| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233492 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 7 Pages |
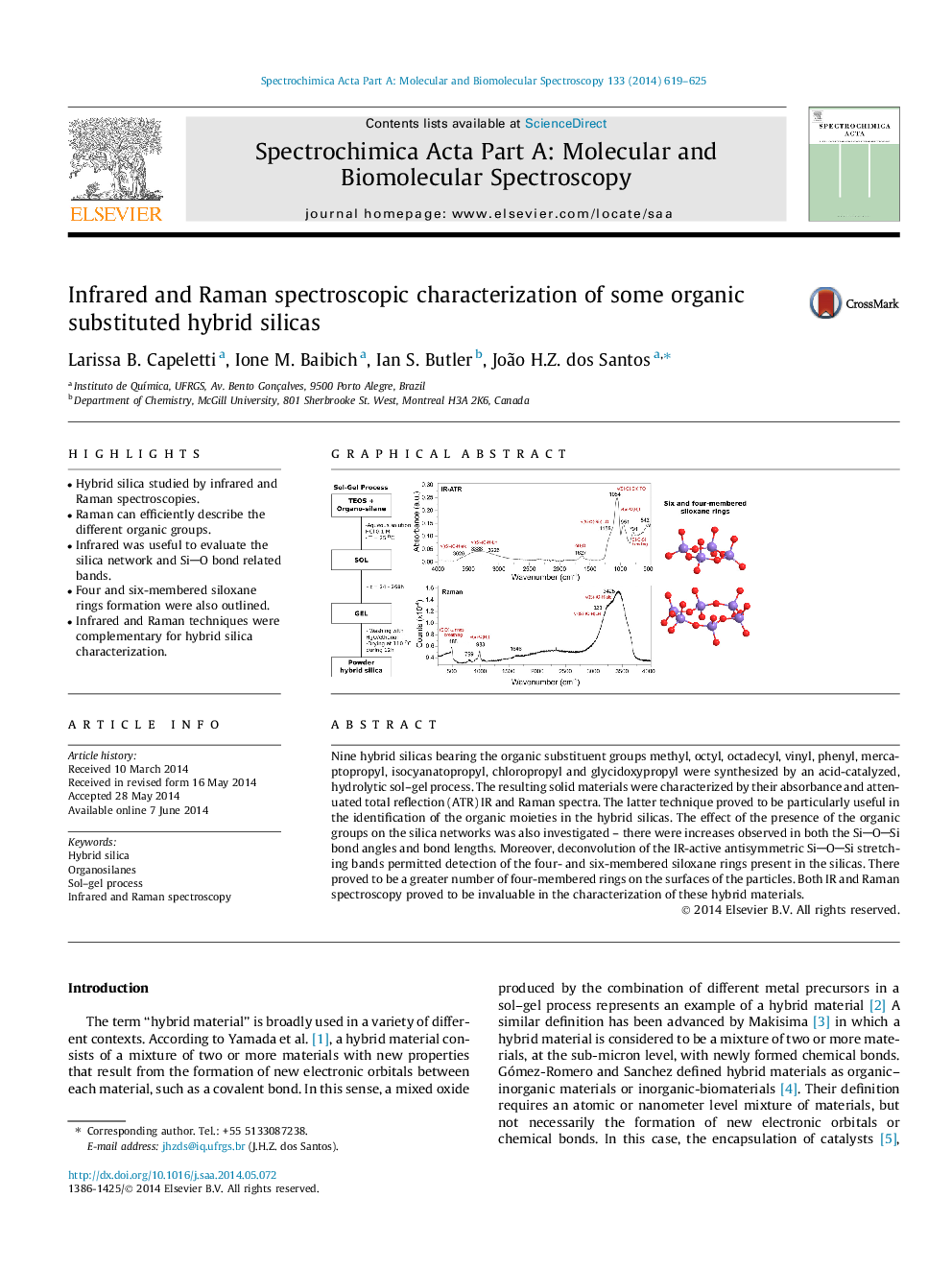
•Hybrid silica studied by infrared and Raman spectroscopies.•Raman can efficiently describe the different organic groups.•Infrared was useful to evaluate the silica network and SiO bond related bands.•Four and six-membered siloxane rings formation were also outlined.•Infrared and Raman techniques were complementary for hybrid silica characterization.
Nine hybrid silicas bearing the organic substituent groups methyl, octyl, octadecyl, vinyl, phenyl, mercaptopropyl, isocyanatopropyl, chloropropyl and glycidoxypropyl were synthesized by an acid-catalyzed, hydrolytic sol–gel process. The resulting solid materials were characterized by their absorbance and attenuated total reflection (ATR) IR and Raman spectra. The latter technique proved to be particularly useful in the identification of the organic moieties in the hybrid silicas. The effect of the presence of the organic groups on the silica networks was also investigated – there were increases observed in both the SiOSi bond angles and bond lengths. Moreover, deconvolution of the IR-active antisymmetric SiOSi stretching bands permitted detection of the four- and six-membered siloxane rings present in the silicas. There proved to be a greater number of four-membered rings on the surfaces of the particles. Both IR and Raman spectroscopy proved to be invaluable in the characterization of these hybrid materials.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide