| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233181 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 5 Pages |
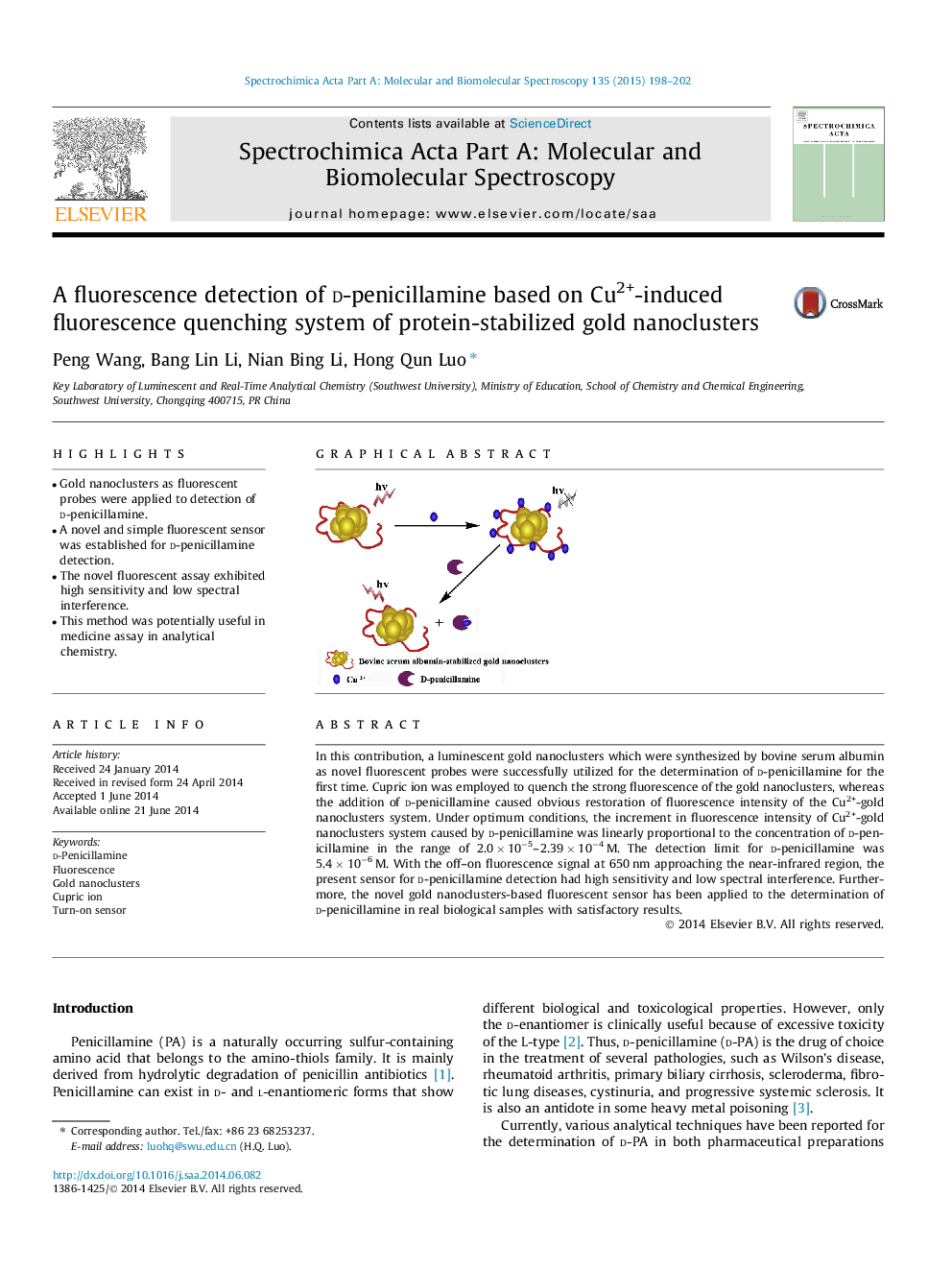
•Gold nanoclusters as fluorescent probes were applied to detection of d-penicillamine.•A novel and simple fluorescent sensor was established for d-penicillamine detection.•The novel fluorescent assay exhibited high sensitivity and low spectral interference.•This method was potentially useful in medicine assay in analytical chemistry.
In this contribution, a luminescent gold nanoclusters which were synthesized by bovine serum albumin as novel fluorescent probes were successfully utilized for the determination of d-penicillamine for the first time. Cupric ion was employed to quench the strong fluorescence of the gold nanoclusters, whereas the addition of d-penicillamine caused obvious restoration of fluorescence intensity of the Cu2+-gold nanoclusters system. Under optimum conditions, the increment in fluorescence intensity of Cu2+-gold nanoclusters system caused by d-penicillamine was linearly proportional to the concentration of d-penicillamine in the range of 2.0 × 10−5–2.39 × 10−4 M. The detection limit for d-penicillamine was 5.4 × 10−6 M. With the off–on fluorescence signal at 650 nm approaching the near-infrared region, the present sensor for d-penicillamine detection had high sensitivity and low spectral interference. Furthermore, the novel gold nanoclusters-based fluorescent sensor has been applied to the determination of d-penicillamine in real biological samples with satisfactory results.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide