| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232324 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2012 | 4 Pages |
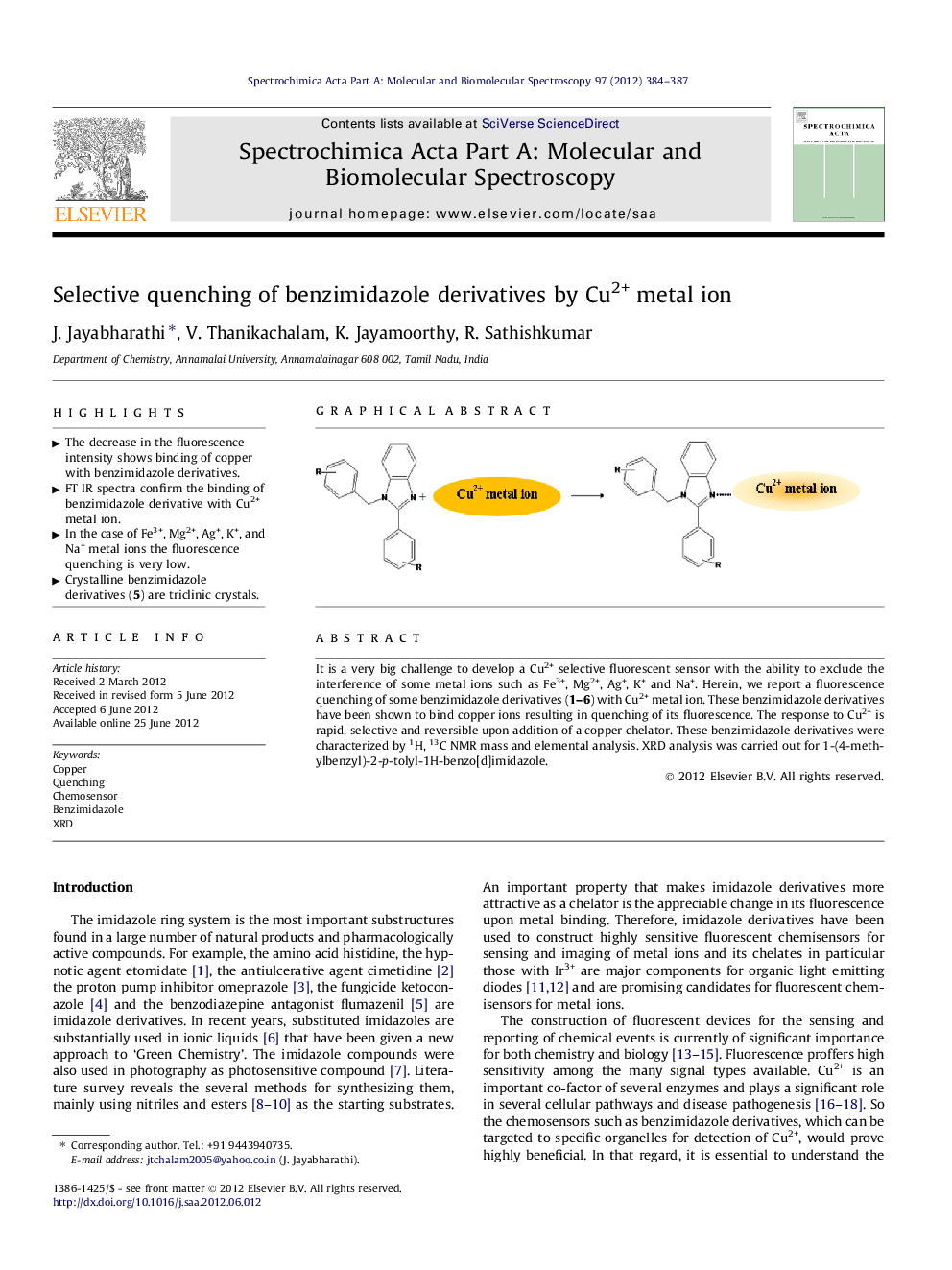
It is a very big challenge to develop a Cu2+ selective fluorescent sensor with the ability to exclude the interference of some metal ions such as Fe3+, Mg2+, Ag+, K+ and Na+. Herein, we report a fluorescence quenching of some benzimidazole derivatives (1–6) with Cu2+ metal ion. These benzimidazole derivatives have been shown to bind copper ions resulting in quenching of its fluorescence. The response to Cu2+ is rapid, selective and reversible upon addition of a copper chelator. These benzimidazole derivatives were characterized by 1H, 13C NMR mass and elemental analysis. XRD analysis was carried out for 1-(4-methylbenzyl)-2-p-tolyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► The decrease in the fluorescence intensity shows binding of copper with benzimidazole derivatives. ► FT IR spectra confirm the binding of benzimidazole derivative with Cu2+ metal ion. ► In the case of Fe3+, Mg2+, Ag+, K+, and Na+ metal ions the fluorescence quenching is very low. ► Crystalline benzimidazole derivatives (5) are triclinic crystals.