| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1234103 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 6 Pages |
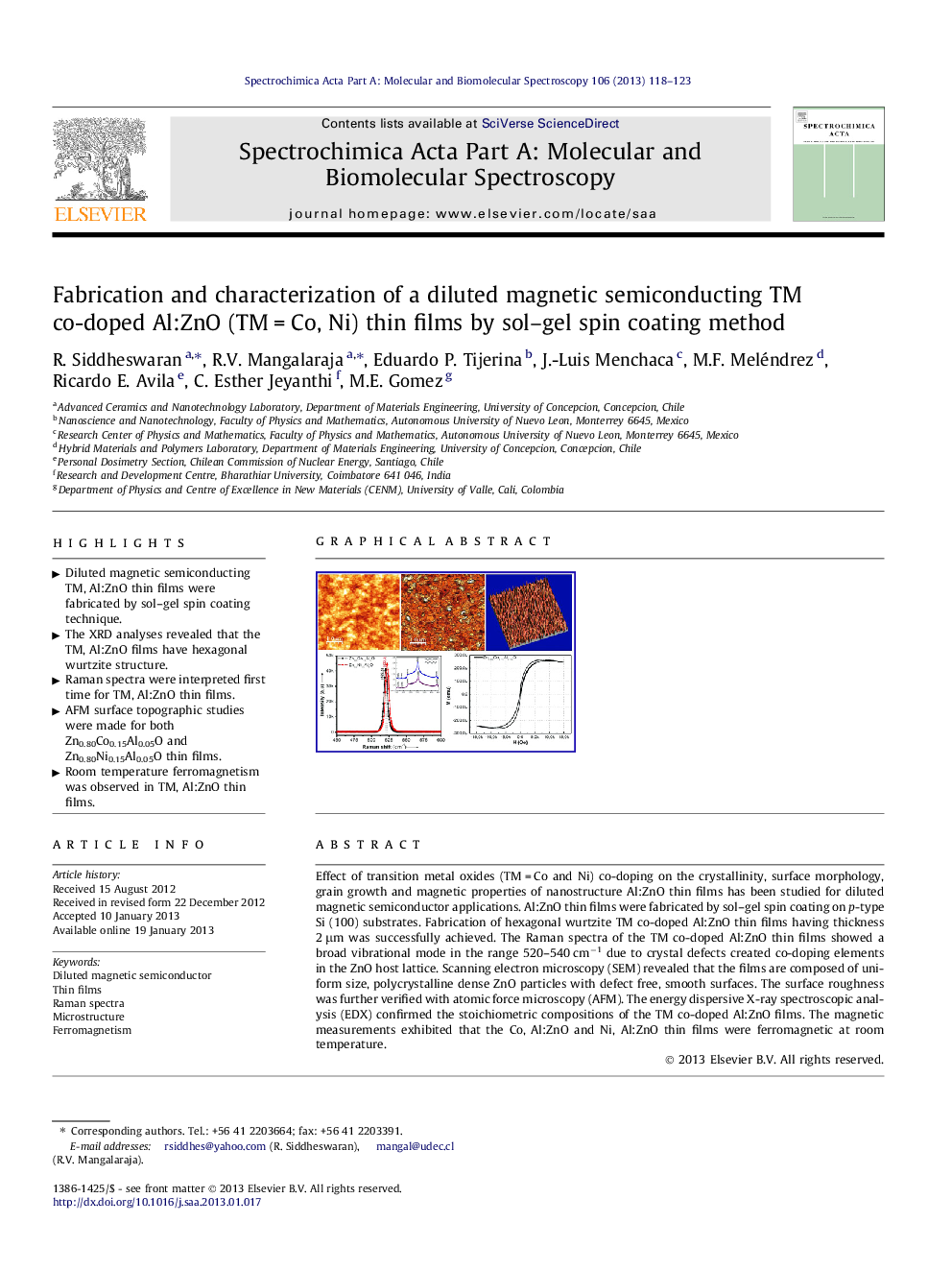
Effect of transition metal oxides (TM = Co and Ni) co-doping on the crystallinity, surface morphology, grain growth and magnetic properties of nanostructure Al:ZnO thin films has been studied for diluted magnetic semiconductor applications. Al:ZnO thin films were fabricated by sol–gel spin coating on p-type Si (100) substrates. Fabrication of hexagonal wurtzite TM co-doped Al:ZnO thin films having thickness 2 μm was successfully achieved. The Raman spectra of the TM co-doped Al:ZnO thin films showed a broad vibrational mode in the range 520–540 cm−1 due to crystal defects created co-doping elements in the ZnO host lattice. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed that the films are composed of uniform size, polycrystalline dense ZnO particles with defect free, smooth surfaces. The surface roughness was further verified with atomic force microscopy (AFM). The energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopic analysis (EDX) confirmed the stoichiometric compositions of the TM co-doped Al:ZnO films. The magnetic measurements exhibited that the Co, Al:ZnO and Ni, Al:ZnO thin films were ferromagnetic at room temperature.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Diluted magnetic semiconducting TM, Al:ZnO thin films were fabricated by sol–gel spin coating technique. ► The XRD analyses revealed that the TM, Al:ZnO films have hexagonal wurtzite structure. ► Raman spectra were interpreted first time for TM, Al:ZnO thin films. ► AFM surface topographic studies were made for both Zn0.80Co0.15Al0.05O and Zn0.80Ni0.15Al0.05O thin films. ► Room temperature ferromagnetism was observed in TM, Al:ZnO thin films.