E)-4-((3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-N-(thiazol-2-yl)benzene sulfonamide (2c) (8.0 μg mL−1) and (E)-4-((3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-N-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)benzene sulfonamide (1c) (16.0 μg mL−1) against sulfonamide resistant pathogens. DFT optimized structures of the Schiff bases have been used to carry out molecular docking studies with DHPS (dihydropteroate synthase) protein structure (downloaded from Protein Data Bank) using Discovery Studio 3.5 to find the most preferred binding mode of the ligand inside the protein cavity. The theoretical data have been well correlated with the experimental results. Cell viability assay and ADMET studies predict that 1c and 2c have good drug like characters.
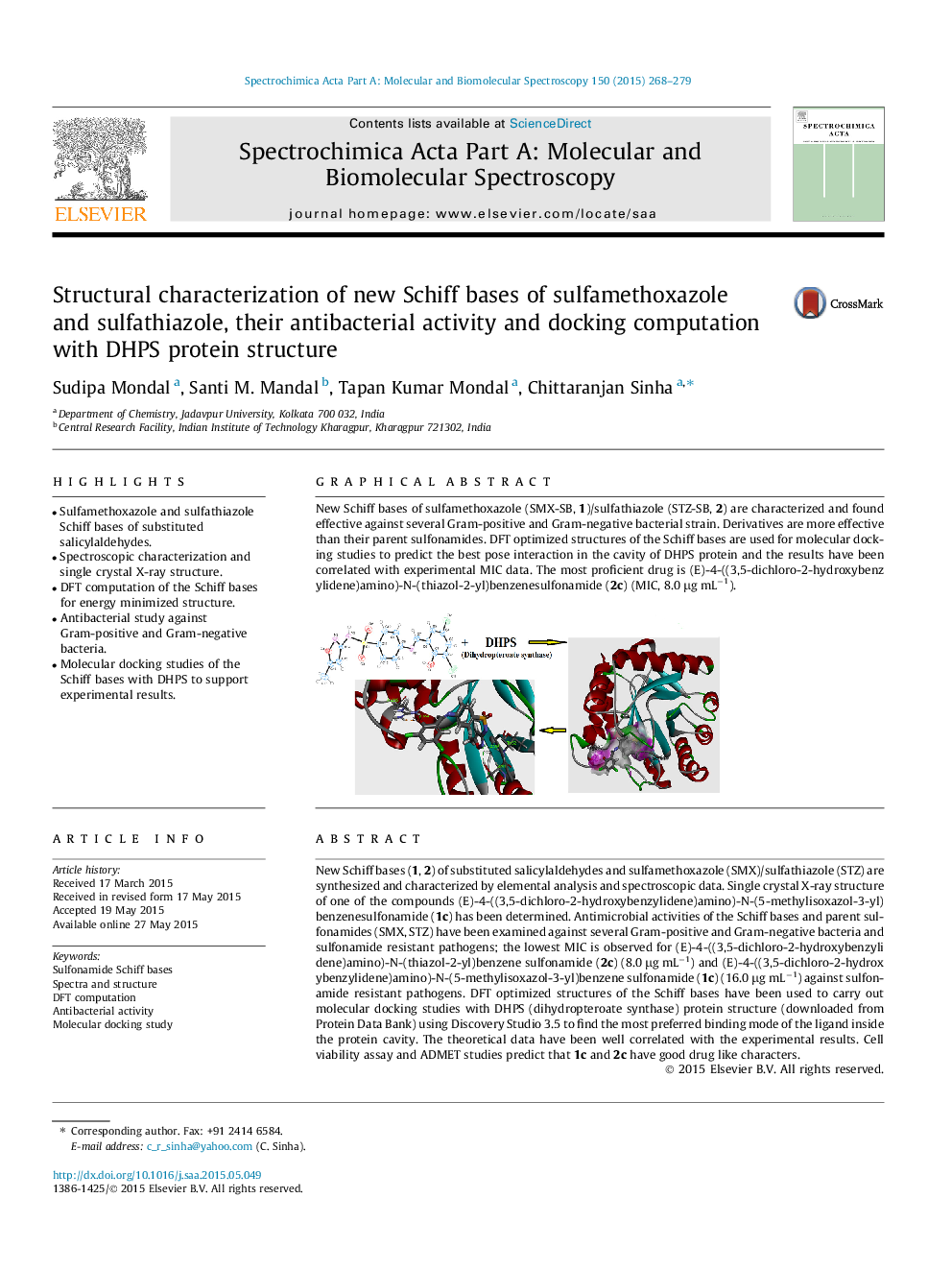
Graphical abstractNew Schiff bases of sulfamethoxazole (SMX-SB, 1)/sulfathiazole (STZ-SB, 2) are characterized and found effective against several Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strain. Derivatives are more effective than their parent sulfonamides. DFT optimized structures of the Schiff bases are used for molecular docking studies to predict the best pose interaction in the cavity of DHPS protein and the results have been correlated with experimental MIC data. The most proficient drug is (E)-4-((3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)-N-(thiazol-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide (2c) (MIC, 8.0 μg mL−1).Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide