| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232394 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 6 Pages |
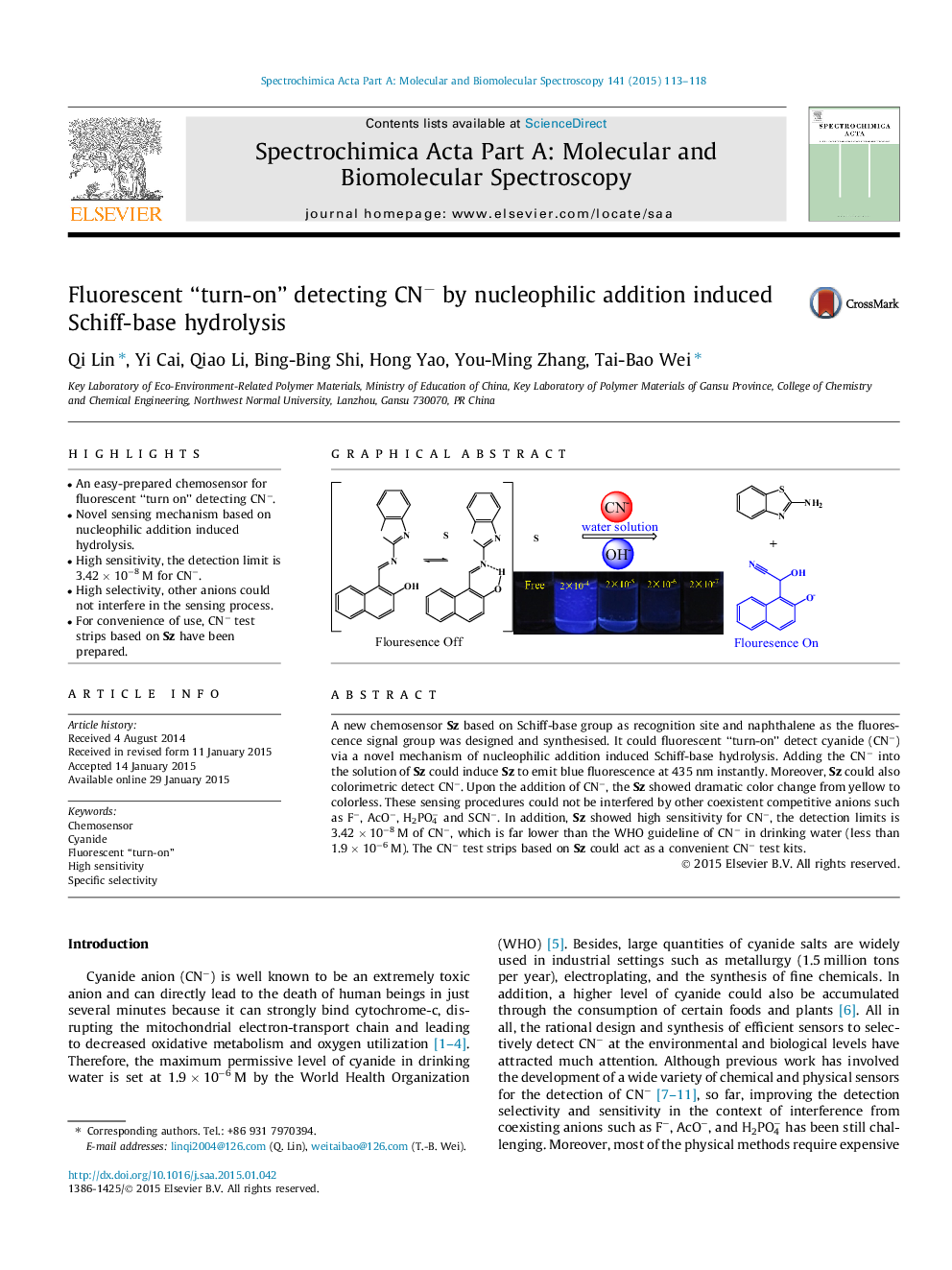
•An easy-prepared chemosensor for fluorescent “turn on” detecting CN−.•Novel sensing mechanism based on nucleophilic addition induced hydrolysis.•High sensitivity, the detection limit is 3.42 × 10−8 M for CN−.•High selectivity, other anions could not interfere in the sensing process.•For convenience of use, CN− test strips based on Sz have been prepared.
A new chemosensor Sz based on Schiff-base group as recognition site and naphthalene as the fluorescence signal group was designed and synthesised. It could fluorescent “turn-on” detect cyanide (CN−) via a novel mechanism of nucleophilic addition induced Schiff-base hydrolysis. Adding the CN− into the solution of Sz could induce Sz to emit blue fluorescence at 435 nm instantly. Moreover, Sz could also colorimetric detect CN−. Upon the addition of CN−, the Sz showed dramatic color change from yellow to colorless. These sensing procedures could not be interfered by other coexistent competitive anions such as F−, AcO−, H2PO4− and SCN−. In addition, Sz showed high sensitivity for CN−, the detection limits is 3.42 × 10−8 M of CN−, which is far lower than the WHO guideline of CN− in drinking water (less than 1.9 × 10−6 M). The CN− test strips based on Sz could act as a convenient CN− test kits.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide