| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232098 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 11 Pages |
•Photophysical properties of quinine sulfate have been monitored in micellar medium at three different pH.•Polarity, viscosity, refractive index and ET (30) of the local environment estimated.•Location of the quinine sulfate in the micellar media has been probed.•The local pH at micellar surfaces is different from the bulk pH of the solution.
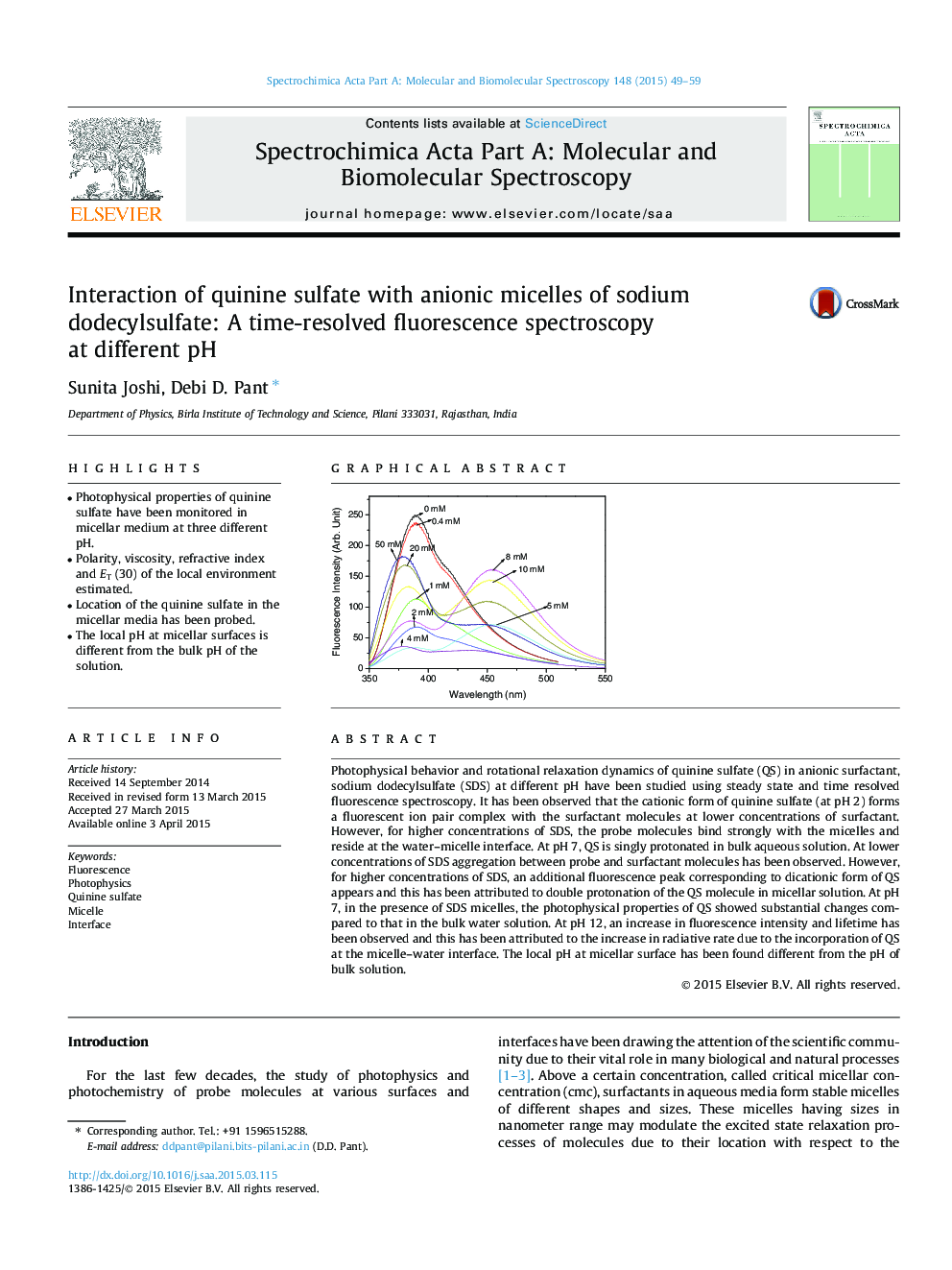
Photophysical behavior and rotational relaxation dynamics of quinine sulfate (QS) in anionic surfactant, sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) at different pH have been studied using steady state and time resolved fluorescence spectroscopy. It has been observed that the cationic form of quinine sulfate (at pH 2) forms a fluorescent ion pair complex with the surfactant molecules at lower concentrations of surfactant. However, for higher concentrations of SDS, the probe molecules bind strongly with the micelles and reside at the water–micelle interface. At pH 7, QS is singly protonated in bulk aqueous solution. At lower concentrations of SDS aggregation between probe and surfactant molecules has been observed. However, for higher concentrations of SDS, an additional fluorescence peak corresponding to dicationic form of QS appears and this has been attributed to double protonation of the QS molecule in micellar solution. At pH 7, in the presence of SDS micelles, the photophysical properties of QS showed substantial changes compared to that in the bulk water solution. At pH 12, an increase in fluorescence intensity and lifetime has been observed and this has been attributed to the increase in radiative rate due to the incorporation of QS at the micelle–water interface. The local pH at micellar surface has been found different from the pH of bulk solution.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide