| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233187 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 4 Pages |
•Eichhornia crassipes is a noxious, aquatic and intransigent weed.•Eichhornia was used as a raw material for production of vermicompost.•Humic substances functional groups were analysed by FT-IR spectroscopy.•GC–MS is used to analysis the compounds of vermicompost and compost.
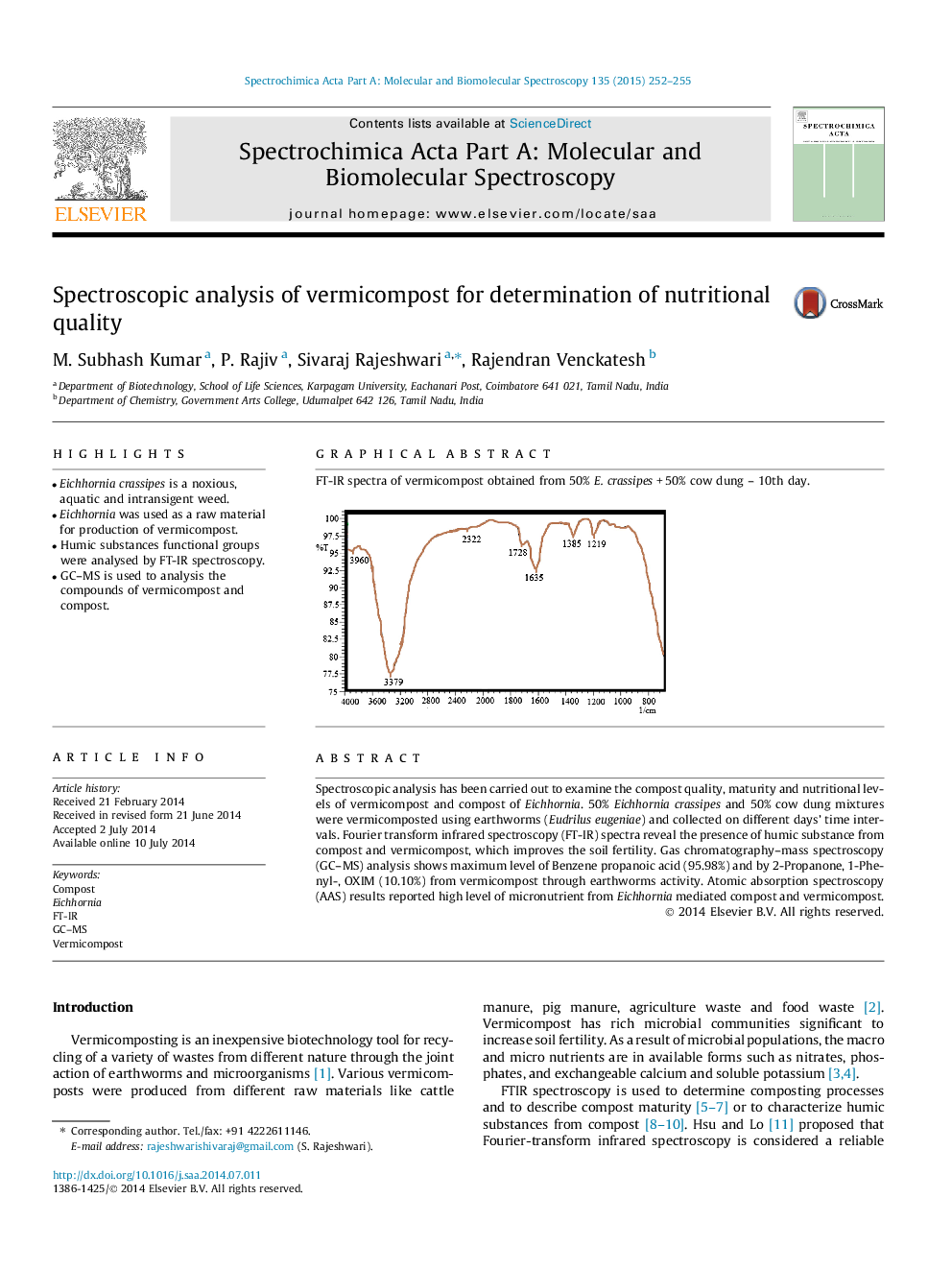
Spectroscopic analysis has been carried out to examine the compost quality, maturity and nutritional levels of vermicompost and compost of Eichhornia. 50% Eichhorniacrassipes and 50% cow dung mixtures were vermicomposted using earthworms (Eudrilus eugeniae) and collected on different days’ time intervals. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) spectra reveal the presence of humic substance from compost and vermicompost, which improves the soil fertility. Gas chromatography–mass spectroscopy (GC–MS) analysis shows maximum level of Benzene propanoic acid (95.98%) and by 2-Propanone, 1-Phenyl-, OXIM (10.10%) from vermicompost through earthworms activity. Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) results reported high level of micronutrient from Eichhornia mediated compost and vermicompost.
Graphical abstractFT-IR spectra of vermicompost obtained from 50% E. crassipes + 50% cow dung – 10th day.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide