| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233234 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 6 Pages |
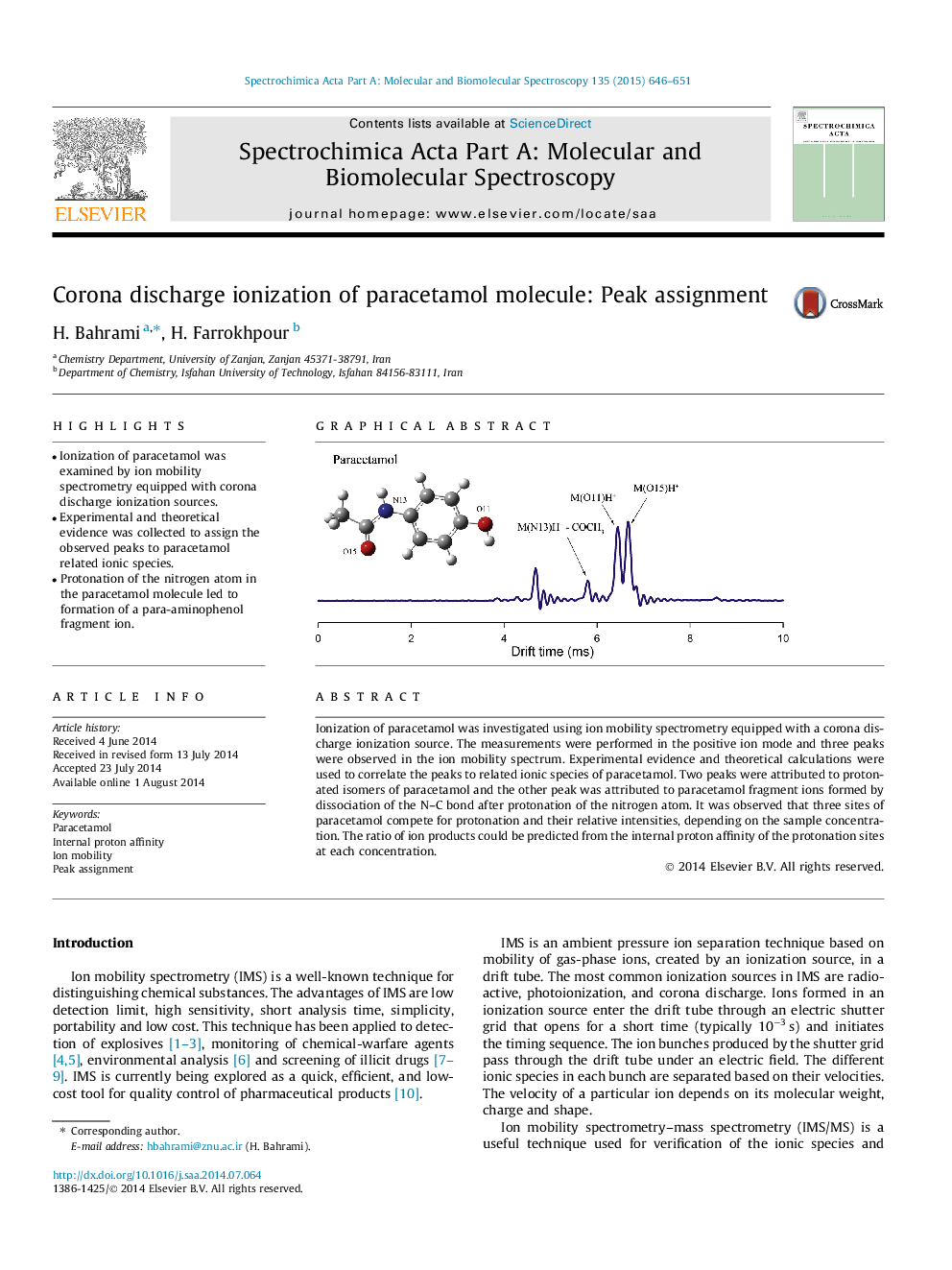
•Ionization of paracetamol was examined by ion mobility spectrometry equipped with corona discharge ionization sources.•Experimental and theoretical evidence was collected to assign the observed peaks to paracetamol related ionic species.•Protonation of the nitrogen atom in the paracetamol molecule led to formation of a para-aminophenol fragment ion.
Ionization of paracetamol was investigated using ion mobility spectrometry equipped with a corona discharge ionization source. The measurements were performed in the positive ion mode and three peaks were observed in the ion mobility spectrum. Experimental evidence and theoretical calculations were used to correlate the peaks to related ionic species of paracetamol. Two peaks were attributed to protonated isomers of paracetamol and the other peak was attributed to paracetamol fragment ions formed by dissociation of the N–C bond after protonation of the nitrogen atom. It was observed that three sites of paracetamol compete for protonation and their relative intensities, depending on the sample concentration. The ratio of ion products could be predicted from the internal proton affinity of the protonation sites at each concentration.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide