| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232392 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 5 Pages |
•We analyze spitzoid skin lesions by using FTIR microspectroscopy.•We carry out a comparative study in combination with the histopathological analysis.•Chemical maps of these lesions are compared with those from control skin and melanoma.•Spectral markers of each pathology are extracted from average spectra of melanocytes.
In the last 10 years, few efforts have been carried out to apply vibrational spectroscopy in the study of dermal pathologies in order to characterize the most relevant spectral markers for distinguishing benign from cancerous lesions.Spitz nevi are a special group of benign melanocytic lesions, characterized by spindled and/or epithelioid nevomelanocytes, with peculiar clinical, dermoscopic and histopathological features. The “atypical forms” of Spitz nevi are among the commonest problems of differential diagnosis with the so-called “spitzoid melanomas”. The clinical and histological criteria for discriminating these two entities are very subtle and often still quite subjective, and, in a significant percentage of cases, can lead to diagnostic pitfalls and inadequate therapies. Therefore, it is noteworthy to outline that the diagnosis of melanocytic lesions still represents a challenging problem and a continue matter of discussion.We exploited FTIR microspectroscopy to study the different kinds of spitzoid melanocytes, in order to define the most relevant spectral markers of each specimen and to achieve objective information on “borderline” histologically atypical lesions. In particular, the spectroscopic investigation was carried out on melanocytes deriving from normal skin (as a normal control), malignant melanoma and Spitz nevi. The presence of the characteristic bands of melanin was investigated, too.
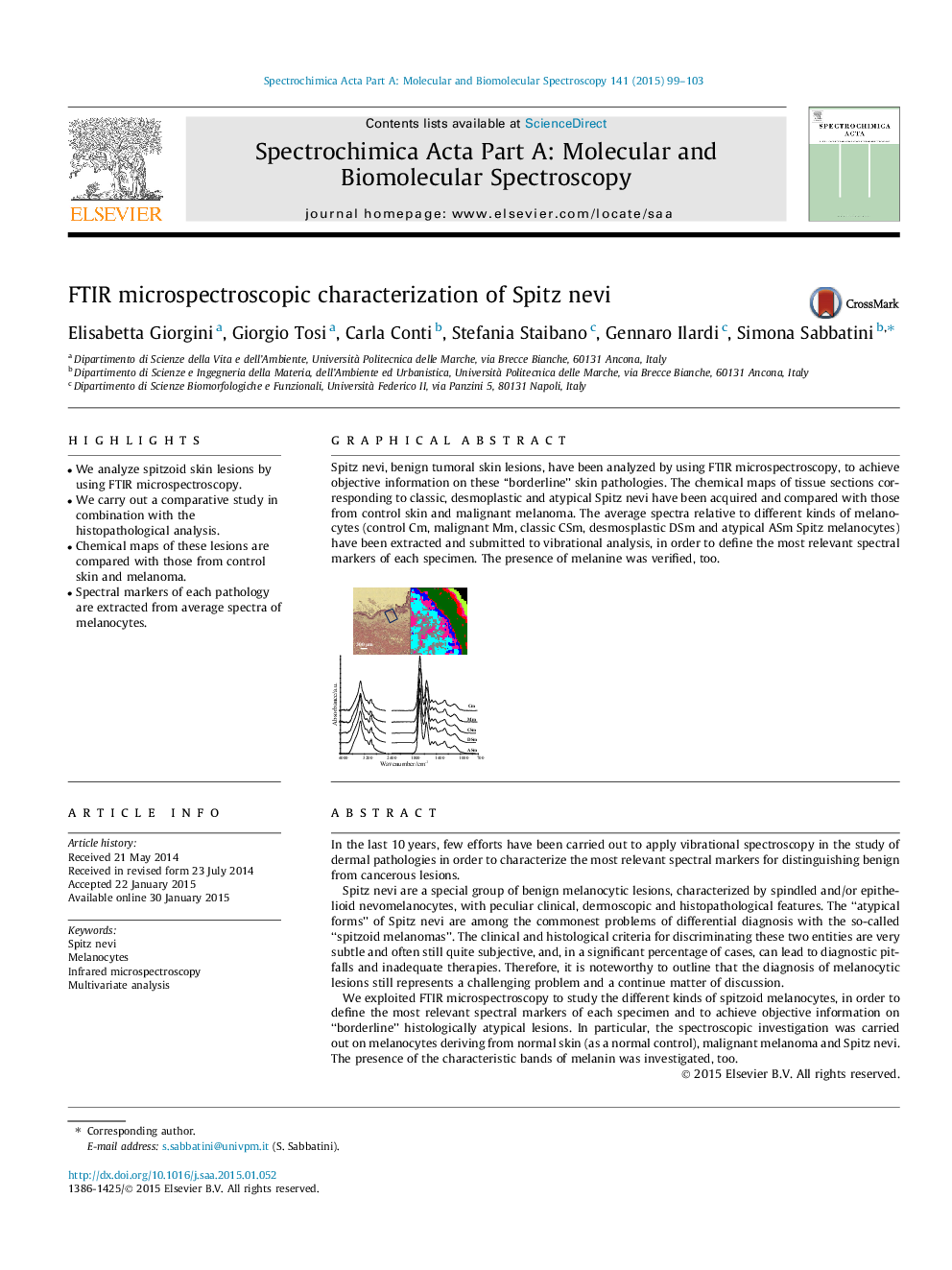
Graphical abstractSpitz nevi, benign tumoral skin lesions, have been analyzed by using FTIR microspectroscopy, to achieve objective information on these ‘‘borderline’’ skin pathologies. The chemical maps of tissue sections corresponding to classic, desmoplastic and atypical Spitz nevi have been acquired and compared with those from control skin and malignant melanoma. The average spectra relative to different kinds of melanocytes (control Cm, malignant Mm, classic CSm, desmosplastic DSm and atypical ASm Spitz melanocytes) have been extracted and submitted to vibrational analysis, in order to define the most relevant spectral markers of each specimen. The presence of melanine was verified, too.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide