| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232405 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 9 Pages |
•Complexation chemistry of drug metronidazole with different acceptors was studied.•The interactions were characterized both in solution and in the solid state.•Spectroscopic, thermal and kinetic properties were determined.
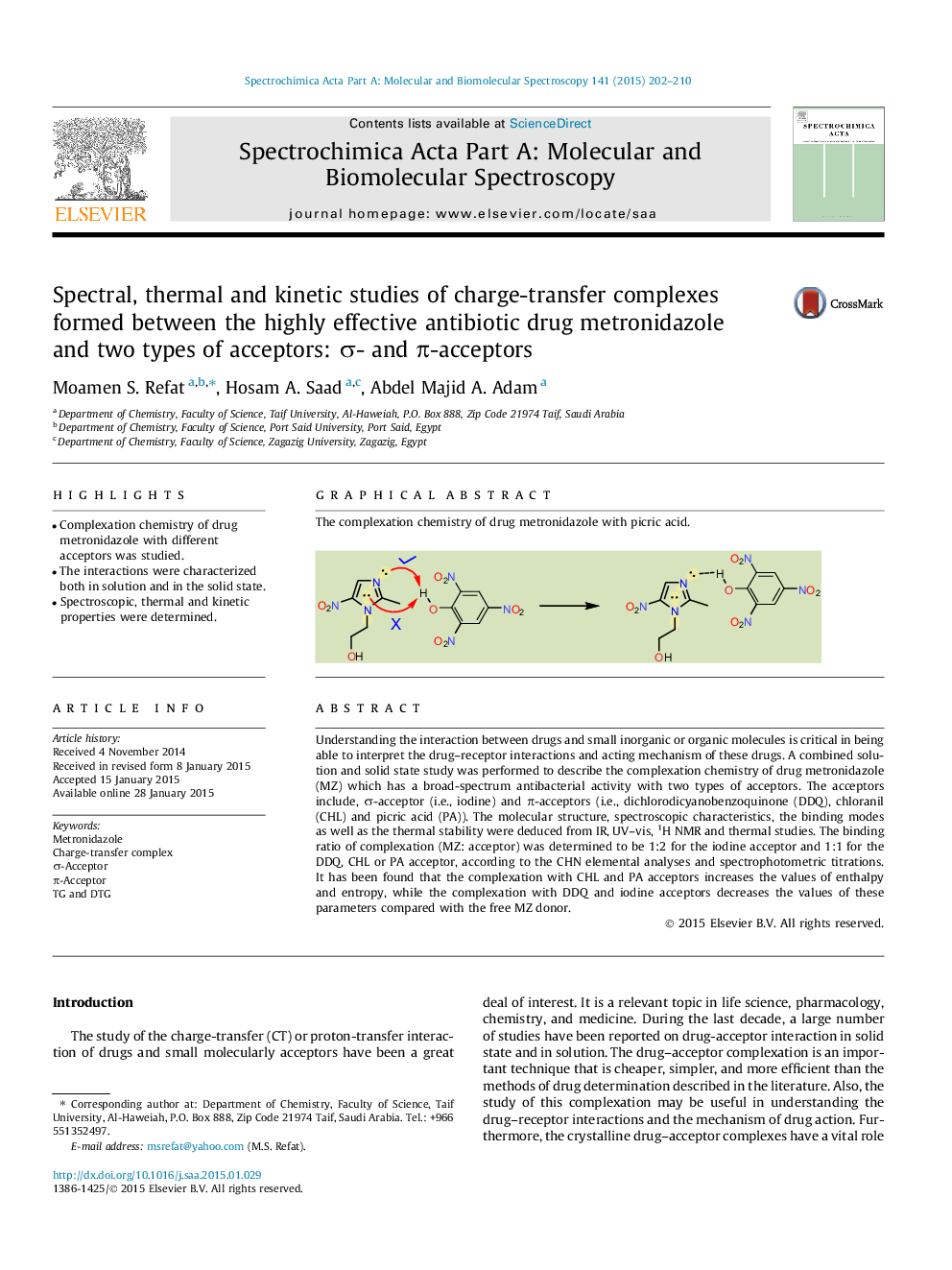
Understanding the interaction between drugs and small inorganic or organic molecules is critical in being able to interpret the drug–receptor interactions and acting mechanism of these drugs. A combined solution and solid state study was performed to describe the complexation chemistry of drug metronidazole (MZ) which has a broad-spectrum antibacterial activity with two types of acceptors. The acceptors include, σ-acceptor (i.e., iodine) and π-acceptors (i.e., dichlorodicyanobenzoquinone (DDQ), chloranil (CHL) and picric acid (PA)). The molecular structure, spectroscopic characteristics, the binding modes as well as the thermal stability were deduced from IR, UV–vis, 1H NMR and thermal studies. The binding ratio of complexation (MZ: acceptor) was determined to be 1:2 for the iodine acceptor and 1:1 for the DDQ, CHL or PA acceptor, according to the CHN elemental analyses and spectrophotometric titrations. It has been found that the complexation with CHL and PA acceptors increases the values of enthalpy and entropy, while the complexation with DDQ and iodine acceptors decreases the values of these parameters compared with the free MZ donor.
Graphical abstractThe complexation chemistry of drug metronidazole with picric acid.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide