| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232852 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 9 Pages |
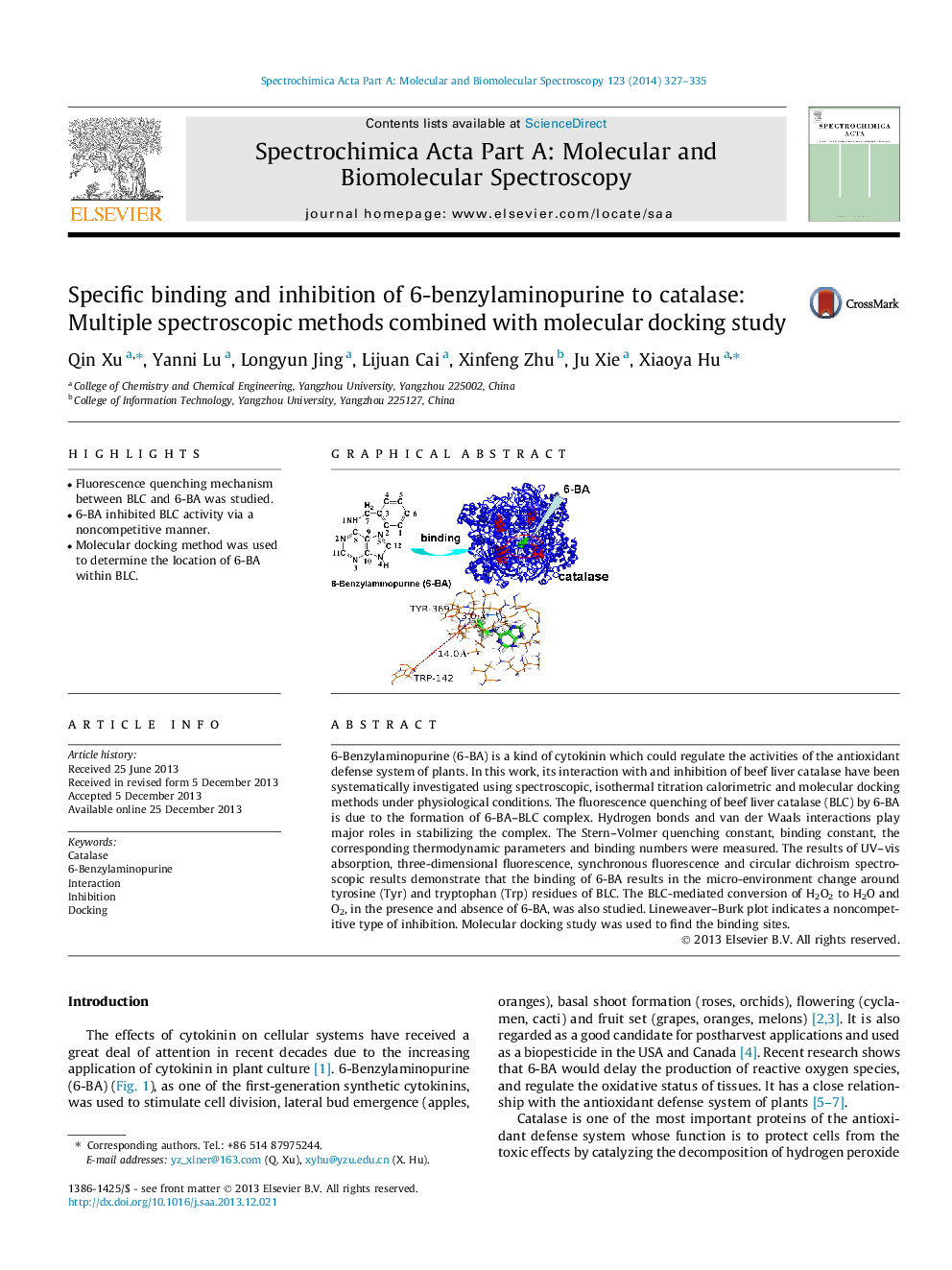
•Fluorescence quenching mechanism between BLC and 6-BA was studied.•6-BA inhibited BLC activity via a noncompetitive manner.•Molecular docking method was used to determine the location of 6-BA within BLC.
6-Benzylaminopurine (6-BA) is a kind of cytokinin which could regulate the activities of the antioxidant defense system of plants. In this work, its interaction with and inhibition of beef liver catalase have been systematically investigated using spectroscopic, isothermal titration calorimetric and molecular docking methods under physiological conditions. The fluorescence quenching of beef liver catalase (BLC) by 6-BA is due to the formation of 6-BA–BLC complex. Hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions play major roles in stabilizing the complex. The Stern–Volmer quenching constant, binding constant, the corresponding thermodynamic parameters and binding numbers were measured. The results of UV–vis absorption, three-dimensional fluorescence, synchronous fluorescence and circular dichroism spectroscopic results demonstrate that the binding of 6-BA results in the micro-environment change around tyrosine (Tyr) and tryptophan (Trp) residues of BLC. The BLC-mediated conversion of H2O2 to H2O and O2, in the presence and absence of 6-BA, was also studied. Lineweaver–Burk plot indicates a noncompetitive type of inhibition. Molecular docking study was used to find the binding sites.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide