| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232721 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 7 Pages |
•Cocos nucifera was utilized for the production of colloidal PbNPs.•Antibacterial study was evaluated for PbNPs.•Photocatalytic property was done with malachite green using PbNPs.
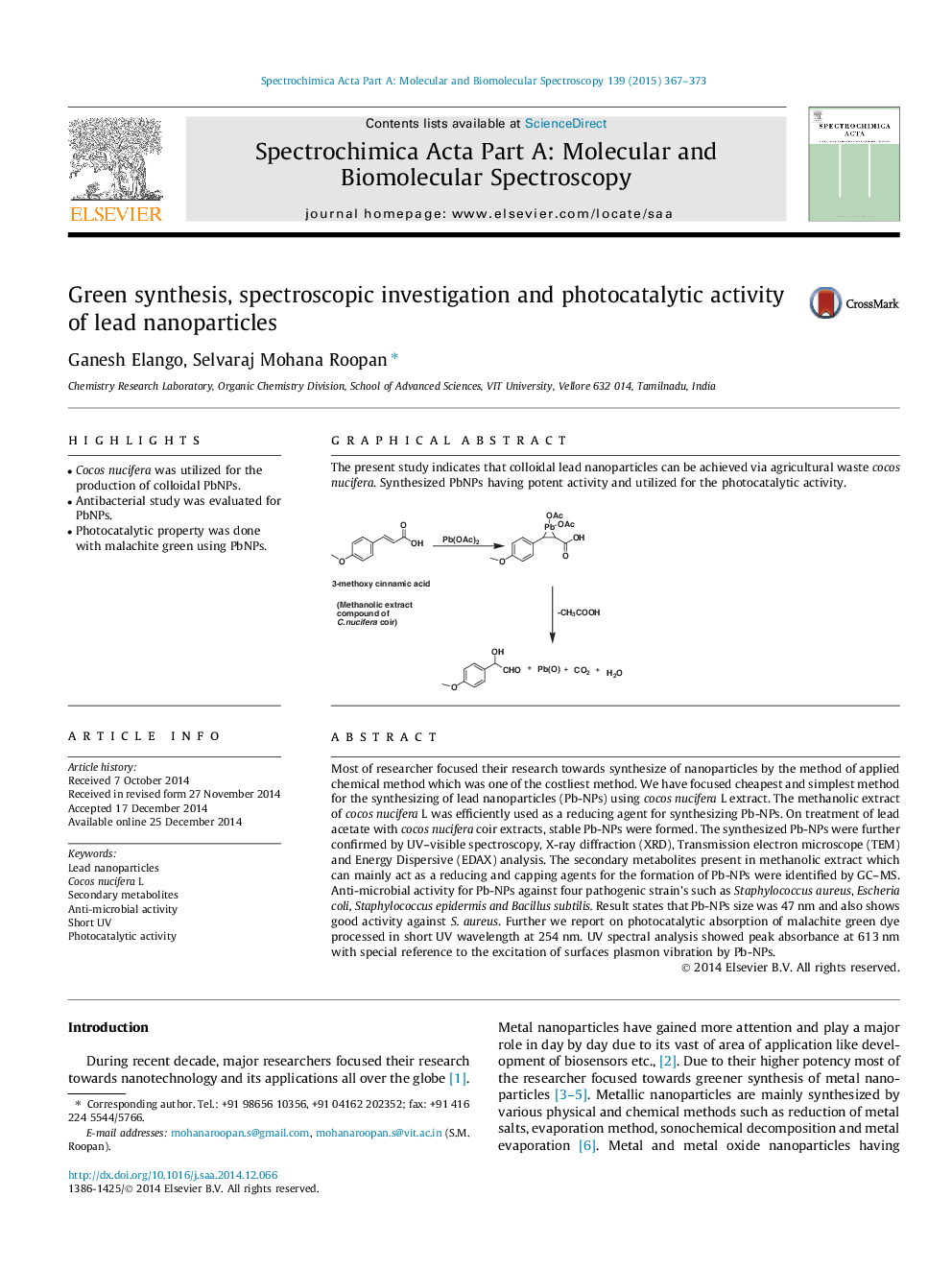
Most of researcher focused their research towards synthesize of nanoparticles by the method of applied chemical method which was one of the costliest method. We have focused cheapest and simplest method for the synthesizing of lead nanoparticles (Pb-NPs) using cocos nucifera L extract. The methanolic extract of cocos nucifera L was efficiently used as a reducing agent for synthesizing Pb-NPs. On treatment of lead acetate with cocos nucifera coir extracts, stable Pb-NPs were formed. The synthesized Pb-NPs were further confirmed by UV–visible spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Transmission electron microscope (TEM) and Energy Dispersive (EDAX) analysis. The secondary metabolites present in methanolic extract which can mainly act as a reducing and capping agents for the formation of Pb-NPs were identified by GC–MS. Anti-microbial activity for Pb-NPs against four pathogenic strain’s such as Staphylococcus aureus, Escheria coli, Staphylococcus epidermis and Bacillus subtilis. Result states that Pb-NPs size was 47 nm and also shows good activity against S. aureus. Further we report on photocatalytic absorption of malachite green dye processed in short UV wavelength at 254 nm. UV spectral analysis showed peak absorbance at 613 nm with special reference to the excitation of surfaces plasmon vibration by Pb-NPs.
Graphical abstractThe present study indicates that colloidal lead nanoparticles can be achieved via agricultural waste cocos nucifera. Synthesized PbNPs having potent activity and utilized for the photocatalytic activity.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide