| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232380 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 6 Pages |
•A novel method determining fenbendazole (FBZ) was proposed.•The method has been applied for the determination of FBZ in pharmaceutical preparations with satisfactory results.•The possible reaction mechanism of QDs and FBZ was discussed.
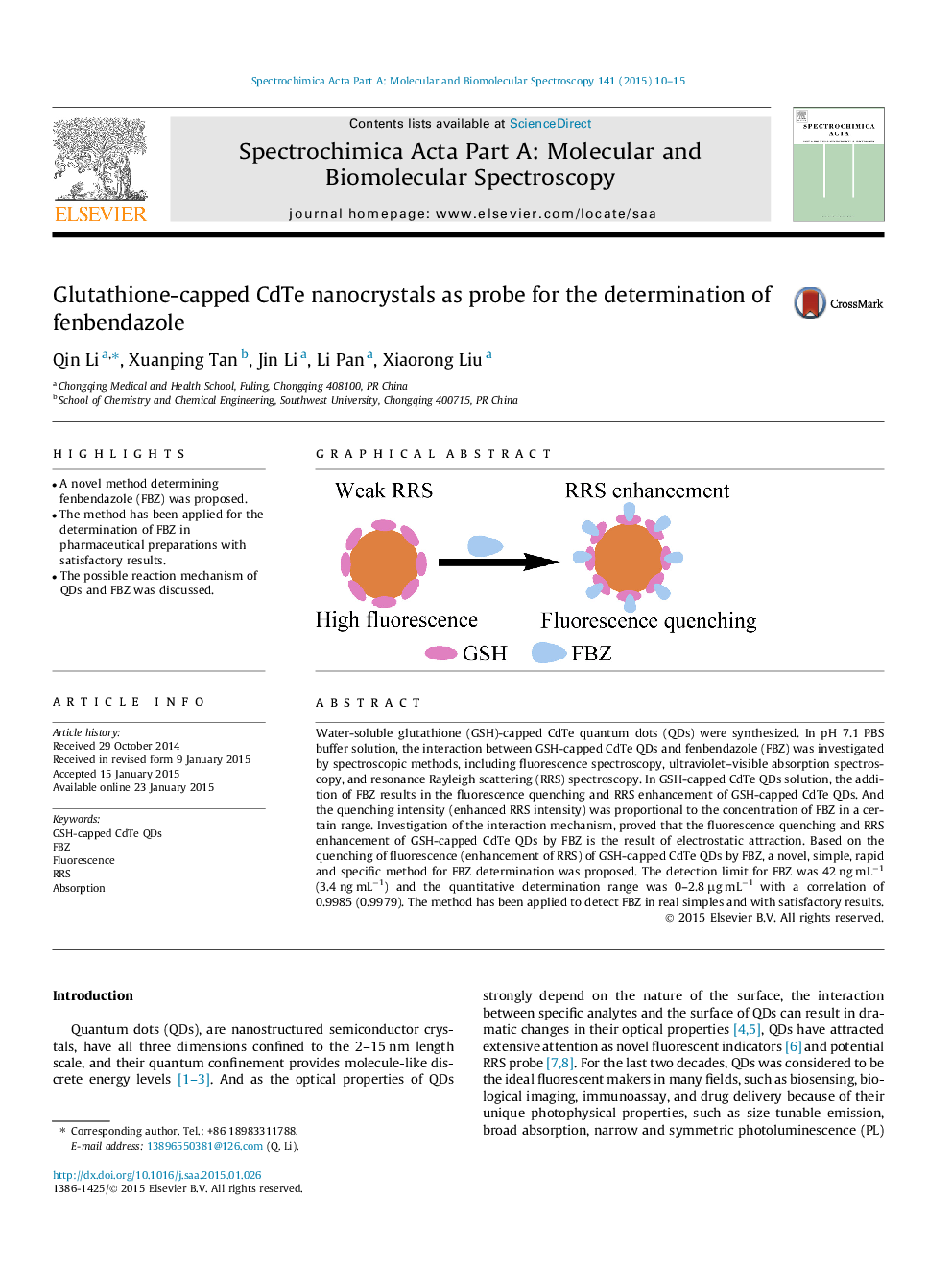
Water-soluble glutathione (GSH)-capped CdTe quantum dots (QDs) were synthesized. In pH 7.1 PBS buffer solution, the interaction between GSH-capped CdTe QDs and fenbendazole (FBZ) was investigated by spectroscopic methods, including fluorescence spectroscopy, ultraviolet–visible absorption spectroscopy, and resonance Rayleigh scattering (RRS) spectroscopy. In GSH-capped CdTe QDs solution, the addition of FBZ results in the fluorescence quenching and RRS enhancement of GSH-capped CdTe QDs. And the quenching intensity (enhanced RRS intensity) was proportional to the concentration of FBZ in a certain range. Investigation of the interaction mechanism, proved that the fluorescence quenching and RRS enhancement of GSH-capped CdTe QDs by FBZ is the result of electrostatic attraction. Based on the quenching of fluorescence (enhancement of RRS) of GSH-capped CdTe QDs by FBZ, a novel, simple, rapid and specific method for FBZ determination was proposed. The detection limit for FBZ was 42 ng mL−1 (3.4 ng mL−1) and the quantitative determination range was 0–2.8 μg mL−1 with a correlation of 0.9985 (0.9979). The method has been applied to detect FBZ in real simples and with satisfactory results.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide