| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232076 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 9 Pages |
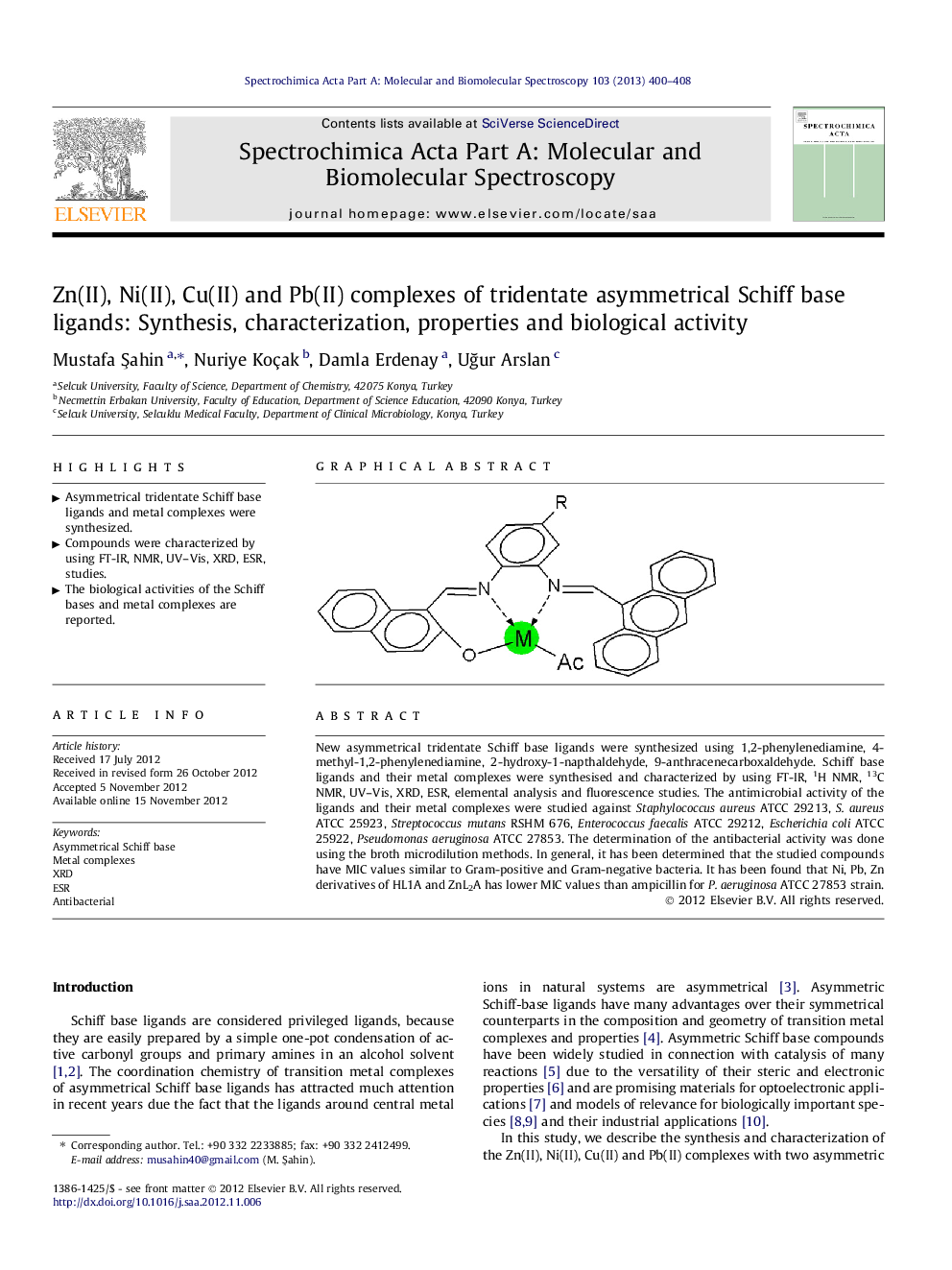
New asymmetrical tridentate Schiff base ligands were synthesized using 1,2-phenylenediamine, 4-methyl-1,2-phenylenediamine, 2-hydroxy-1-napthaldehyde, 9-anthracenecarboxaldehyde. Schiff base ligands and their metal complexes were synthesised and characterized by using FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, UV–Vis, XRD, ESR, elemental analysis and fluorescence studies. The antimicrobial activity of the ligands and their metal complexes were studied against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213, S. aureus ATCC 25923, Streptococcus mutans RSHM 676, Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853. The determination of the antibacterial activity was done using the broth microdilution methods. In general, it has been determined that the studied compounds have MIC values similar to Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It has been found that Ni, Pb, Zn derivatives of HL1A and ZnL2A has lower MIC values than ampicillin for P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 strain.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Asymmetrical tridentate Schiff base ligands and metal complexes were synthesized. ► Compounds were characterized by using FT-IR, NMR, UV–Vis, XRD, ESR, studies. ► The biological activities of the Schiff bases and metal complexes are reported.