| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233818 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 4 Pages |
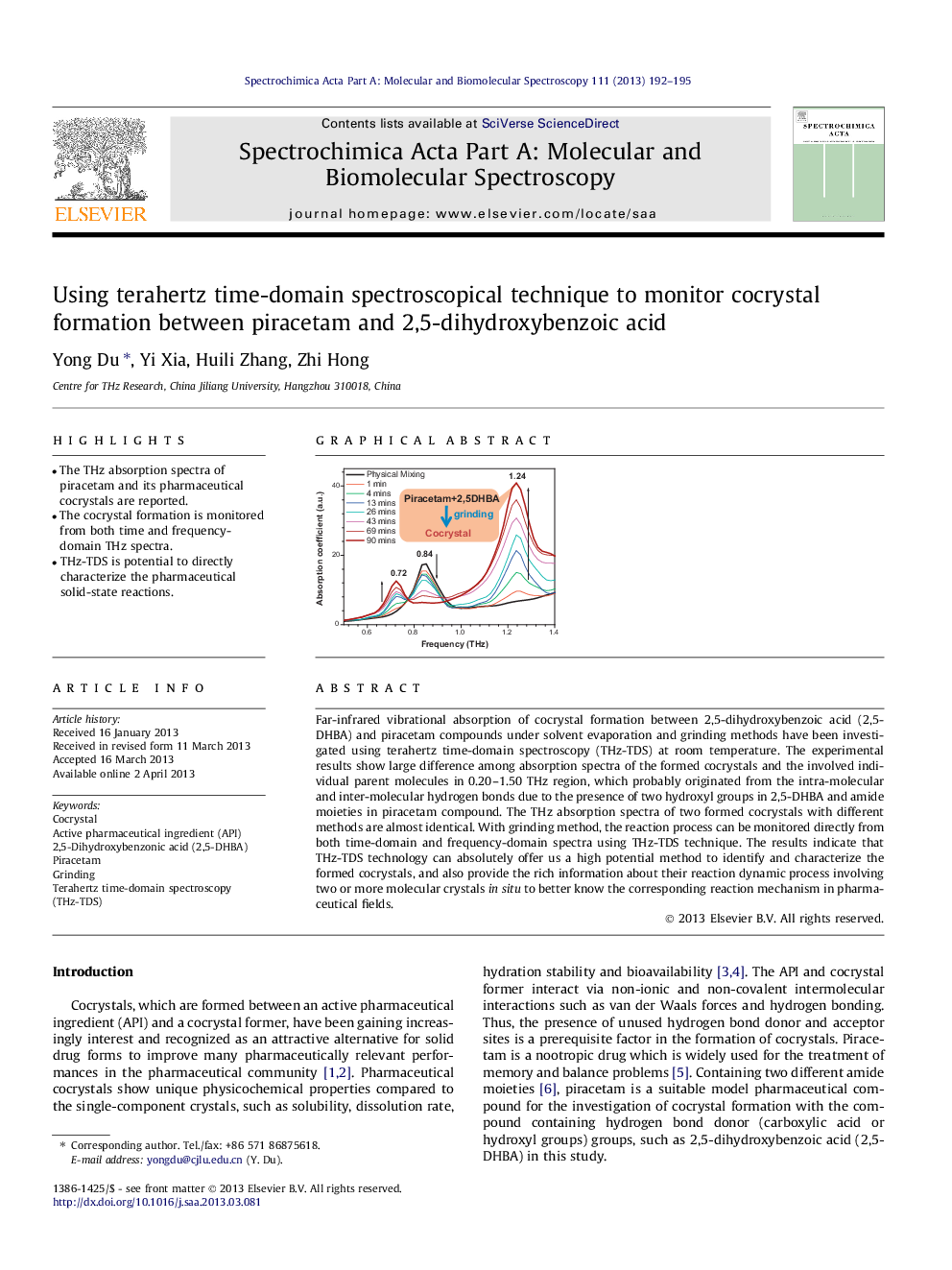
•The THz absorption spectra of piracetam and its pharmaceutical cocrystals are reported.•The cocrystal formation is monitored from both time and frequency-domain THz spectra.•THz-TDS is potential to directly characterize the pharmaceutical solid-state reactions.
Far-infrared vibrational absorption of cocrystal formation between 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (2,5-DHBA) and piracetam compounds under solvent evaporation and grinding methods have been investigated using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) at room temperature. The experimental results show large difference among absorption spectra of the formed cocrystals and the involved individual parent molecules in 0.20–1.50 THz region, which probably originated from the intra-molecular and inter-molecular hydrogen bonds due to the presence of two hydroxyl groups in 2,5-DHBA and amide moieties in piracetam compound. The THz absorption spectra of two formed cocrystals with different methods are almost identical. With grinding method, the reaction process can be monitored directly from both time-domain and frequency-domain spectra using THz-TDS technique. The results indicate that THz-TDS technology can absolutely offer us a high potential method to identify and characterize the formed cocrystals, and also provide the rich information about their reaction dynamic process involving two or more molecular crystals in situ to better know the corresponding reaction mechanism in pharmaceutical fields.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide