| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1231678 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 7 Pages |
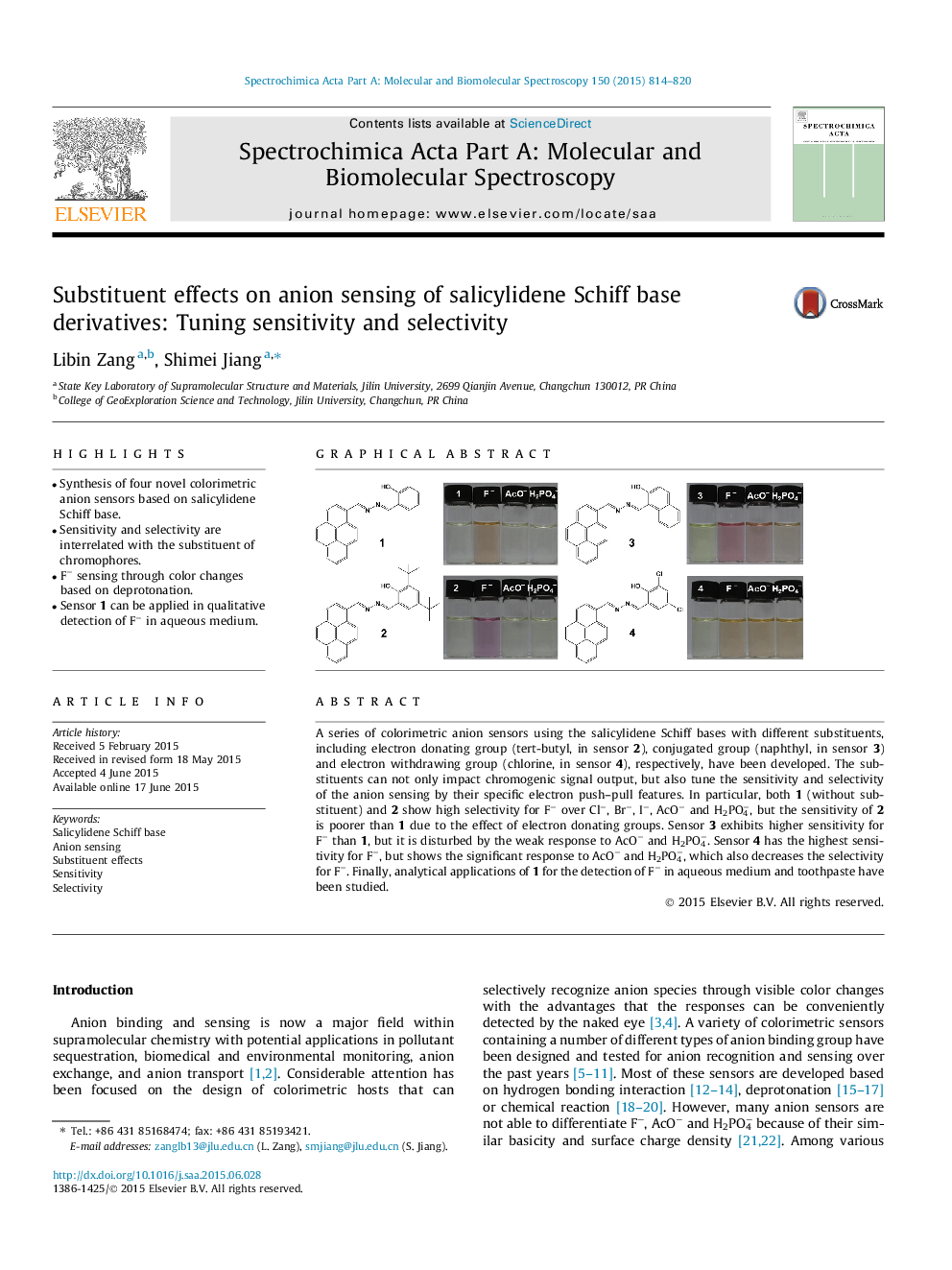
•Synthesis of four novel colorimetric anion sensors based on salicylidene Schiff base.•Sensitivity and selectivity are interrelated with the substituent of chromophores.•F− sensing through color changes based on deprotonation.•Sensor 1 can be applied in qualitative detection of F− in aqueous medium.
A series of colorimetric anion sensors using the salicylidene Schiff bases with different substituents, including electron donating group (tert-butyl, in sensor 2), conjugated group (naphthyl, in sensor 3) and electron withdrawing group (chlorine, in sensor 4), respectively, have been developed. The substituents can not only impact chromogenic signal output, but also tune the sensitivity and selectivity of the anion sensing by their specific electron push–pull features. In particular, both 1 (without substituent) and 2 show high selectivity for F− over Cl−, Br−, I−, AcO− and H2PO4−, but the sensitivity of 2 is poorer than 1 due to the effect of electron donating groups. Sensor 3 exhibits higher sensitivity for F− than 1, but it is disturbed by the weak response to AcO− and H2PO4−. Sensor 4 has the highest sensitivity for F−, but shows the significant response to AcO− and H2PO4−, which also decreases the selectivity for F−. Finally, analytical applications of 1 for the detection of F− in aqueous medium and toothpaste have been studied.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide