| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233220 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 7 Pages |
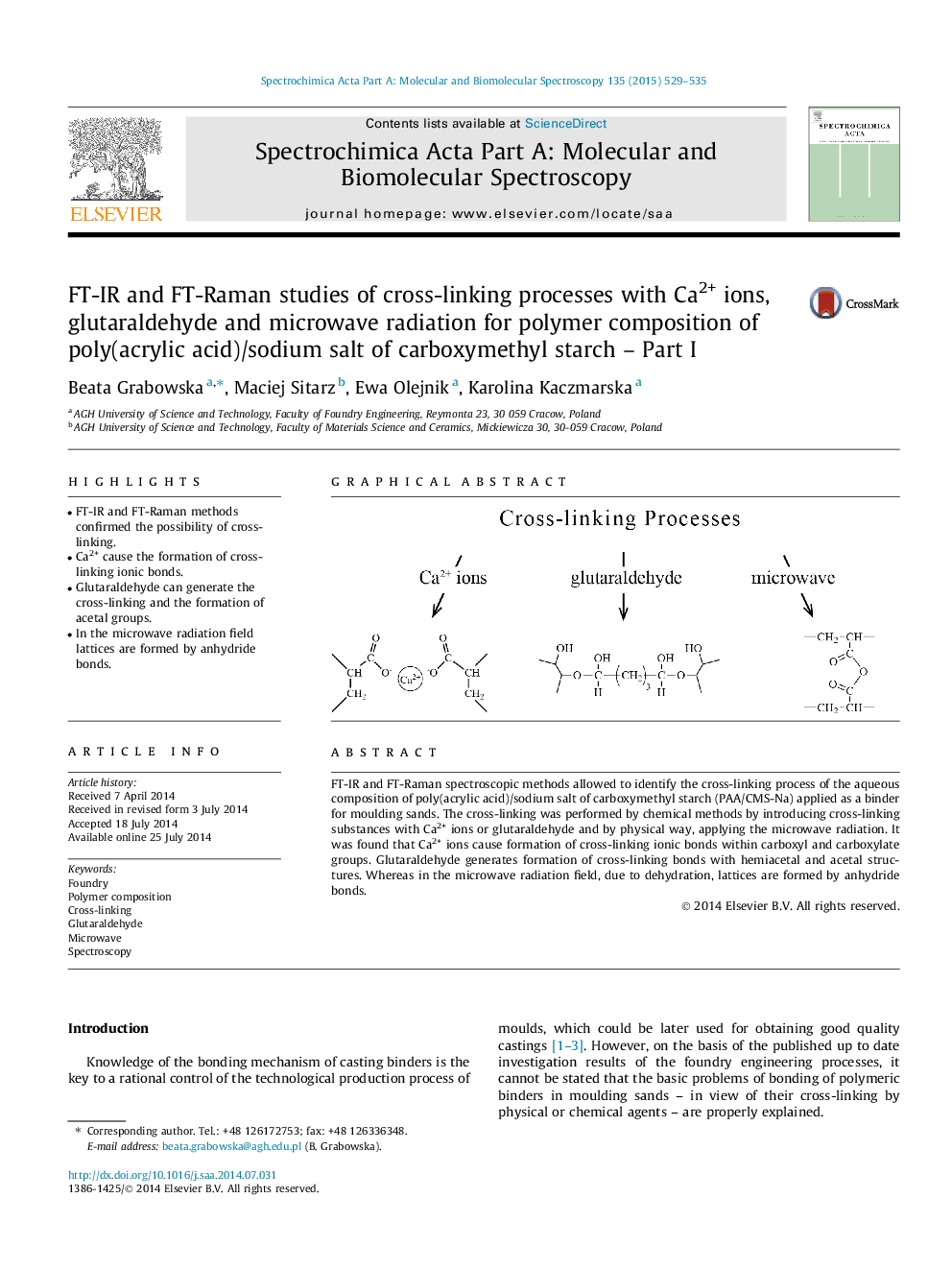
•FT-IR and FT-Raman methods confirmed the possibility of cross-linking.•Ca2+ cause the formation of cross-linking ionic bonds.•Glutaraldehyde can generate the cross-linking and the formation of acetal groups.•In the microwave radiation field lattices are formed by anhydride bonds.
FT-IR and FT-Raman spectroscopic methods allowed to identify the cross-linking process of the aqueous composition of poly(acrylic acid)/sodium salt of carboxymethyl starch (PAA/CMS-Na) applied as a binder for moulding sands. The cross-linking was performed by chemical methods by introducing cross-linking substances with Ca2+ ions or glutaraldehyde and by physical way, applying the microwave radiation. It was found that Ca2+ ions cause formation of cross-linking ionic bonds within carboxyl and carboxylate groups. Glutaraldehyde generates formation of cross-linking bonds with hemiacetal and acetal structures. Whereas in the microwave radiation field, due to dehydration, lattices are formed by anhydride bonds.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide