| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232413 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 9 Pages |
•PbO–Bi2O3–SiO2: xNiO glasses were synthesized.•IR, Raman optical absorption and luminescence studies have been carried out.•Analysis of the results indicated that Ni ions occupy octa and tetrahedral positions.•The photoluminescence (PL) efficiency found to be the highest for the glass N10.•The reasons for high PL efficiency were analyzed in the light of structural changes.
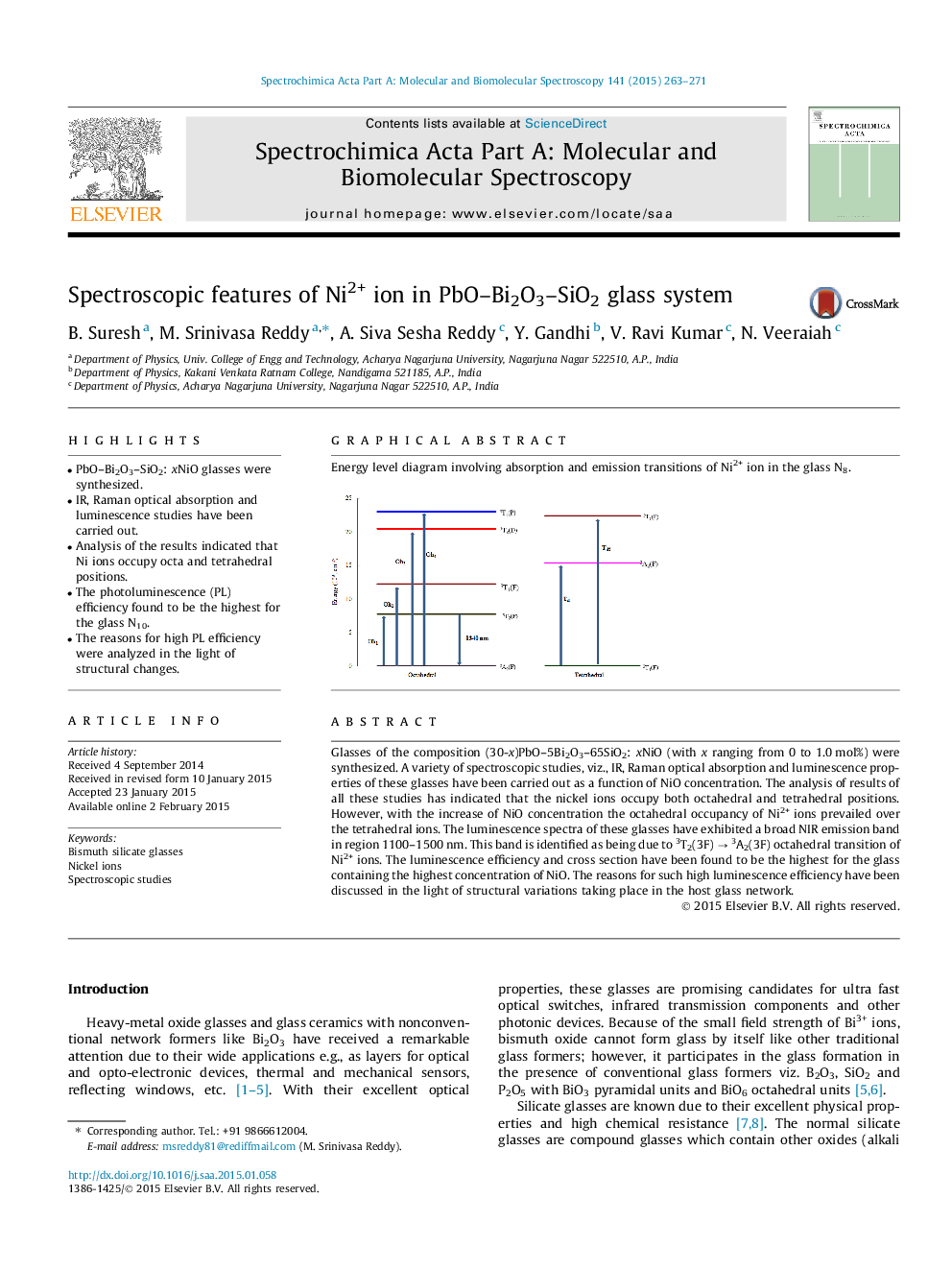
Glasses of the composition (30-x)PbO–5Bi2O3–65SiO2: xNiO (with x ranging from 0 to 1.0 mol%) were synthesized. A variety of spectroscopic studies, viz., IR, Raman optical absorption and luminescence properties of these glasses have been carried out as a function of NiO concentration. The analysis of results of all these studies has indicated that the nickel ions occupy both octahedral and tetrahedral positions. However, with the increase of NiO concentration the octahedral occupancy of Ni2+ ions prevailed over the tetrahedral ions. The luminescence spectra of these glasses have exhibited a broad NIR emission band in region 1100–1500 nm. This band is identified as being due to 3T2(3F) → 3A2(3F) octahedral transition of Ni2+ ions. The luminescence efficiency and cross section have been found to be the highest for the glass containing the highest concentration of NiO. The reasons for such high luminescence efficiency have been discussed in the light of structural variations taking place in the host glass network.
Graphical abstractEnergy level diagram involving absorption and emission transitions of Ni2+ ion in the glass N8.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide