| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1231669 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 8 Pages |
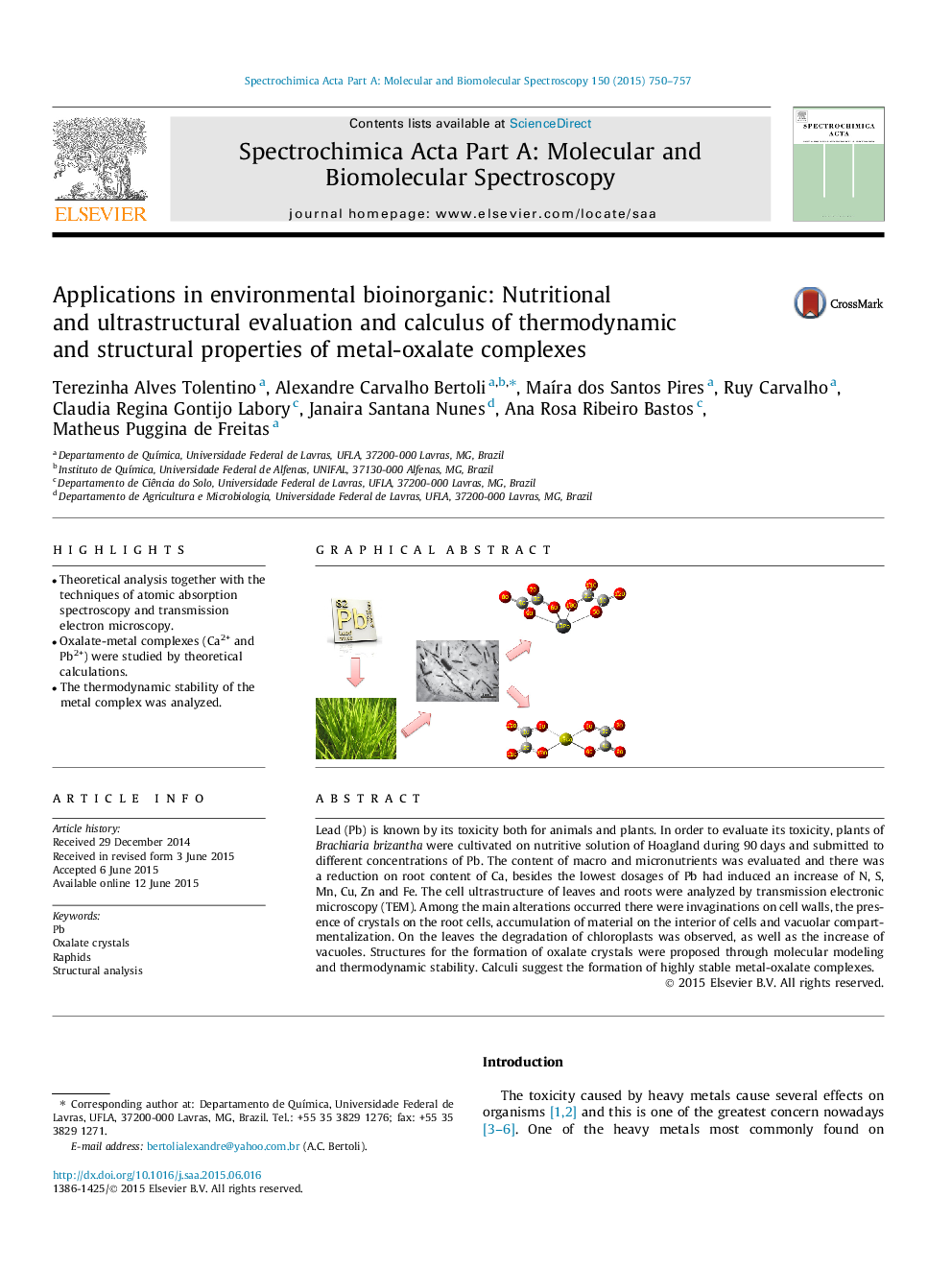
•Theoretical analysis together with the techniques of atomic absorption spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy.•Oxalate-metal complexes (Ca2+ and Pb2+) were studied by theoretical calculations.•The thermodynamic stability of the metal complex was analyzed.
Lead (Pb) is known by its toxicity both for animals and plants. In order to evaluate its toxicity, plants of Brachiaria brizantha were cultivated on nutritive solution of Hoagland during 90 days and submitted to different concentrations of Pb. The content of macro and micronutrients was evaluated and there was a reduction on root content of Ca, besides the lowest dosages of Pb had induced an increase of N, S, Mn, Cu, Zn and Fe. The cell ultrastructure of leaves and roots were analyzed by transmission electronic microscopy (TEM). Among the main alterations occurred there were invaginations on cell walls, the presence of crystals on the root cells, accumulation of material on the interior of cells and vacuolar compartmentalization. On the leaves the degradation of chloroplasts was observed, as well as the increase of vacuoles. Structures for the formation of oxalate crystals were proposed through molecular modeling and thermodynamic stability. Calculi suggest the formation of highly stable metal-oxalate complexes.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide