| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233227 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 14 Pages |
•Spectral investigation has been carried out on insecticide compound BONA.•Hydrogen bonding and charge transfer interactions are also analyzed.•The vibrational spectral analysis supports the existence of strong intra- and inter-molecular hydrogen bonding.•N–H⋯O hydrogen bonding between the drug molecule and the amino acids of the protein binding site shows bioactive nature.
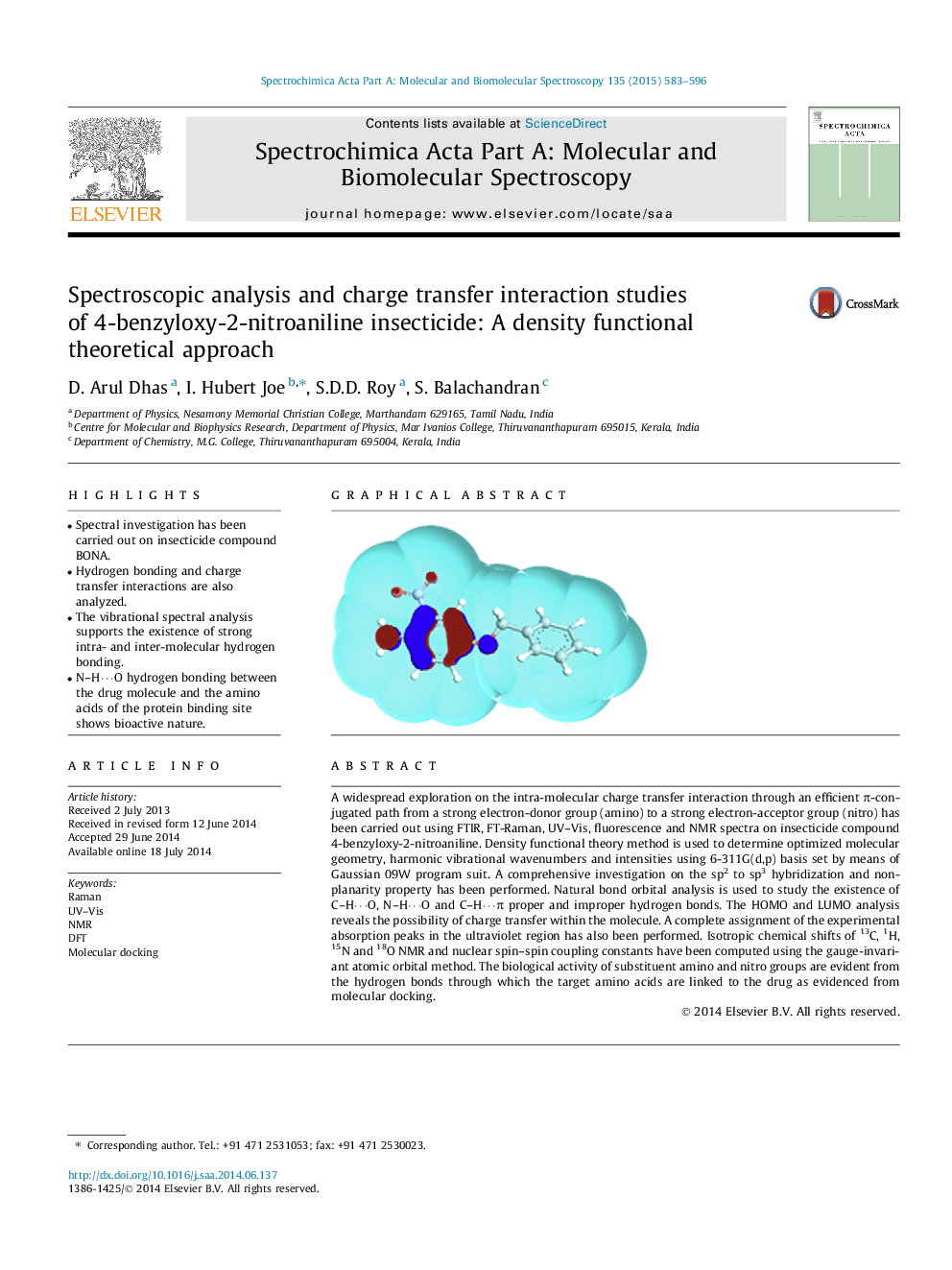
A widespread exploration on the intra-molecular charge transfer interaction through an efficient π-conjugated path from a strong electron-donor group (amino) to a strong electron-acceptor group (nitro) has been carried out using FTIR, FT-Raman, UV–Vis, fluorescence and NMR spectra on insecticide compound 4-benzyloxy-2-nitroaniline. Density functional theory method is used to determine optimized molecular geometry, harmonic vibrational wavenumbers and intensities using 6-311G(d,p) basis set by means of Gaussian 09W program suit. A comprehensive investigation on the sp2 to sp3 hybridization and non-planarity property has been performed. Natural bond orbital analysis is used to study the existence of C–H⋯O, N–H⋯O and C–H⋯π proper and improper hydrogen bonds. The HOMO and LUMO analysis reveals the possibility of charge transfer within the molecule. A complete assignment of the experimental absorption peaks in the ultraviolet region has also been performed. Isotropic chemical shifts of 13C, 1H, 15N and 18O NMR and nuclear spin–spin coupling constants have been computed using the gauge-invariant atomic orbital method. The biological activity of substituent amino and nitro groups are evident from the hydrogen bonds through which the target amino acids are linked to the drug as evidenced from molecular docking.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide