| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232696 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 5 Pages |
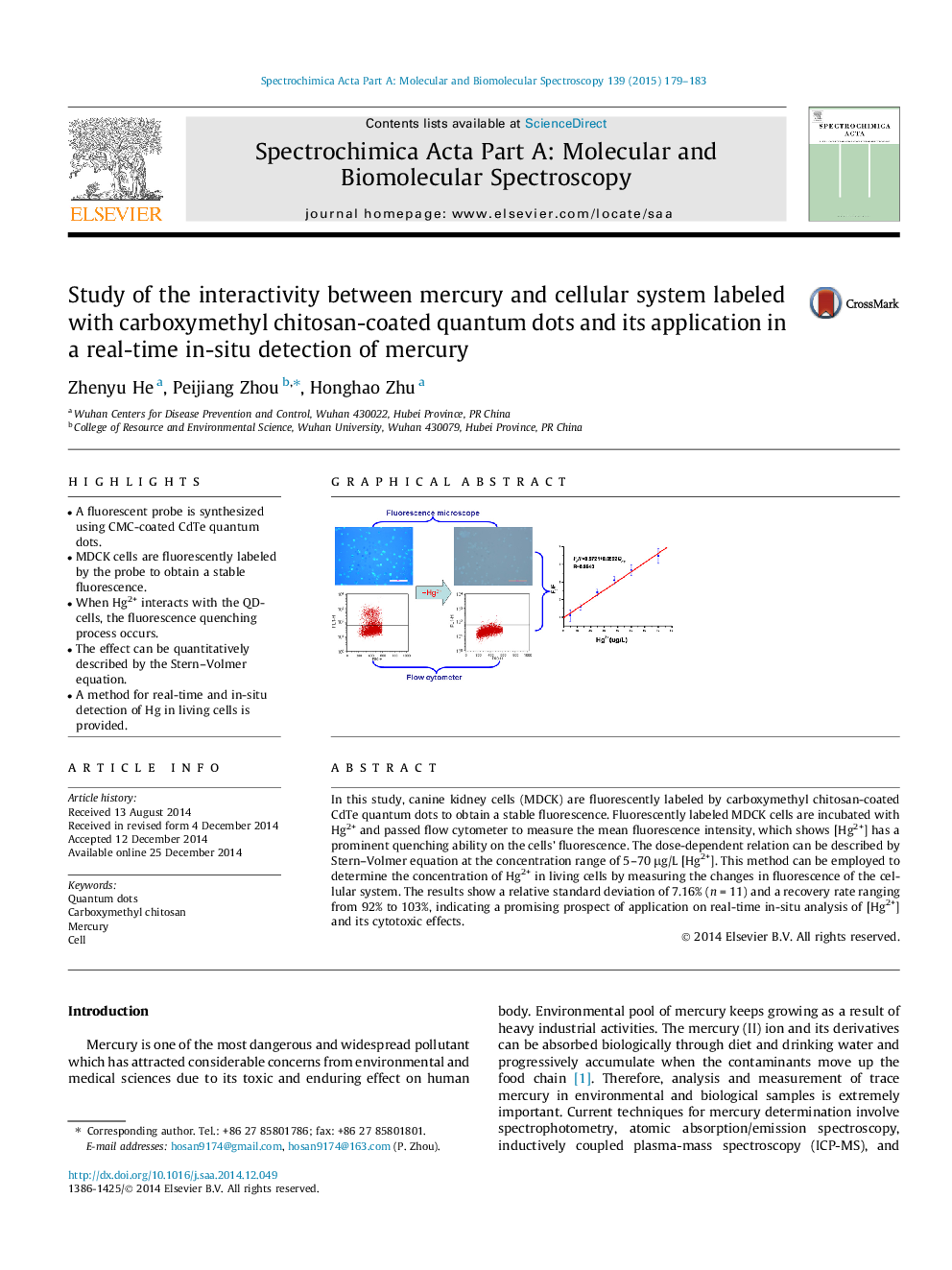
•A fluorescent probe is synthesized using CMC-coated CdTe quantum dots.•MDCK cells are fluorescently labeled by the probe to obtain a stable fluorescence.•When Hg2+ interacts with the QD-cells, the fluorescence quenching process occurs.•The effect can be quantitatively described by the Stern–Volmer equation.•A method for real-time and in-situ detection of Hg in living cells is provided.
In this study, canine kidney cells (MDCK) are fluorescently labeled by carboxymethyl chitosan-coated CdTe quantum dots to obtain a stable fluorescence. Fluorescently labeled MDCK cells are incubated with Hg2+ and passed flow cytometer to measure the mean fluorescence intensity, which shows [Hg2+] has a prominent quenching ability on the cells’ fluorescence. The dose-dependent relation can be described by Stern–Volmer equation at the concentration range of 5–70 μg/L [Hg2+]. This method can be employed to determine the concentration of Hg2+ in living cells by measuring the changes in fluorescence of the cellular system. The results show a relative standard deviation of 7.16% (n = 11) and a recovery rate ranging from 92% to 103%, indicating a promising prospect of application on real-time in-situ analysis of [Hg2+] and its cytotoxic effects.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide