| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232060 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 6 Pages |
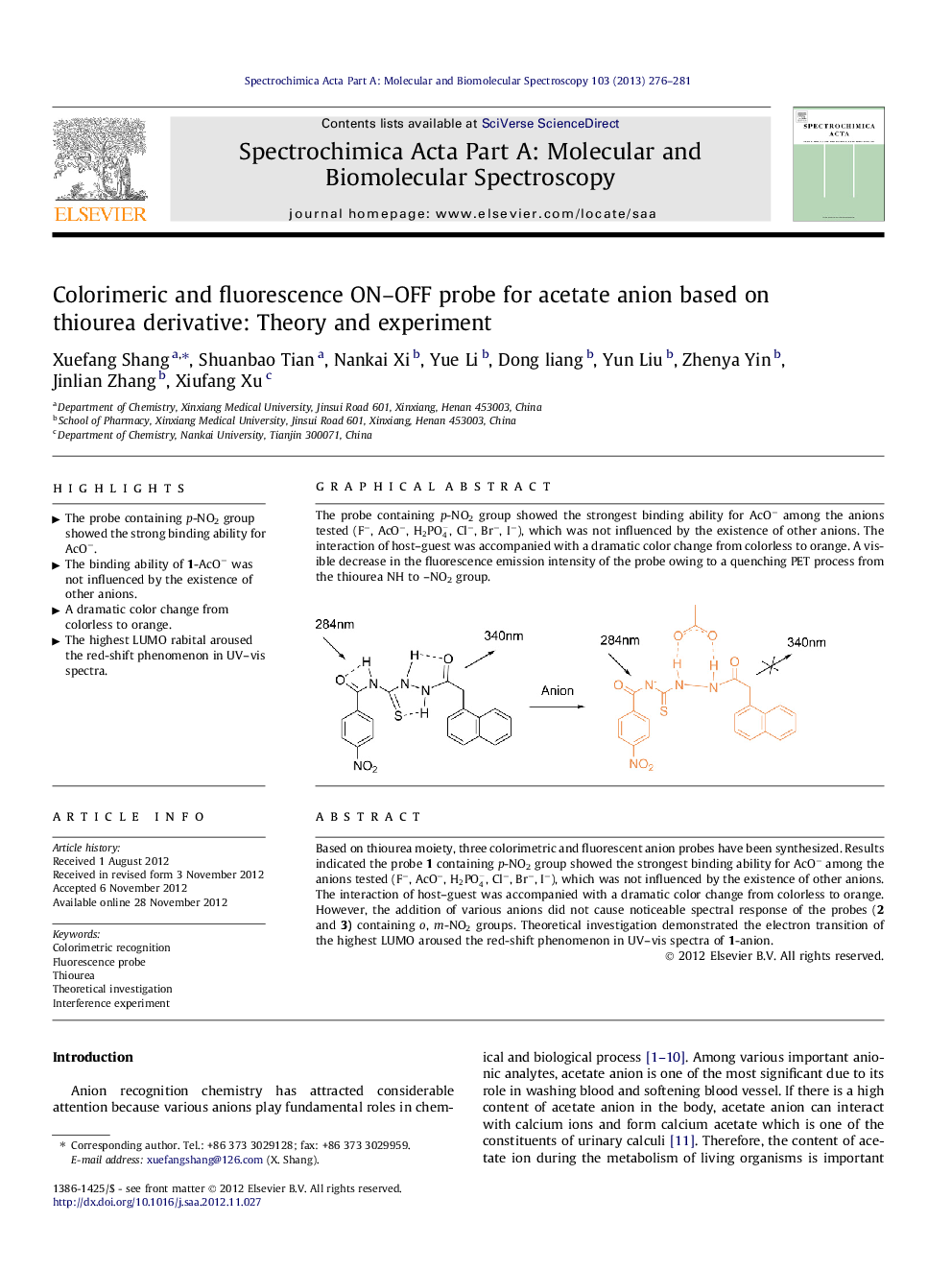
Based on thiourea moiety, three colorimetric and fluorescent anion probes have been synthesized. Results indicated the probe 1 containing p-NO2 group showed the strongest binding ability for AcO− among the anions tested (F−, AcO−, H2PO4-, Cl−, Br−, I−), which was not influenced by the existence of other anions. The interaction of host–guest was accompanied with a dramatic color change from colorless to orange. However, the addition of various anions did not cause noticeable spectral response of the probes (2 and 3) containing o, m-NO2 groups. Theoretical investigation demonstrated the electron transition of the highest LUMO aroused the red-shift phenomenon in UV–vis spectra of 1-anion.
Graphical abstractThe probe containing p-NO2 group showed the strongest binding ability for AcO− among the anions tested (F−, AcO−, H2PO4-, Cl−, Br−, I−), which was not influenced by the existence of other anions. The interaction of host–guest was accompanied with a dramatic color change from colorless to orange. A visible decrease in the fluorescence emission intensity of the probe owing to a quenching PET process from the thiourea NH to –NO2 group.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► The probe containing p-NO2 group showed the strong binding ability for AcO−. ► The binding ability of 1-AcO− was not influenced by the existence of other anions. ► A dramatic color change from colorless to orange. ► The highest LUMO rabital aroused the red-shift phenomenon in UV–vis spectra.