| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1234109 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2013 | 5 Pages |
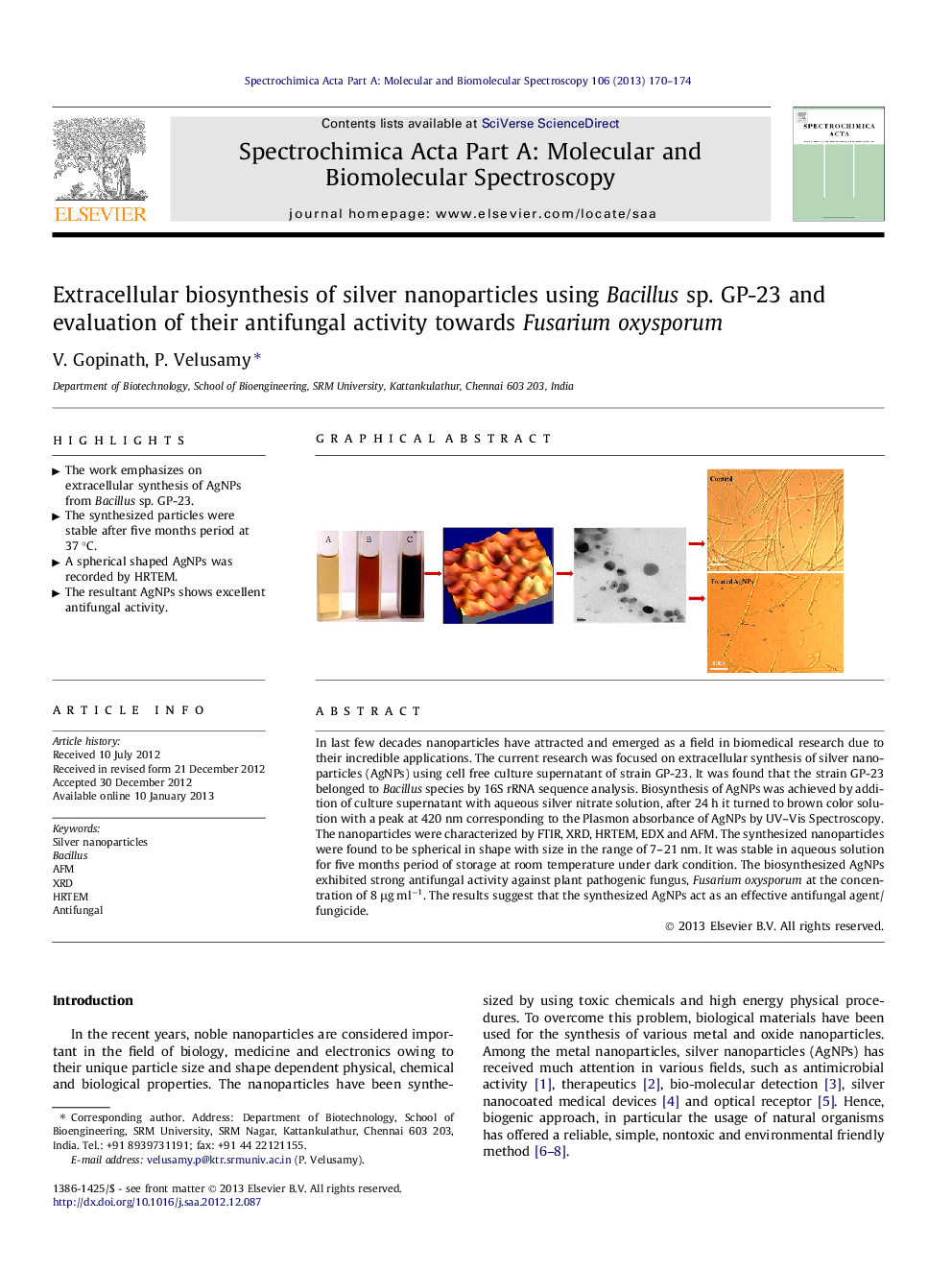
In last few decades nanoparticles have attracted and emerged as a field in biomedical research due to their incredible applications. The current research was focused on extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using cell free culture supernatant of strain GP-23. It was found that the strain GP-23 belonged to Bacillus species by 16S rRNA sequence analysis. Biosynthesis of AgNPs was achieved by addition of culture supernatant with aqueous silver nitrate solution, after 24 h it turned to brown color solution with a peak at 420 nm corresponding to the Plasmon absorbance of AgNPs by UV–Vis Spectroscopy. The nanoparticles were characterized by FTIR, XRD, HRTEM, EDX and AFM. The synthesized nanoparticles were found to be spherical in shape with size in the range of 7–21 nm. It was stable in aqueous solution for five months period of storage at room temperature under dark condition. The biosynthesized AgNPs exhibited strong antifungal activity against plant pathogenic fungus, Fusarium oxysporum at the concentration of 8 μg ml−1. The results suggest that the synthesized AgNPs act as an effective antifungal agent/fungicide.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► The work emphasizes on extracellular synthesis of AgNPs from Bacillus sp. GP-23. ► The synthesized particles were stable after five months period at 37 °C. ► A spherical shaped AgNPs was recorded by HRTEM. ► The resultant AgNPs shows excellent antifungal activity.