| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1231810 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 5 Pages |
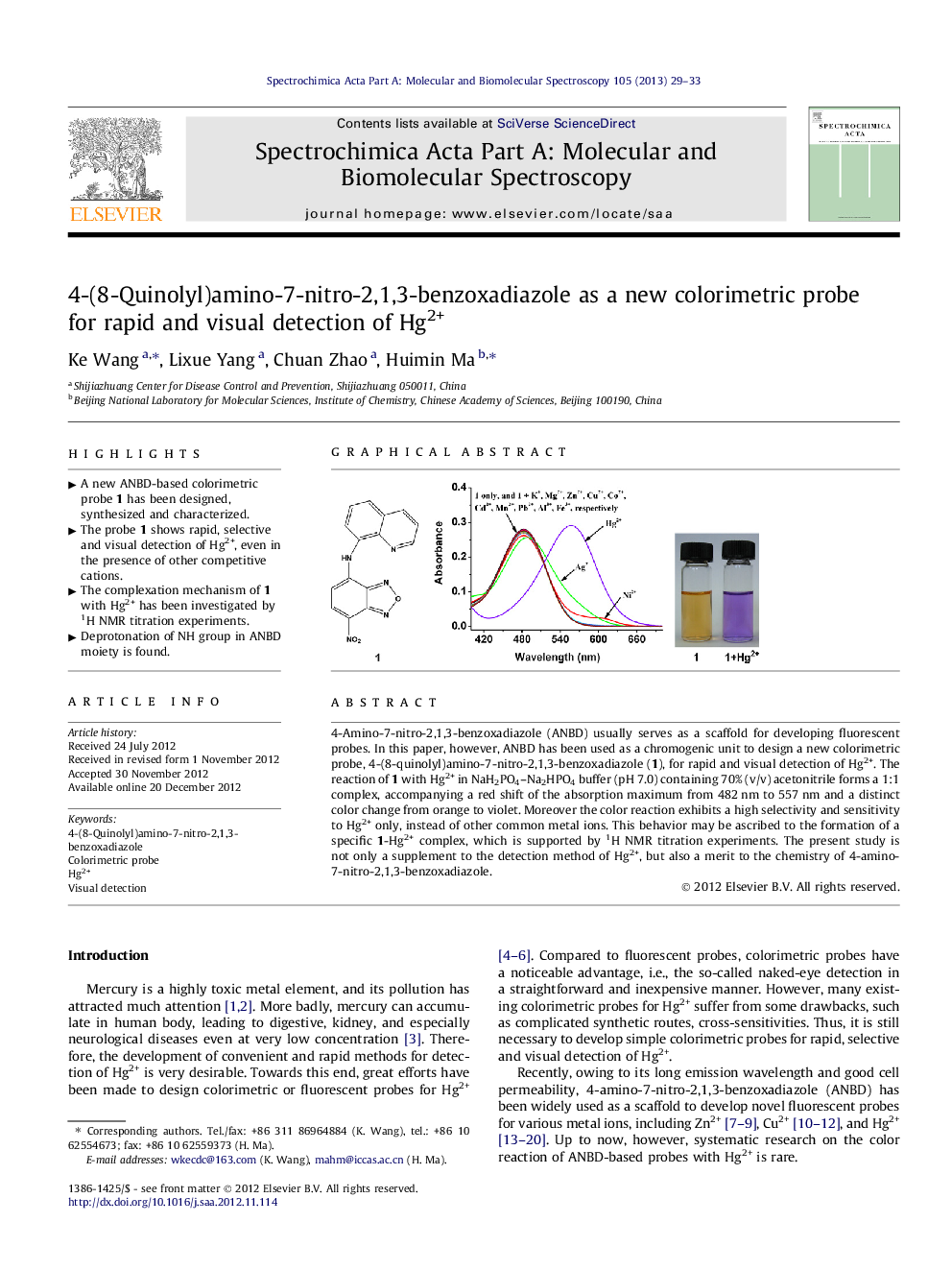
4-Amino-7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole (ANBD) usually serves as a scaffold for developing fluorescent probes. In this paper, however, ANBD has been used as a chromogenic unit to design a new colorimetric probe, 4-(8-quinolyl)amino-7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole (1), for rapid and visual detection of Hg2+. The reaction of 1 with Hg2+ in NaH2PO4–Na2HPO4 buffer (pH 7.0) containing 70% (v/v) acetonitrile forms a 1:1 complex, accompanying a red shift of the absorption maximum from 482 nm to 557 nm and a distinct color change from orange to violet. Moreover the color reaction exhibits a high selectivity and sensitivity to Hg2+ only, instead of other common metal ions. This behavior may be ascribed to the formation of a specific 1-Hg2+ complex, which is supported by 1H NMR titration experiments. The present study is not only a supplement to the detection method of Hg2+, but also a merit to the chemistry of 4-amino-7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► A new ANBD-based colorimetric probe 1 has been designed, synthesized and characterized. ► The probe 1 shows rapid, selective and visual detection of Hg2+, even in the presence of other competitive cations. ► The complexation mechanism of 1 with Hg2+ has been investigated by 1H NMR titration experiments. ► Deprotonation of NH group in ANBD moiety is found.