| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232849 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 5 Pages |
•A one-pot method to prepare CdTe QDs was developed using NH2OH·HCl as a reduction.•CdTe QDs were synthesized in an aqueous solution without supernumerary protection.•The maximum photoluminescence quantum yields of the QDs can achieve to 47%.
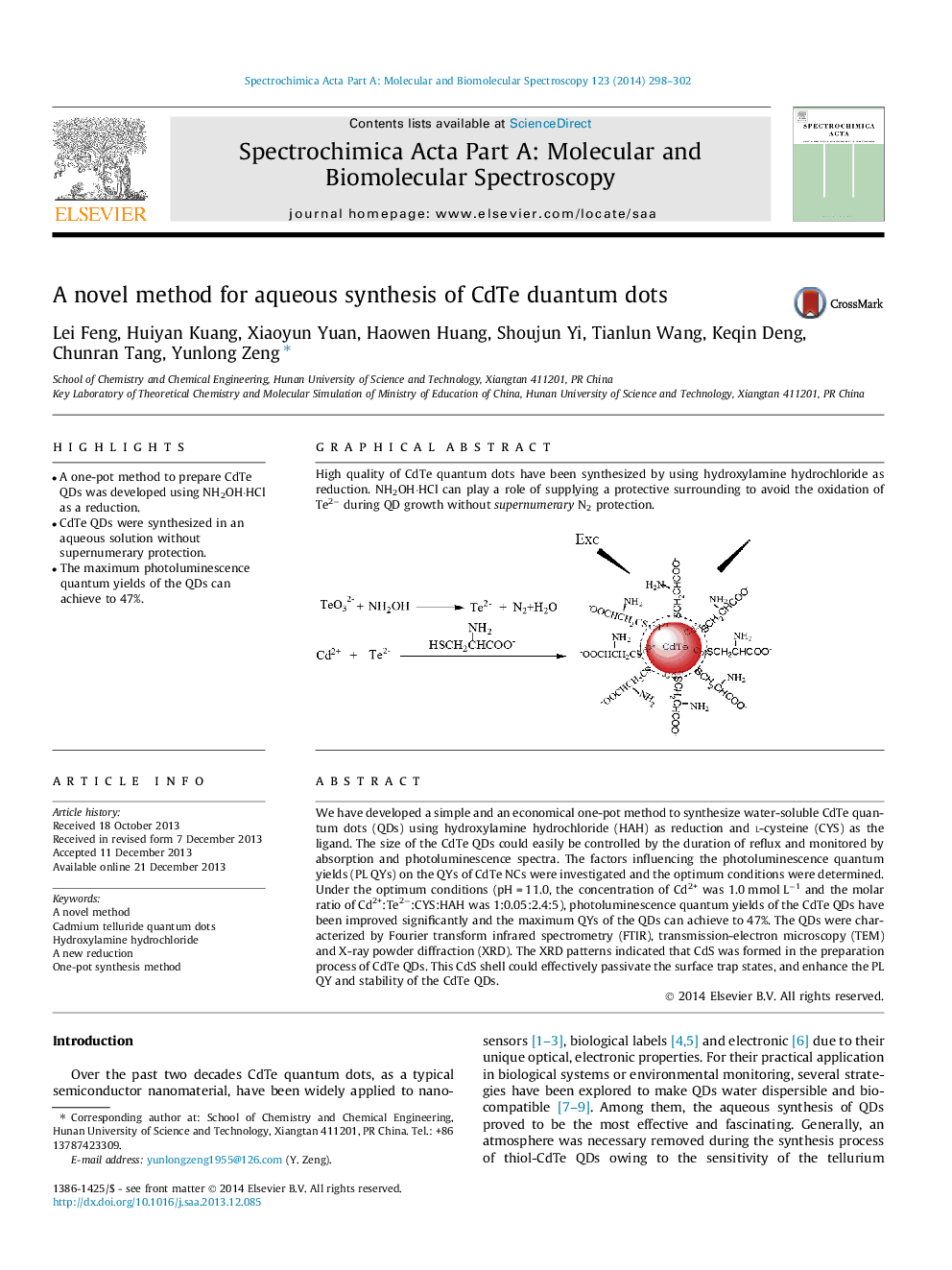
We have developed a simple and an economical one-pot method to synthesize water-soluble CdTe quantum dots (QDs) using hydroxylamine hydrochloride (HAH) as reduction and l-cysteine (CYS) as the ligand. The size of the CdTe QDs could easily be controlled by the duration of reflux and monitored by absorption and photoluminescence spectra. The factors influencing the photoluminescence quantum yields (PL QYs) on the QYs of CdTe NCs were investigated and the optimum conditions were determined. Under the optimum conditions (pH = 11.0, the concentration of Cd2+ was 1.0 mmol L−1 and the molar ratio of Cd2+:Te2−:CYS:HAH was 1:0.05:2.4:5), photoluminescence quantum yields of the CdTe QDs have been improved significantly and the maximum QYs of the QDs can achieve to 47%. The QDs were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR), transmission-electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). The XRD patterns indicated that CdS was formed in the preparation process of CdTe QDs. This CdS shell could effectively passivate the surface trap states, and enhance the PL QY and stability of the CdTe QDs.
Graphical abstractHigh quality of CdTe quantum dots have been synthesized by using hydroxylamine hydrochloride as reduction. NH2OH·HCl can play a role of supplying a protective surrounding to avoid the oxidation of Te2− during QD growth without supernumerary N2 protection.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide