| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232327 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2012 | 5 Pages |
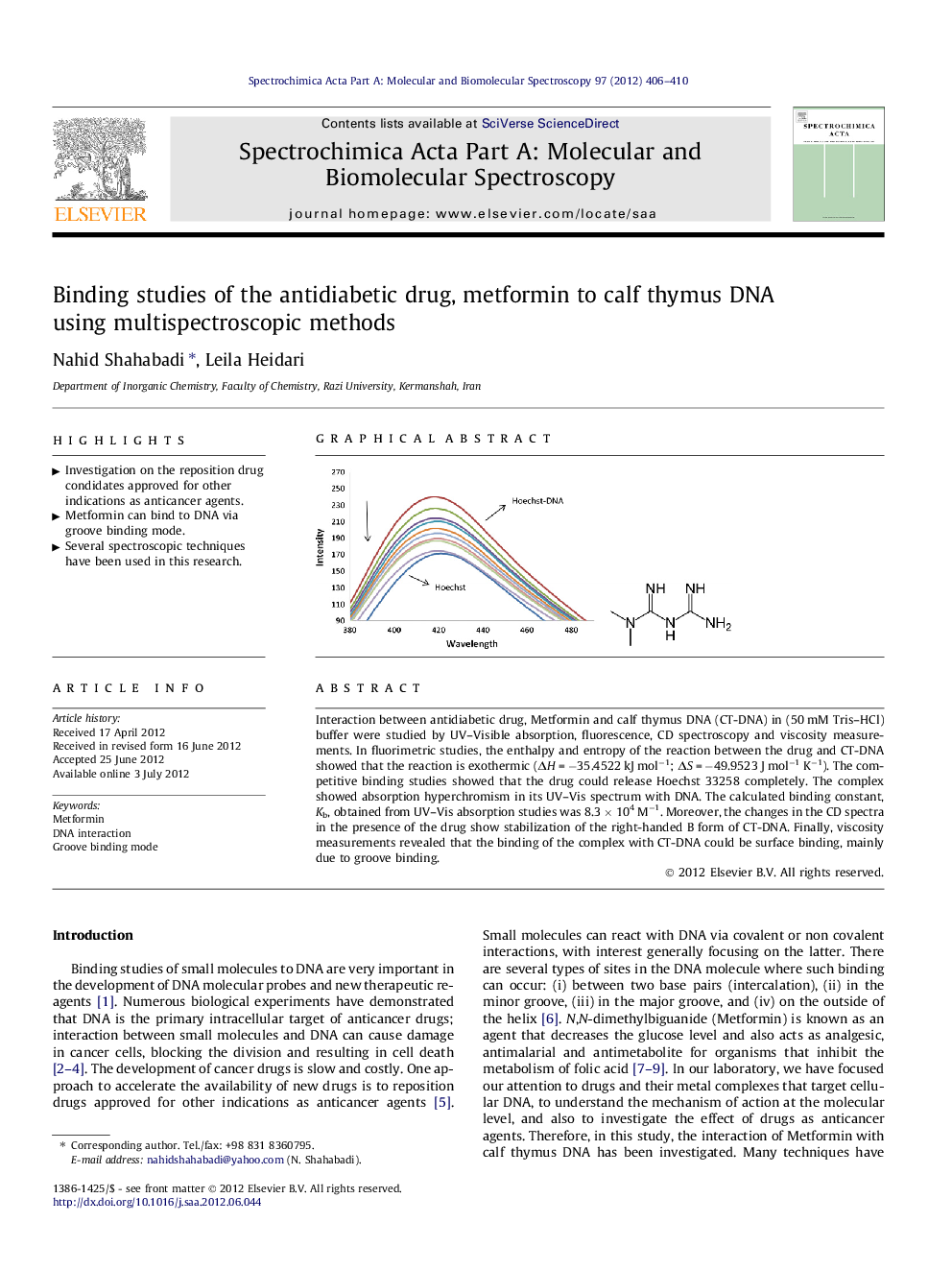
Interaction between antidiabetic drug, Metformin and calf thymus DNA (CT-DNA) in (50 mM Tris–HCl) buffer were studied by UV–Visible absorption, fluorescence, CD spectroscopy and viscosity measurements. In fluorimetric studies, the enthalpy and entropy of the reaction between the drug and CT-DNA showed that the reaction is exothermic (ΔH = −35.4522 kJ mol−1; ΔS = −49.9523 J mol−1 K−1). The competitive binding studies showed that the drug could release Hoechst 33258 completely. The complex showed absorption hyperchromism in its UV–Vis spectrum with DNA. The calculated binding constant, Kb, obtained from UV–Vis absorption studies was 8.3 × 104 M−1. Moreover, the changes in the CD spectra in the presence of the drug show stabilization of the right-handed B form of CT-DNA. Finally, viscosity measurements revealed that the binding of the complex with CT-DNA could be surface binding, mainly due to groove binding.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Investigation on the reposition drug condidates approved for other indications as anticancer agents. ► Metformin can bind to DNA via groove binding mode. ► Several spectroscopic techniques have been used in this research.