| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233240 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 14 Pages |
•Synthesis of H2PAPS, H2PAPT, H2PABT and their Ni(II) complexes.•Experimental IR spectra of ligands are compared with those obtained theoretically from DFT calculations.•The free ligands showed a higher antibacterial and antitumor effect than their Ni(II) complexes.
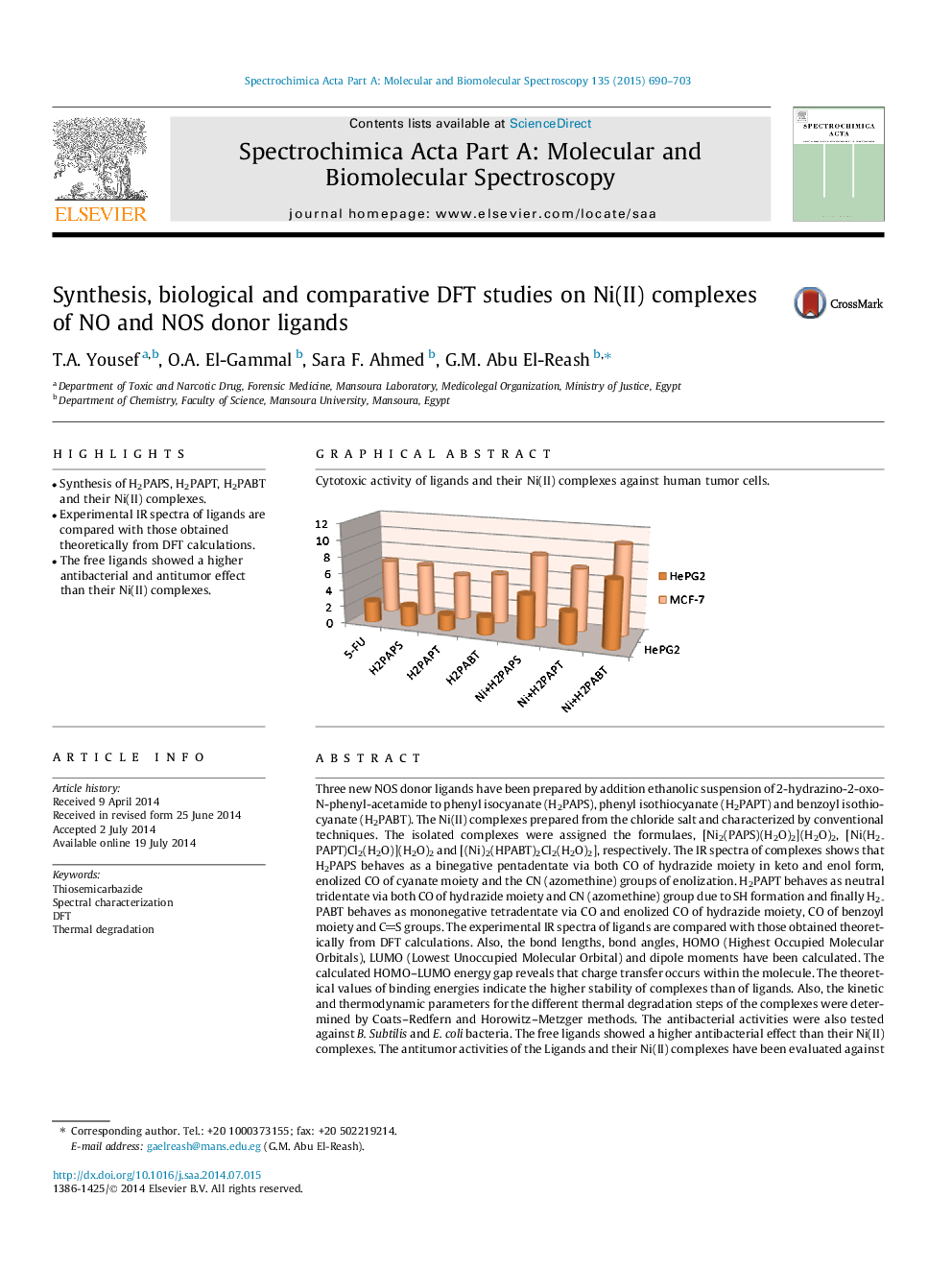
Three new NOS donor ligands have been prepared by addition ethanolic suspension of 2-hydrazino-2-oxo-N-phenyl-acetamide to phenyl isocyanate (H2PAPS), phenyl isothiocyanate (H2PAPT) and benzoyl isothiocyanate (H2PABT). The Ni(II) complexes prepared from the chloride salt and characterized by conventional techniques. The isolated complexes were assigned the formulaes, [Ni2(PAPS)(H2O)2](H2O)2, [Ni(H2PAPT)Cl2(H2O)](H2O)2 and [(Ni)2(HPABT)2Cl2(H2O)2], respectively. The IR spectra of complexes shows that H2PAPS behaves as a binegative pentadentate via both CO of hydrazide moiety in keto and enol form, enolized CO of cyanate moiety and the CN (azomethine) groups of enolization. H2PAPT behaves as neutral tridentate via both CO of hydrazide moiety and CN (azomethine) group due to SH formation and finally H2PABT behaves as mononegative tetradentate via CO and enolized CO of hydrazide moiety, CO of benzoyl moiety and CS groups. The experimental IR spectra of ligands are compared with those obtained theoretically from DFT calculations. Also, the bond lengths, bond angles, HOMO (Highest Occupied Molecular Orbitals), LUMO (Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) and dipole moments have been calculated. The calculated HOMO–LUMO energy gap reveals that charge transfer occurs within the molecule. The theoretical values of binding energies indicate the higher stability of complexes than of ligands. Also, the kinetic and thermodynamic parameters for the different thermal degradation steps of the complexes were determined by Coats–Redfern and Horowitz–Metzger methods. The antibacterial activities were also tested against B. Subtilis and E. coli bacteria. The free ligands showed a higher antibacterial effect than their Ni(II) complexes. The antitumor activities of the Ligands and their Ni(II) complexes have been evaluated against liver (HePG2) and breast (MCF-7) cancer cells. All ligands were found to display cytotoxicity that are better than that of Fluorouracil (5-FU), while Ni(II) complexes show low activity.
Graphical abstractCytotoxic activity of ligands and their Ni(II) complexes against human tumor cells.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide