| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232842 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 8 Pages |
•Fluorescence and UV–vis data matrices were combined.•Four data matrices related to the interaction of the BDM with BSA were analysed.•Chemometrics were used to interpret the interaction of the BDM and DXM with BSA.•DXM competed with the BDM molecules bound in the BDM–BSA complex.•Two multi-way calibration approaches, MCR–ALS and PARAFAC, were used.
Interactions between the anti-carcinogens, bendamustine (BDM) and dexamethasone (DXM), with bovine serum albumin (BSA) were investigated with the use of fluorescence and UV–vis spectroscopies under pseudo-physiological conditions (Tris–HCl buffer, pH 7.4). The static mechanism was responsible for the fluorescence quenching during the interactions; the binding formation constant of the BSA–BDM complex and the binding number were 5.14 × 105 L mol−1 and 1.0, respectively. Spectroscopic studies for the formation of BDM–BSA complex were interpreted with the use of multivariate curve resolution – alternating least squares (MCR–ALS), which supported the complex formation. The BSA samples treated with site markers (warfarin – site I and ibuprofen – site II) were reacted separately with BDM and DXM; while both anti-carcinogens bound to site I, the binding constants suggested that DXM formed a more stable complex. Relative concentration profiles and the fluorescence spectra associated with BDM, DXM and BSA, were recovered simultaneously from the full fluorescence excitation–emission data with the use of the parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) method. The results confirmed that on addition of DXM to the BDM–BSA complex, the BDM was replaced and the DXM–BSA complex formed; free BDM was released. This finding may have consequences for the transport of these drugs during any anti-cancer treatment.
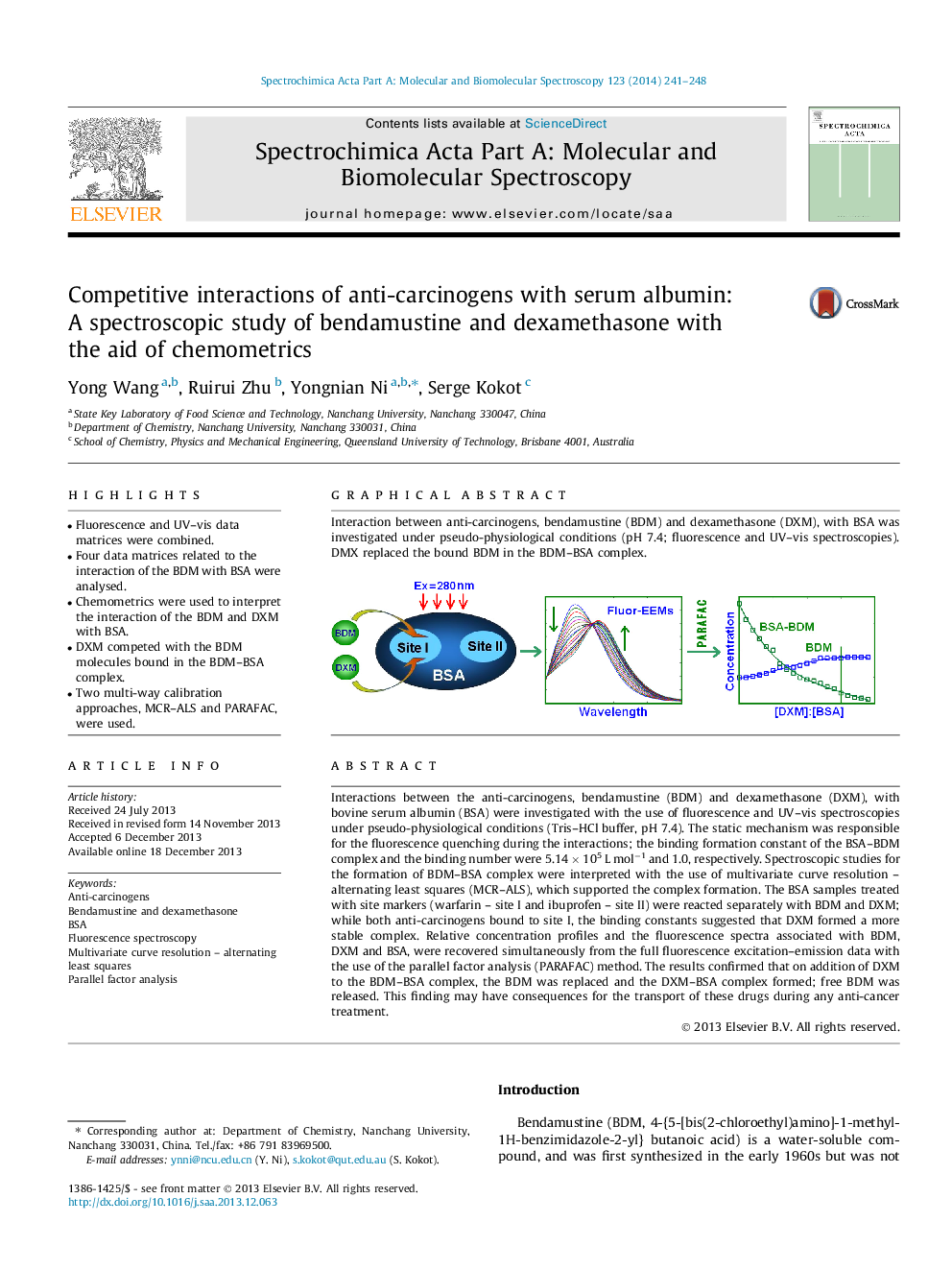
Graphical abstractInteraction between anti-carcinogens, bendamustine (BDM) and dexamethasone (DXM), with BSA was investigated under pseudo-physiological conditions (pH 7.4; fluorescence and UV–vis spectroscopies). DMX replaced the bound BDM in the BDM–BSA complex.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide