| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232315 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2012 | 5 Pages |
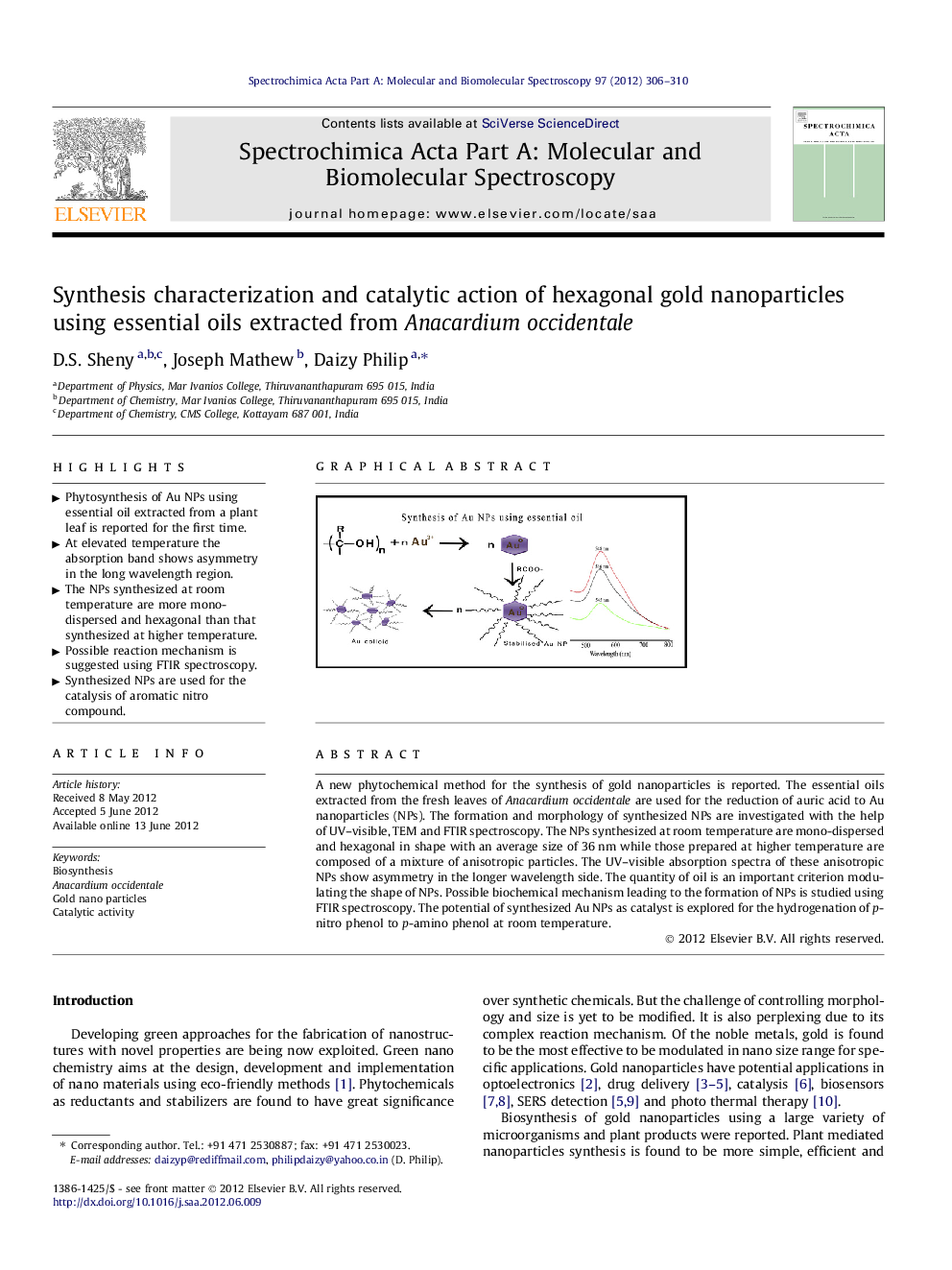
A new phytochemical method for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles is reported. The essential oils extracted from the fresh leaves of Anacardium occidentale are used for the reduction of auric acid to Au nanoparticles (NPs). The formation and morphology of synthesized NPs are investigated with the help of UV–visible, TEM and FTIR spectroscopy. The NPs synthesized at room temperature are mono-dispersed and hexagonal in shape with an average size of 36 nm while those prepared at higher temperature are composed of a mixture of anisotropic particles. The UV–visible absorption spectra of these anisotropic NPs show asymmetry in the longer wavelength side. The quantity of oil is an important criterion modulating the shape of NPs. Possible biochemical mechanism leading to the formation of NPs is studied using FTIR spectroscopy. The potential of synthesized Au NPs as catalyst is explored for the hydrogenation of p-nitro phenol to p-amino phenol at room temperature.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Phytosynthesis of Au NPs using essential oil extracted from a plant leaf is reported for the first time. ► At elevated temperature the absorption band shows asymmetry in the long wavelength region. ► The NPs synthesized at room temperature are more mono-dispersed and hexagonal than that synthesized at higher temperature. ► Possible reaction mechanism is suggested using FTIR spectroscopy. ► Synthesized NPs are used for the catalysis of aromatic nitro compound.