| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233242 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2015 | 10 Pages |
•Synthesis and characterization of Schiff bases and their complexes.•In vitro antimicrobial activity of compounds.•Biocidal activity of ligands increased upon coordination with metal ions.•Compound Cu(LIV)(Q)⋅H2O is found to be most potent.
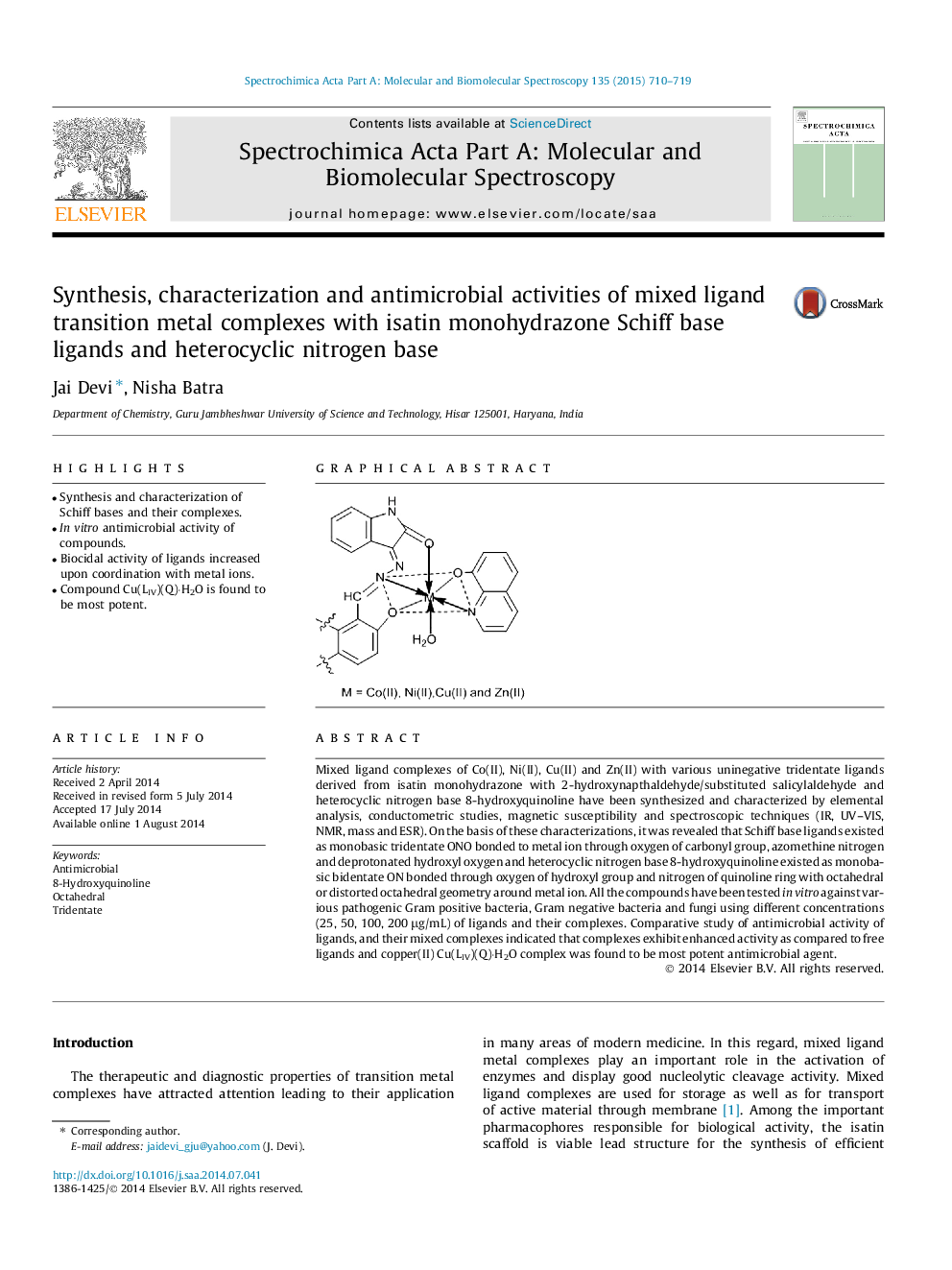
Mixed ligand complexes of Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) with various uninegative tridentate ligands derived from isatin monohydrazone with 2-hydroxynapthaldehyde/substituted salicylaldehyde and heterocyclic nitrogen base 8-hydroxyquinoline have been synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis, conductometric studies, magnetic susceptibility and spectroscopic techniques (IR, UV–VIS, NMR, mass and ESR). On the basis of these characterizations, it was revealed that Schiff base ligands existed as monobasic tridentate ONO bonded to metal ion through oxygen of carbonyl group, azomethine nitrogen and deprotonated hydroxyl oxygen and heterocyclic nitrogen base 8-hydroxyquinoline existed as monobasic bidentate ON bonded through oxygen of hydroxyl group and nitrogen of quinoline ring with octahedral or distorted octahedral geometry around metal ion. All the compounds have been tested in vitro against various pathogenic Gram positive bacteria, Gram negative bacteria and fungi using different concentrations (25, 50, 100, 200 μg/mL) of ligands and their complexes. Comparative study of antimicrobial activity of ligands, and their mixed complexes indicated that complexes exhibit enhanced activity as compared to free ligands and copper(II) Cu(LIV)(Q)⋅H2O complex was found to be most potent antimicrobial agent.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide