| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233950 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 6 Pages |
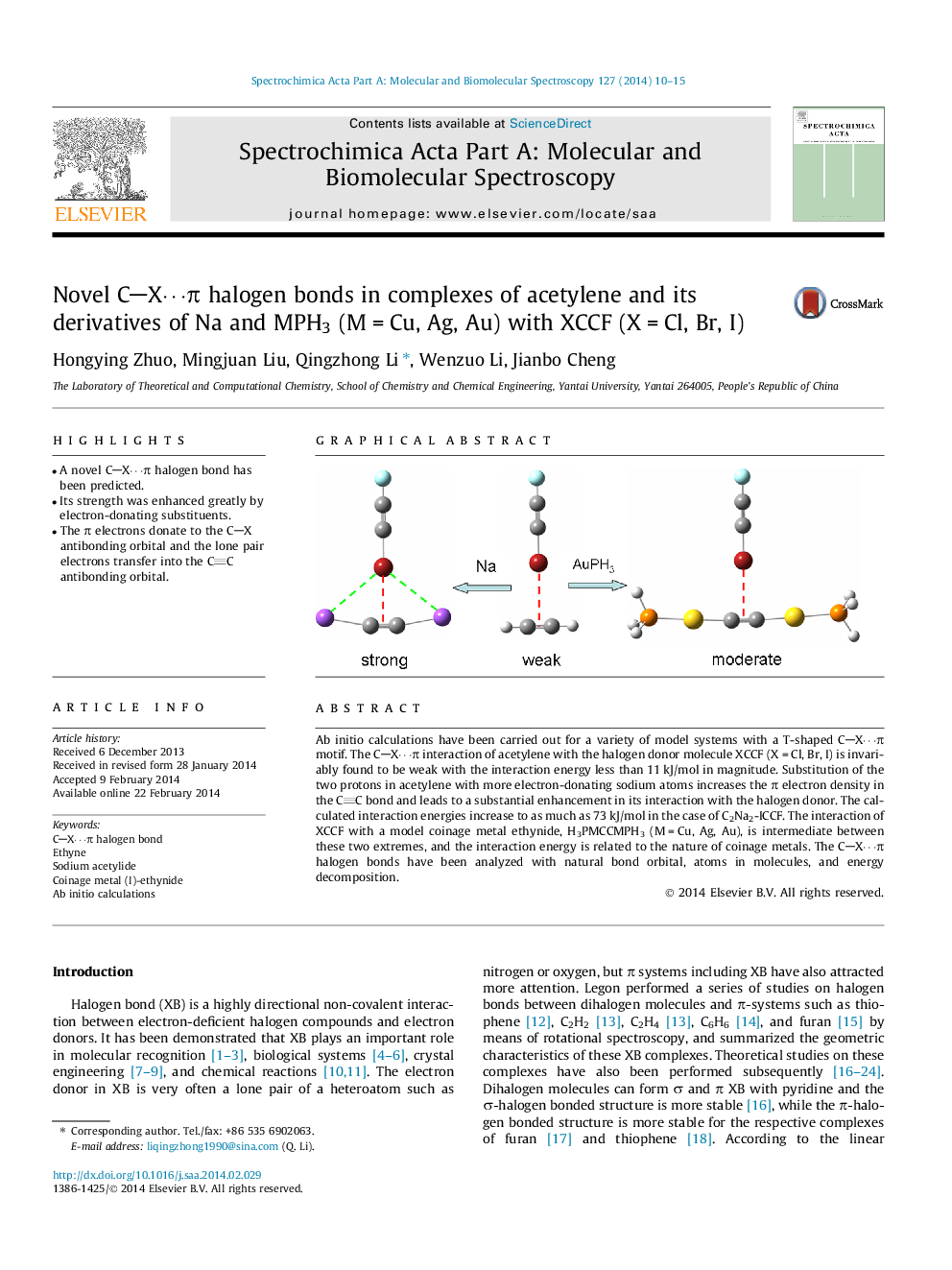
•A novel CX⋯π halogen bond has been predicted.•Its strength was enhanced greatly by electron-donating substituents.•The π electrons donate to the CX antibonding orbital and the lone pair electrons transfer into the CC antibonding orbital.
Ab initio calculations have been carried out for a variety of model systems with a T-shaped CX⋯π motif. The CX⋯π interaction of acetylene with the halogen donor molecule XCCF (X = Cl, Br, I) is invariably found to be weak with the interaction energy less than 11 kJ/mol in magnitude. Substitution of the two protons in acetylene with more electron-donating sodium atoms increases the π electron density in the CC bond and leads to a substantial enhancement in its interaction with the halogen donor. The calculated interaction energies increase to as much as 73 kJ/mol in the case of C2Na2-ICCF. The interaction of XCCF with a model coinage metal ethynide, H3PMCCMPH3 (M = Cu, Ag, Au), is intermediate between these two extremes, and the interaction energy is related to the nature of coinage metals. The CX⋯π halogen bonds have been analyzed with natural bond orbital, atoms in molecules, and energy decomposition.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide