| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1232861 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 8 Pages |
•Synthesis of NiS nanoparticle-loaded activated carbon as a novel adsorbent.•Synthesis of the adsorbent with high surface area of 1018 m2/g according BET.•Efficient and rapid removal of dyes in binary solutions within 5 min.•Response optimization by using response surface methodology.
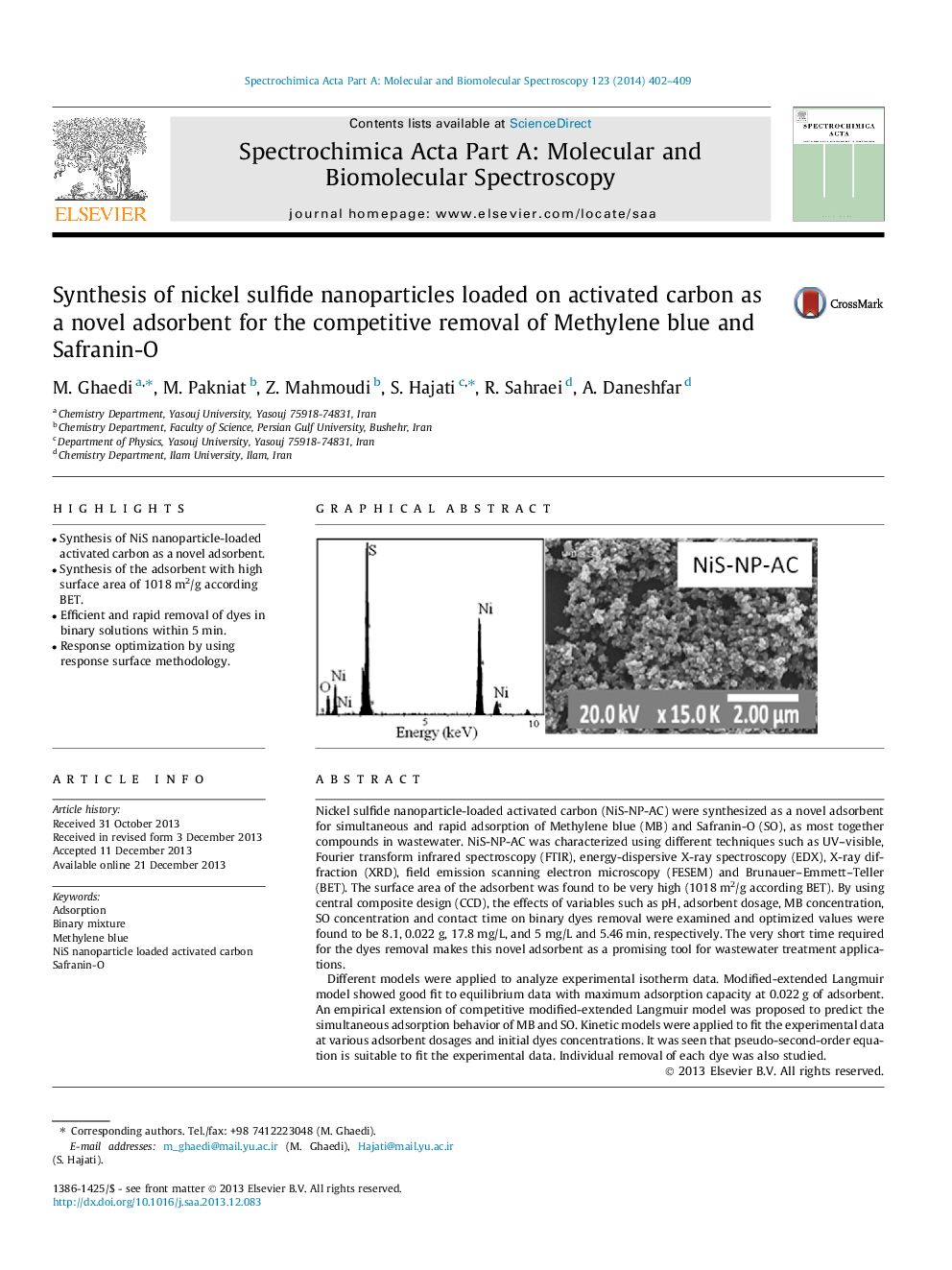
Nickel sulfide nanoparticle-loaded activated carbon (NiS-NP-AC) were synthesized as a novel adsorbent for simultaneous and rapid adsorption of Methylene blue (MB) and Safranin-O (SO), as most together compounds in wastewater. NiS-NP-AC was characterized using different techniques such as UV–visible, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET). The surface area of the adsorbent was found to be very high (1018 m2/g according BET). By using central composite design (CCD), the effects of variables such as pH, adsorbent dosage, MB concentration, SO concentration and contact time on binary dyes removal were examined and optimized values were found to be 8.1, 0.022 g, 17.8 mg/L, and 5 mg/L and 5.46 min, respectively. The very short time required for the dyes removal makes this novel adsorbent as a promising tool for wastewater treatment applications.Different models were applied to analyze experimental isotherm data. Modified-extended Langmuir model showed good fit to equilibrium data with maximum adsorption capacity at 0.022 g of adsorbent. An empirical extension of competitive modified-extended Langmuir model was proposed to predict the simultaneous adsorption behavior of MB and SO. Kinetic models were applied to fit the experimental data at various adsorbent dosages and initial dyes concentrations. It was seen that pseudo-second-order equation is suitable to fit the experimental data. Individual removal of each dye was also studied.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide