| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232040 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 4 Pages |
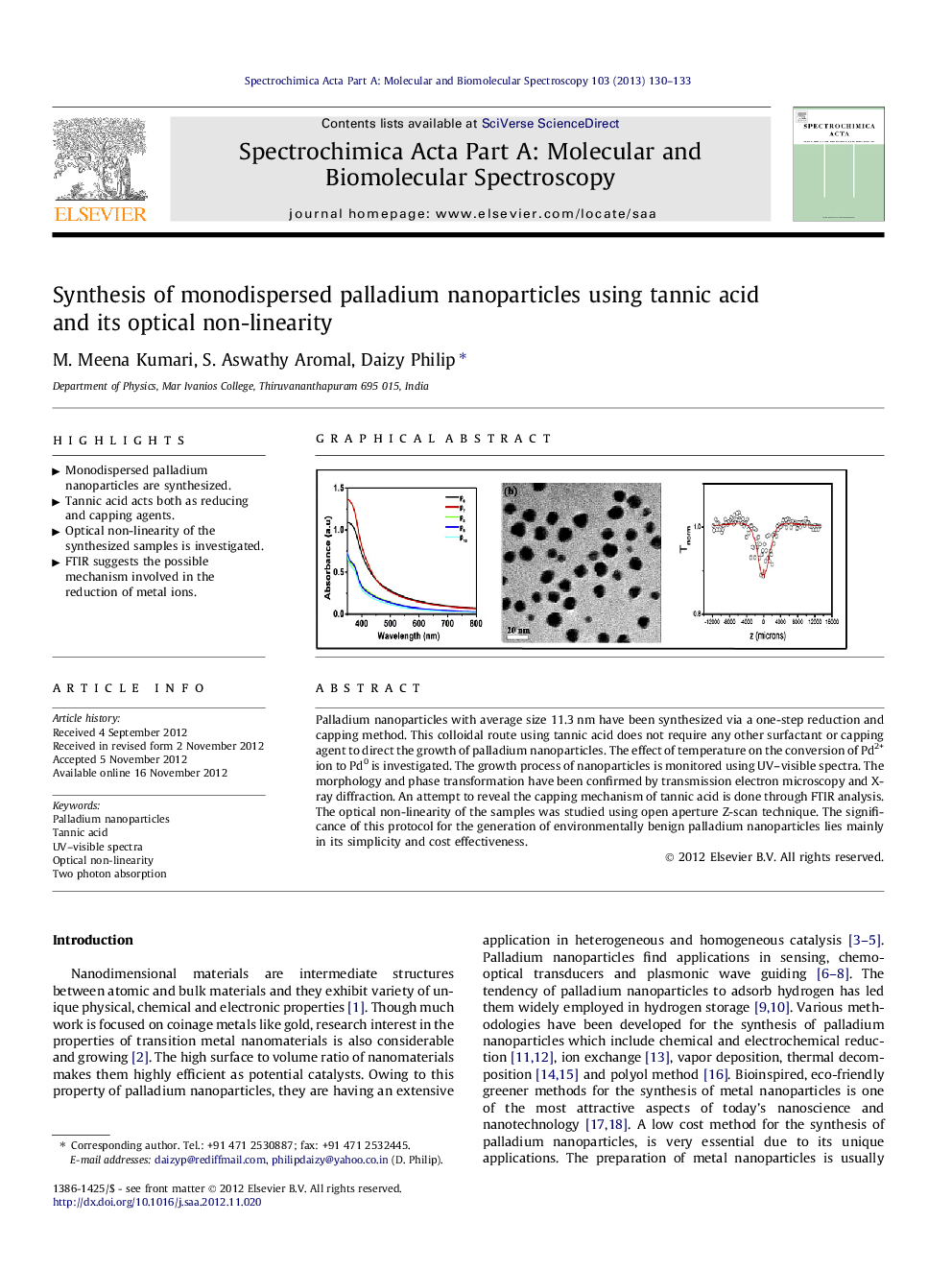
Palladium nanoparticles with average size 11.3 nm have been synthesized via a one-step reduction and capping method. This colloidal route using tannic acid does not require any other surfactant or capping agent to direct the growth of palladium nanoparticles. The effect of temperature on the conversion of Pd2+ ion to Pd0 is investigated. The growth process of nanoparticles is monitored using UV–visible spectra. The morphology and phase transformation have been confirmed by transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. An attempt to reveal the capping mechanism of tannic acid is done through FTIR analysis. The optical non-linearity of the samples was studied using open aperture Z-scan technique. The significance of this protocol for the generation of environmentally benign palladium nanoparticles lies mainly in its simplicity and cost effectiveness.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Monodispersed palladium nanoparticles are synthesized. ► Tannic acid acts both as reducing and capping agents. ► Optical non-linearity of the synthesized samples is investigated. ► FTIR suggests the possible mechanism involved in the reduction of metal ions.