| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232219 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 7 Pages |
•The proposed method is exceptionally simple, rapid, and sensitive.•No complicated protocols or expensive instrumentation is required.•Method gains are higher sensitivity, broader linear range, lower detection limit.•Common coexisting compounds in medicines do not affect Amoxicillin analysis.
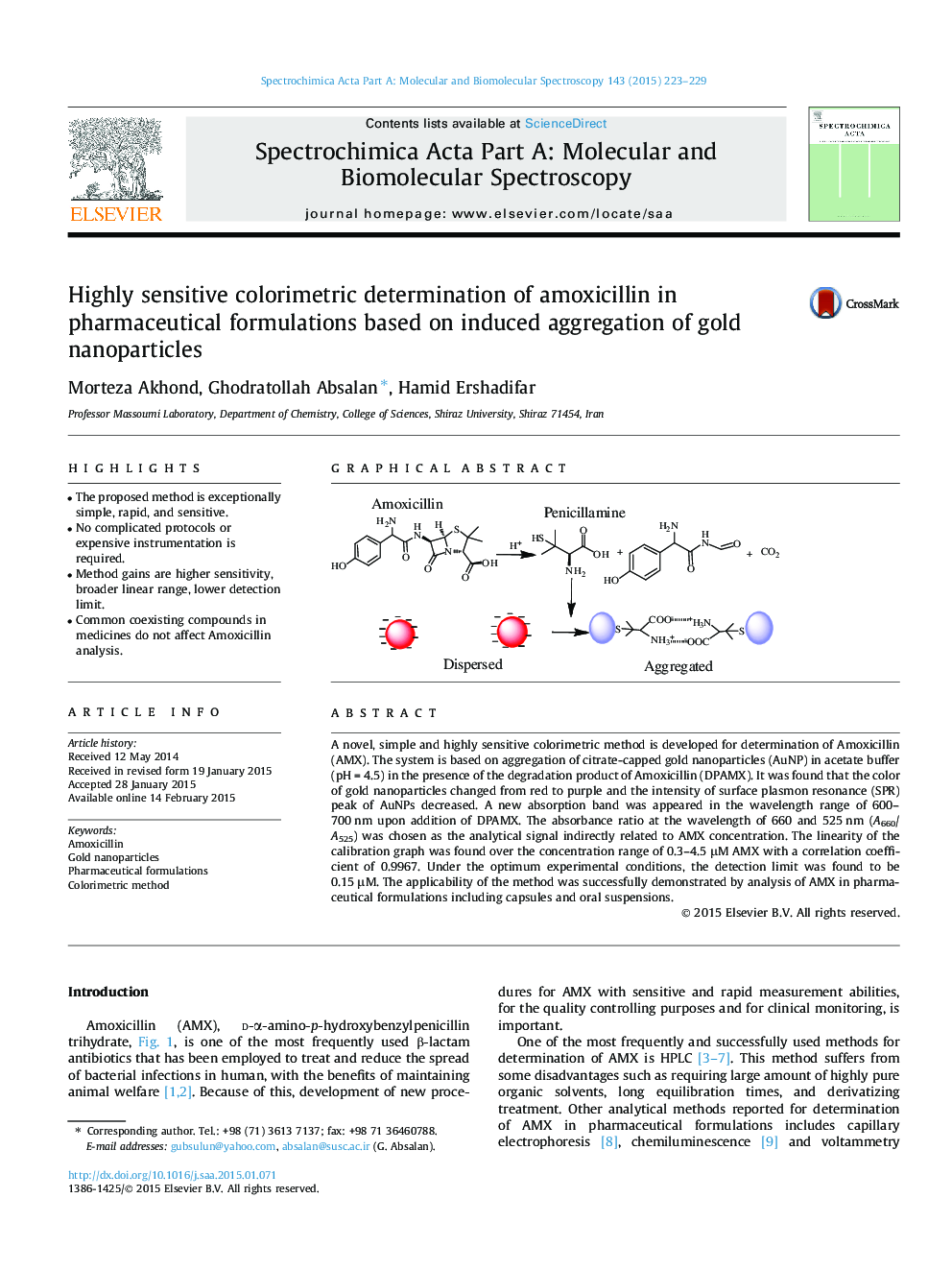
A novel, simple and highly sensitive colorimetric method is developed for determination of Amoxicillin (AMX). The system is based on aggregation of citrate-capped gold nanoparticles (AuNP) in acetate buffer (pH = 4.5) in the presence of the degradation product of Amoxicillin (DPAMX). It was found that the color of gold nanoparticles changed from red to purple and the intensity of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peak of AuNPs decreased. A new absorption band was appeared in the wavelength range of 600–700 nm upon addition of DPAMX. The absorbance ratio at the wavelength of 660 and 525 nm (A660/A525) was chosen as the analytical signal indirectly related to AMX concentration. The linearity of the calibration graph was found over the concentration range of 0.3–4.5 μM AMX with a correlation coefficient of 0.9967. Under the optimum experimental conditions, the detection limit was found to be 0.15 μM. The applicability of the method was successfully demonstrated by analysis of AMX in pharmaceutical formulations including capsules and oral suspensions.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide