| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232429 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 11 Pages |
•Dimethylphenyl betaine crystallizes with two molecules of 2,6-dichloro-4-nitro-phenol.•Molecules are linked by two different OH⋯O hydrogen bonds without the proton transfer.•The structures in crystal, gas phase and DMSO solution are analyzed.•The experimental and calculated frequencies have been assigned.•The magnetic isotropic shielding constants reproduce the experimental chemical shifts.
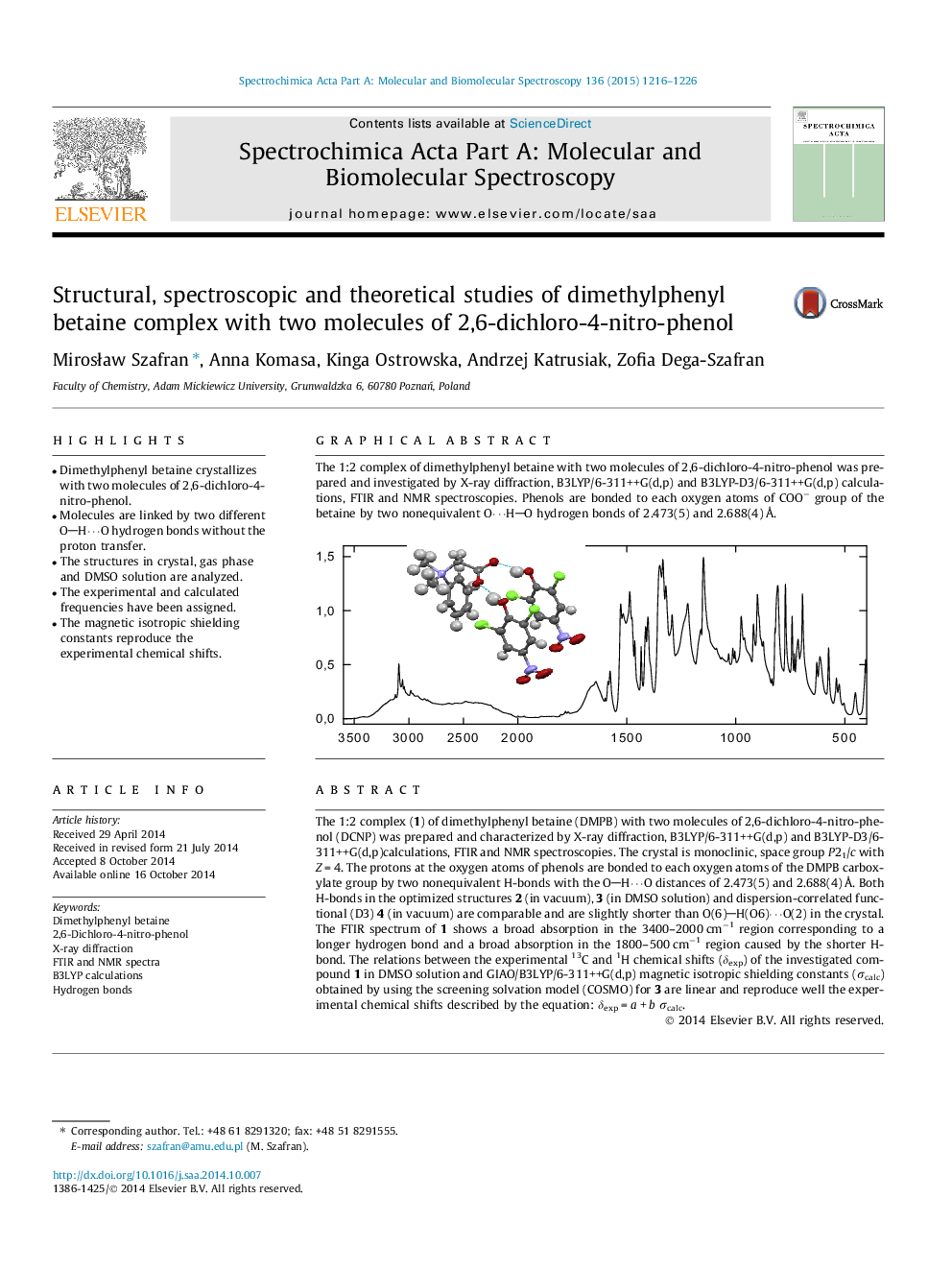
The 1:2 complex (1) of dimethylphenyl betaine (DMPB) with two molecules of 2,6-dichloro-4-nitro-phenol (DCNP) was prepared and characterized by X-ray diffraction, B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) and B3LYP-D3/6-311++G(d,p)calculations, FTIR and NMR spectroscopies. The crystal is monoclinic, space group P21/c with Z = 4. The protons at the oxygen atoms of phenols are bonded to each oxygen atoms of the DMPB carboxylate group by two nonequivalent H-bonds with the OH⋯O distances of 2.473(5) and 2.688(4) Å. Both H-bonds in the optimized structures 2 (in vacuum), 3 (in DMSO solution) and dispersion-correlated functional (D3) 4 (in vacuum) are comparable and are slightly shorter than O(6)H(O6)⋯O(2) in the crystal. The FTIR spectrum of 1 shows a broad absorption in the 3400–2000 cm−1 region corresponding to a longer hydrogen bond and a broad absorption in the 1800–500 cm−1 region caused by the shorter H-bond. The relations between the experimental 13C and 1H chemical shifts (δexp) of the investigated compound 1 in DMSO solution and GIAO/B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) magnetic isotropic shielding constants (σcalc) obtained by using the screening solvation model (COSMO) for 3 are linear and reproduce well the experimental chemical shifts described by the equation: δexp = a + b σcalc.
Graphical abstractThe 1:2 complex of dimethylphenyl betaine with two molecules of 2,6-dichloro-4-nitro-phenol was prepared and investigated by X-ray diffraction, B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) and B3LYP-D3/6-311++G(d,p) calculations, FTIR and NMR spectroscopies. Phenols are bonded to each oxygen atoms of COO− group of the betaine by two nonequivalent O⋯HO hydrogen bonds of 2.473(5) and 2.688(4) Å.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide