| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232054 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 10 Pages |
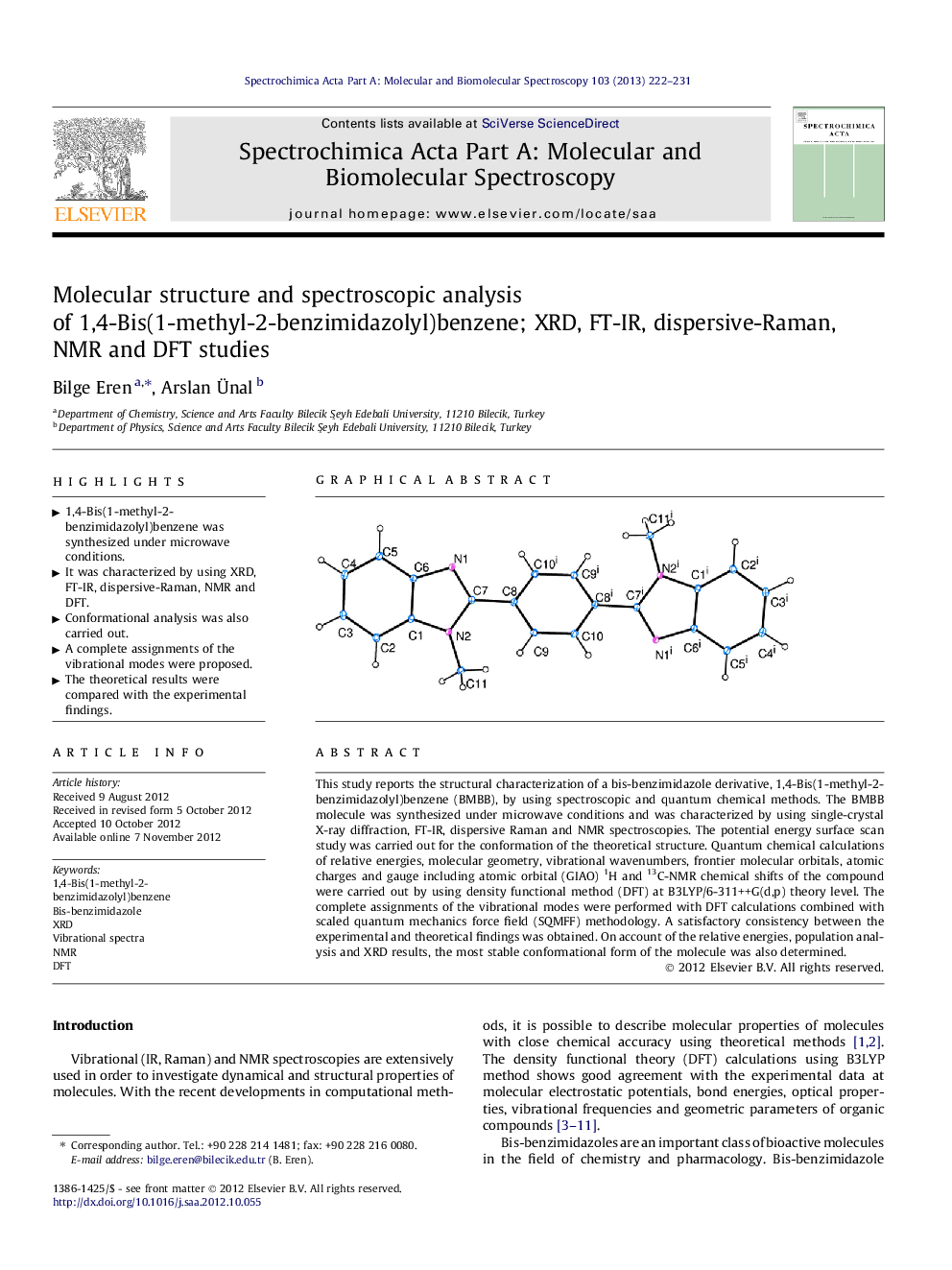
This study reports the structural characterization of a bis-benzimidazole derivative, 1,4-Bis(1-methyl-2-benzimidazolyl)benzene (BMBB), by using spectroscopic and quantum chemical methods. The BMBB molecule was synthesized under microwave conditions and was characterized by using single-crystal X-ray diffraction, FT-IR, dispersive Raman and NMR spectroscopies. The potential energy surface scan study was carried out for the conformation of the theoretical structure. Quantum chemical calculations of relative energies, molecular geometry, vibrational wavenumbers, frontier molecular orbitals, atomic charges and gauge including atomic orbital (GIAO) 1H and 13C-NMR chemical shifts of the compound were carried out by using density functional method (DFT) at B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) theory level. The complete assignments of the vibrational modes were performed with DFT calculations combined with scaled quantum mechanics force field (SQMFF) methodology. A satisfactory consistency between the experimental and theoretical findings was obtained. On account of the relative energies, population analysis and XRD results, the most stable conformational form of the molecule was also determined.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► 1,4-Bis(1-methyl-2-benzimidazolyl)benzene was synthesized under microwave conditions. ► It was characterized by using XRD, FT-IR, dispersive-Raman, NMR and DFT. ► Conformational analysis was also carried out. ► A complete assignments of the vibrational modes were proposed. ► The theoretical results were compared with the experimental findings.