| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232044 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 4 Pages |
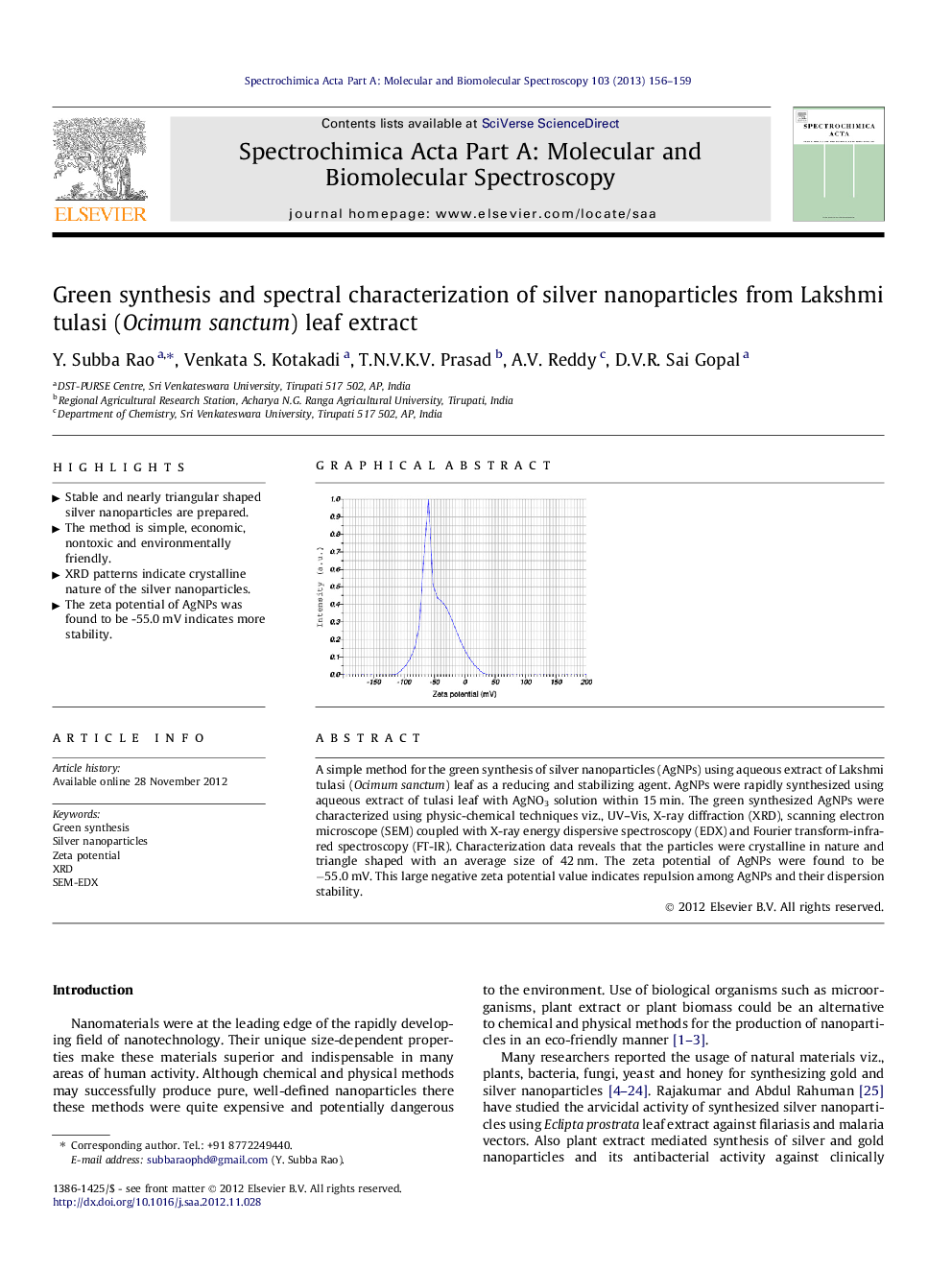
A simple method for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using aqueous extract of Lakshmi tulasi (Ocimum sanctum) leaf as a reducing and stabilizing agent. AgNPs were rapidly synthesized using aqueous extract of tulasi leaf with AgNO3 solution within 15 min. The green synthesized AgNPs were characterized using physic-chemical techniques viz., UV–Vis, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) coupled with X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDX) and Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). Characterization data reveals that the particles were crystalline in nature and triangle shaped with an average size of 42 nm. The zeta potential of AgNPs were found to be −55.0 mV. This large negative zeta potential value indicates repulsion among AgNPs and their dispersion stability.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Stable and nearly triangular shaped silver nanoparticles are prepared. ► The method is simple, economic, nontoxic and environmentally friendly. ► XRD patterns indicate crystalline nature of the silver nanoparticles. ► The zeta potential of AgNPs was found to be -55.0 mV indicates more stability.