| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232436 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 16 Pages |
•Simultaneous photocatalytic-ozonation of pharmaceuticals using immobilized TiO2 NPs.•Analyzing the surface morphology of TiO2-coated ceramic plates by SEM and AFM.•Retrieving the concentration and spectral profiles of all compounds by MCR-ALS.•Assessing the influence of operational parameters by CCD.•Simultaneous maximization of three RE (%) by MRO and desirability function.
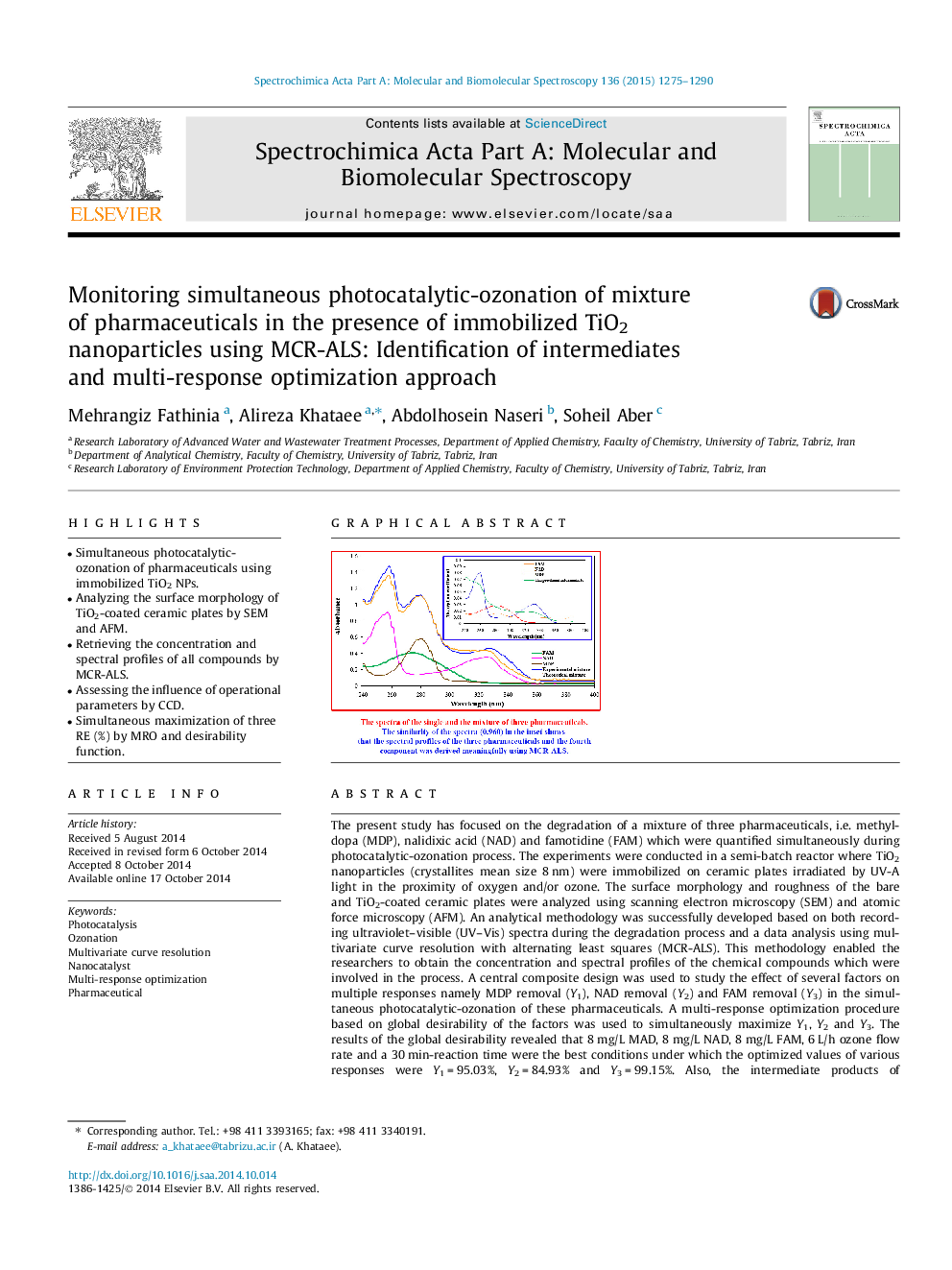
The present study has focused on the degradation of a mixture of three pharmaceuticals, i.e. methyldopa (MDP), nalidixic acid (NAD) and famotidine (FAM) which were quantified simultaneously during photocatalytic-ozonation process. The experiments were conducted in a semi-batch reactor where TiO2 nanoparticles (crystallites mean size 8 nm) were immobilized on ceramic plates irradiated by UV-A light in the proximity of oxygen and/or ozone. The surface morphology and roughness of the bare and TiO2-coated ceramic plates were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). An analytical methodology was successfully developed based on both recording ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis) spectra during the degradation process and a data analysis using multivariate curve resolution with alternating least squares (MCR-ALS). This methodology enabled the researchers to obtain the concentration and spectral profiles of the chemical compounds which were involved in the process. A central composite design was used to study the effect of several factors on multiple responses namely MDP removal (Y1), NAD removal (Y2) and FAM removal (Y3) in the simultaneous photocatalytic-ozonation of these pharmaceuticals. A multi-response optimization procedure based on global desirability of the factors was used to simultaneously maximize Y1, Y2 and Y3. The results of the global desirability revealed that 8 mg/L MAD, 8 mg/L NAD, 8 mg/L FAM, 6 L/h ozone flow rate and a 30 min-reaction time were the best conditions under which the optimized values of various responses were Y1 = 95.03%, Y2 = 84.93% and Y3 = 99.15%. Also, the intermediate products of pharmaceuticals generated in the photocatalytic-ozonation process were identified by gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide