| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1233964 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2014 | 8 Pages |
•Complexes of reserpine and quinidine with chloranilic acid were obtained.•IR measurements confirmed the existing of intermolecular H-bond.•Microstructure properties of the reported complexes were observed.•Debye–Scherrer equation indicates that complexes are in the nano-range.•One of the complex exhibited a remarkable morphology feature.
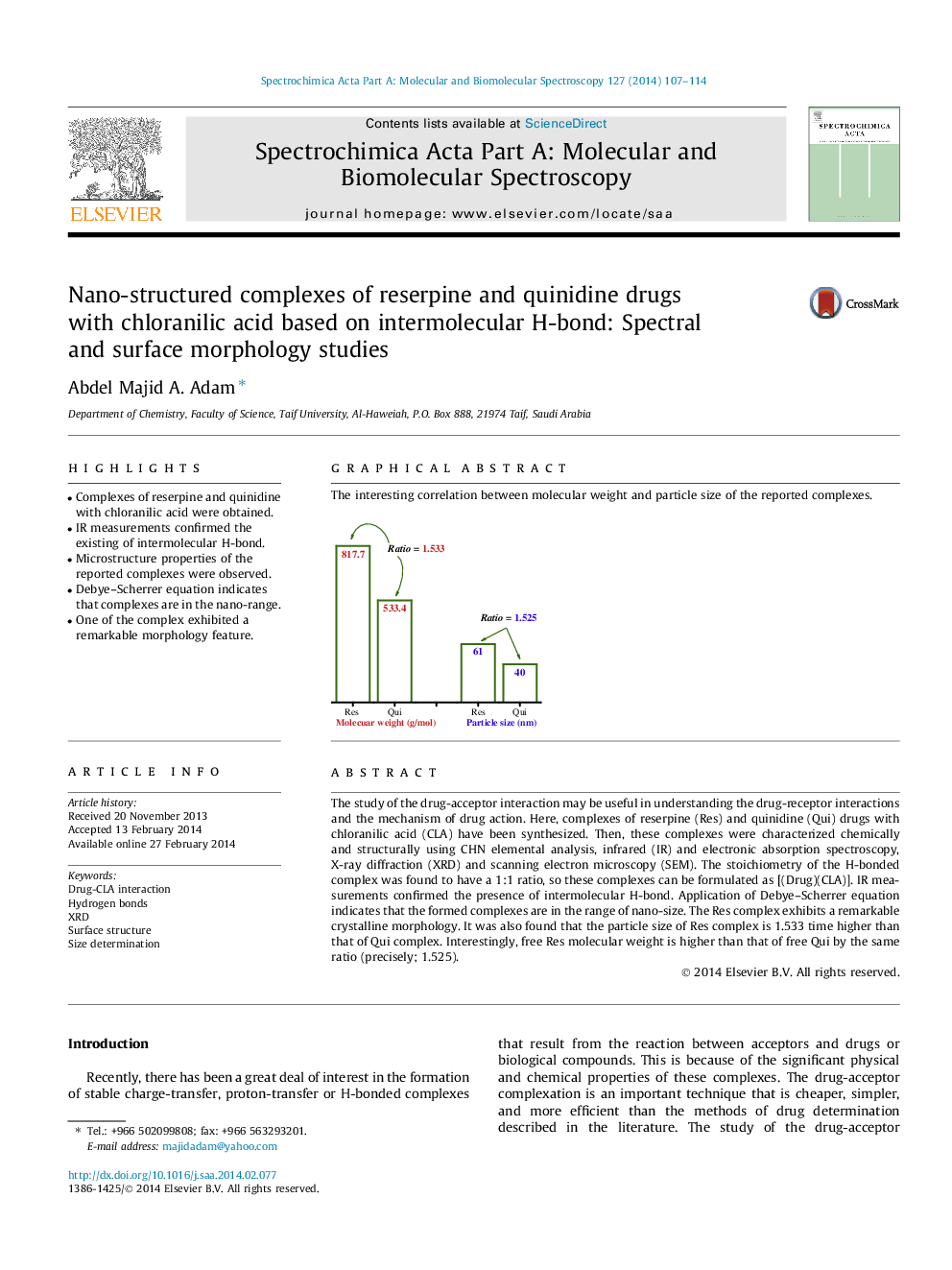
The study of the drug-acceptor interaction may be useful in understanding the drug-receptor interactions and the mechanism of drug action. Here, complexes of reserpine (Res) and quinidine (Qui) drugs with chloranilic acid (CLA) have been synthesized. Then, these complexes were characterized chemically and structurally using CHN elemental analysis, infrared (IR) and electronic absorption spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The stoichiometry of the H-bonded complex was found to have a 1:1 ratio, so these complexes can be formulated as [(Drug)(CLA)]. IR measurements confirmed the presence of intermolecular H-bond. Application of Debye–Scherrer equation indicates that the formed complexes are in the range of nano-size. The Res complex exhibits a remarkable crystalline morphology. It was also found that the particle size of Res complex is 1.533 time higher than that of Qui complex. Interestingly, free Res molecular weight is higher than that of free Qui by the same ratio (precisely; 1.525).
Graphical abstractThe interesting correlation between molecular weight and particle size of the reported complexes.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide