| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1231644 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 10 Pages |
•A salophen templated Schiff base have been prepared and fully characterized.•The compound have been applied as effective ionophore for trace Cu2+ detection.•The obtained electrode has revealed Nernstian response over a wide Cu2+ range.•The ionophore reduces the charge transfer resistance of the electrode.•The electrode has a very low detection limit for Cu2+ in the order 10−8 M.
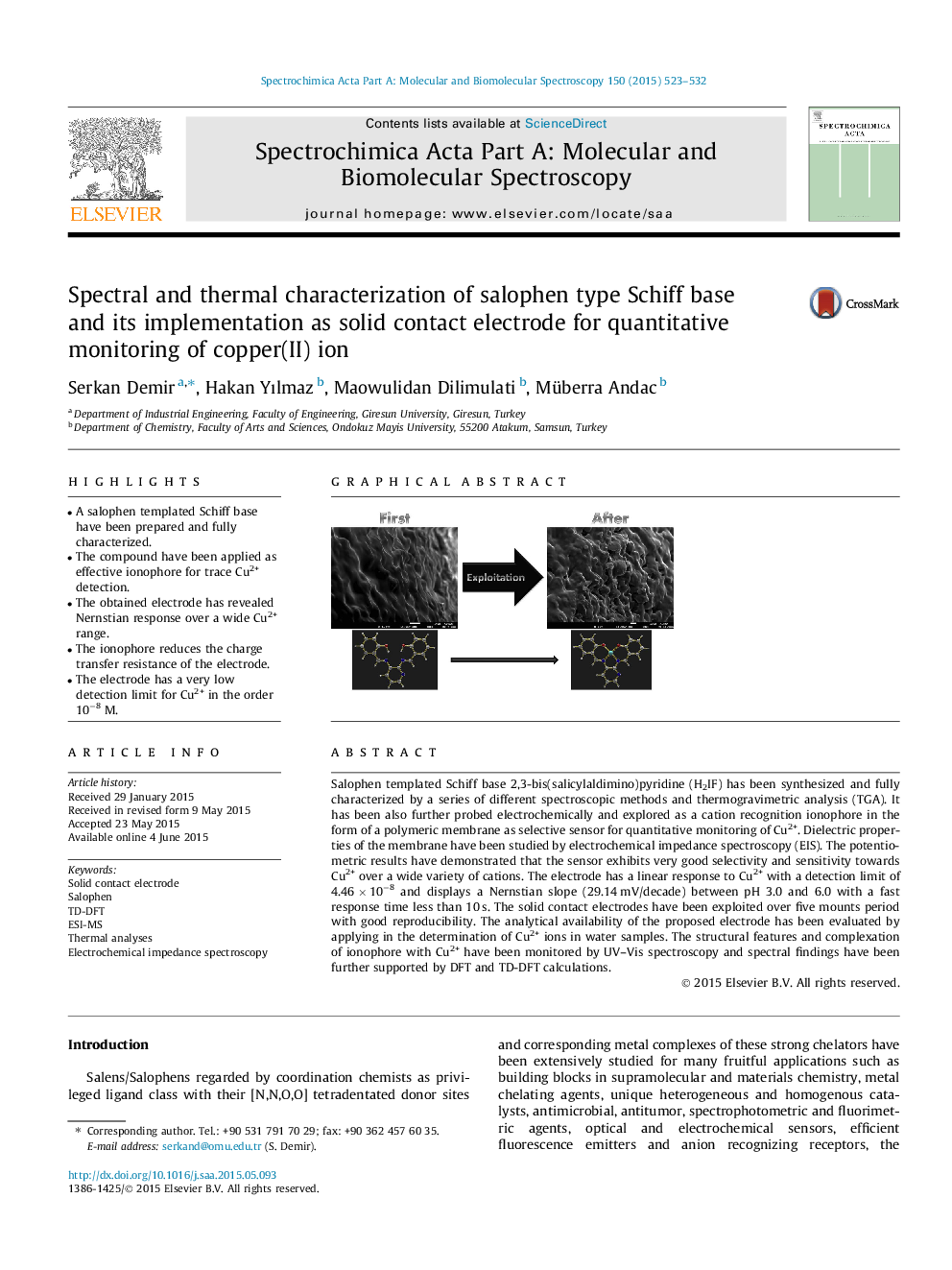
Salophen templated Schiff base 2,3-bis(salicylaldimino)pyridine (H2IF) has been synthesized and fully characterized by a series of different spectroscopic methods and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). It has been also further probed electrochemically and explored as a cation recognition ionophore in the form of a polymeric membrane as selective sensor for quantitative monitoring of Cu2+. Dielectric properties of the membrane have been studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The potentiometric results have demonstrated that the sensor exhibits very good selectivity and sensitivity towards Cu2+ over a wide variety of cations. The electrode has a linear response to Cu2+ with a detection limit of 4.46 × 10−8 and displays a Nernstian slope (29.14 mV/decade) between pH 3.0 and 6.0 with a fast response time less than 10 s. The solid contact electrodes have been exploited over five mounts period with good reproducibility. The analytical availability of the proposed electrode has been evaluated by applying in the determination of Cu2+ ions in water samples. The structural features and complexation of ionophore with Cu2+ have been monitored by UV–Vis spectroscopy and spectral findings have been further supported by DFT and TD-DFT calculations.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide