| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233218 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 10 Pages |
•Interaction of CYA and UA with BSA and Mel were studied by spectroscopy.•Binding sites of CYA and UA to BSA were confirmed by synchronous fluorescence.•Interaction mechanism of CYA and UA with MEL was proposed.
In this work, the fluorescence quenching was used to study the interaction of cyanuric acid (CYA) and uric acid (UA) with bovine serum albumin (BSA) at two different temperatures (283 K and 310 K). The bimolecular quenching constant (Kq), apparent quenching constant (Ksv), effective binding constant (KA) and corresponding dissociation constant (KD), binding site number (n) and binding distance (r) were calculated by adopting Stern–Volmer, Lineweaver–Burk, Double logarithm and overlap integral equations. The results show that CYA and UA are both able to obviously bind to BSA, but the binding strength order is BSA + CYA < BSA + UA. And then, the interactions of CYA and UA with melamine (MEL) under the same conditions were also studied by using similar methods. The results indicates that both CYA and UA can bind together closely with melamine (MEL). It is wished that these research results would facilitate the understanding the formation of kidney stones and gout in the body after ingesting excess MEL.
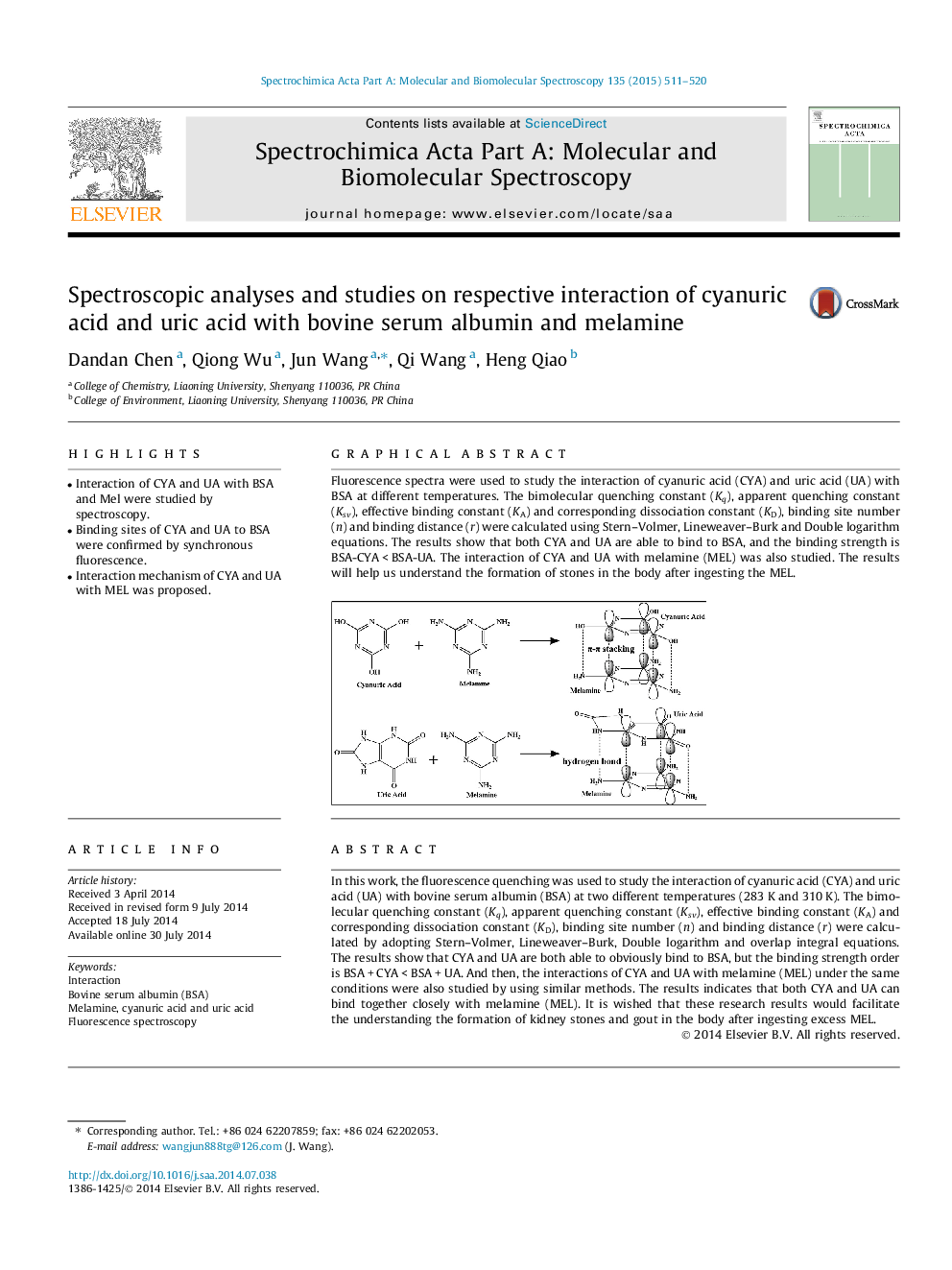
Graphical abstractFluorescence spectra were used to study the interaction of cyanuric acid (CYA) and uric acid (UA) with BSA at different temperatures. The bimolecular quenching constant (Kq), apparent quenching constant (Ksv), effective binding constant (KA) and corresponding dissociation constant (KD), binding site number (n) and binding distance (r) were calculated using Stern–Volmer, Lineweaver–Burk and Double logarithm equations. The results show that both CYA and UA are able to bind to BSA, and the binding strength is BSA-CYA < BSA-UA. The interaction of CYA and UA with melamine (MEL) was also studied. The results will help us understand the formation of stones in the body after ingesting the MEL.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide