| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232835 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 6 Pages |
•An ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted dual magnetic microextraction was developed.•Cadmium was selected as analyte.•Various analytical parameters were optimized.•Matrix effects of concomitants were also examined.•The procedure was applied to the determination of cadmium in real samples.
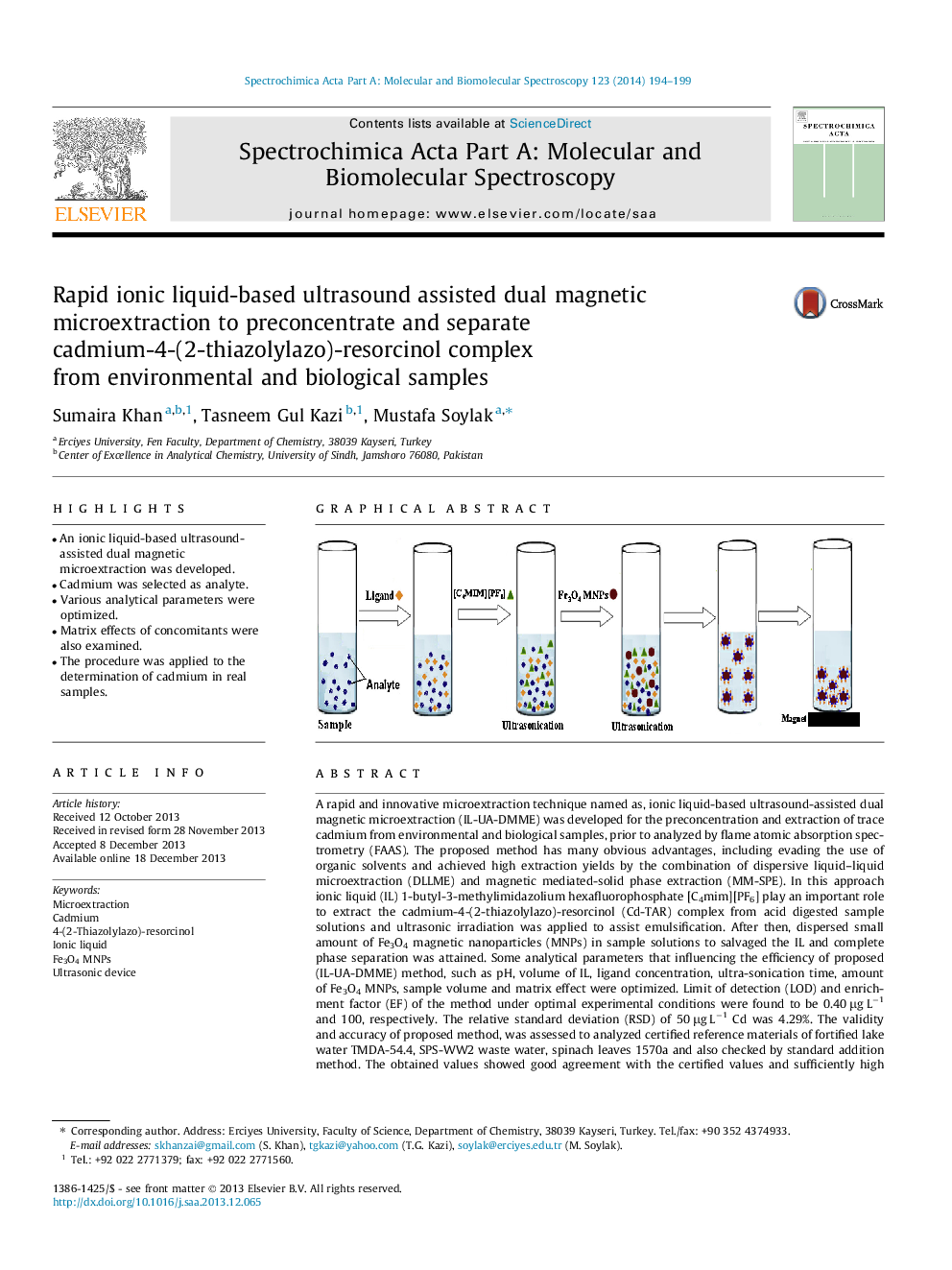
A rapid and innovative microextraction technique named as, ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted dual magnetic microextraction (IL-UA-DMME) was developed for the preconcentration and extraction of trace cadmium from environmental and biological samples, prior to analyzed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS). The proposed method has many obvious advantages, including evading the use of organic solvents and achieved high extraction yields by the combination of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) and magnetic mediated-solid phase extraction (MM-SPE). In this approach ionic liquid (IL) 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate [C4mim][PF6] play an important role to extract the cadmium-4-(2-thiazolylazo)-resorcinol (Cd-TAR) complex from acid digested sample solutions and ultrasonic irradiation was applied to assist emulsification. After then, dispersed small amount of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) in sample solutions to salvaged the IL and complete phase separation was attained. Some analytical parameters that influencing the efficiency of proposed (IL-UA-DMME) method, such as pH, volume of IL, ligand concentration, ultra-sonication time, amount of Fe3O4 MNPs, sample volume and matrix effect were optimized. Limit of detection (LOD) and enrichment factor (EF) of the method under optimal experimental conditions were found to be 0.40 μg L−1 and 100, respectively. The relative standard deviation (RSD) of 50 μg L−1 Cd was 4.29%. The validity and accuracy of proposed method, was assessed to analyzed certified reference materials of fortified lake water TMDA-54.4, SPS-WW2 waste water, spinach leaves 1570a and also checked by standard addition method. The obtained values showed good agreement with the certified values and sufficiently high recovery were found in the range of 98.1–101% for Cd. The proposed method was facile, rapid and successfully applied for the determination of Cd in environmental and different biological samples.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide