| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1234410 | Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy | 2012 | 6 Pages |
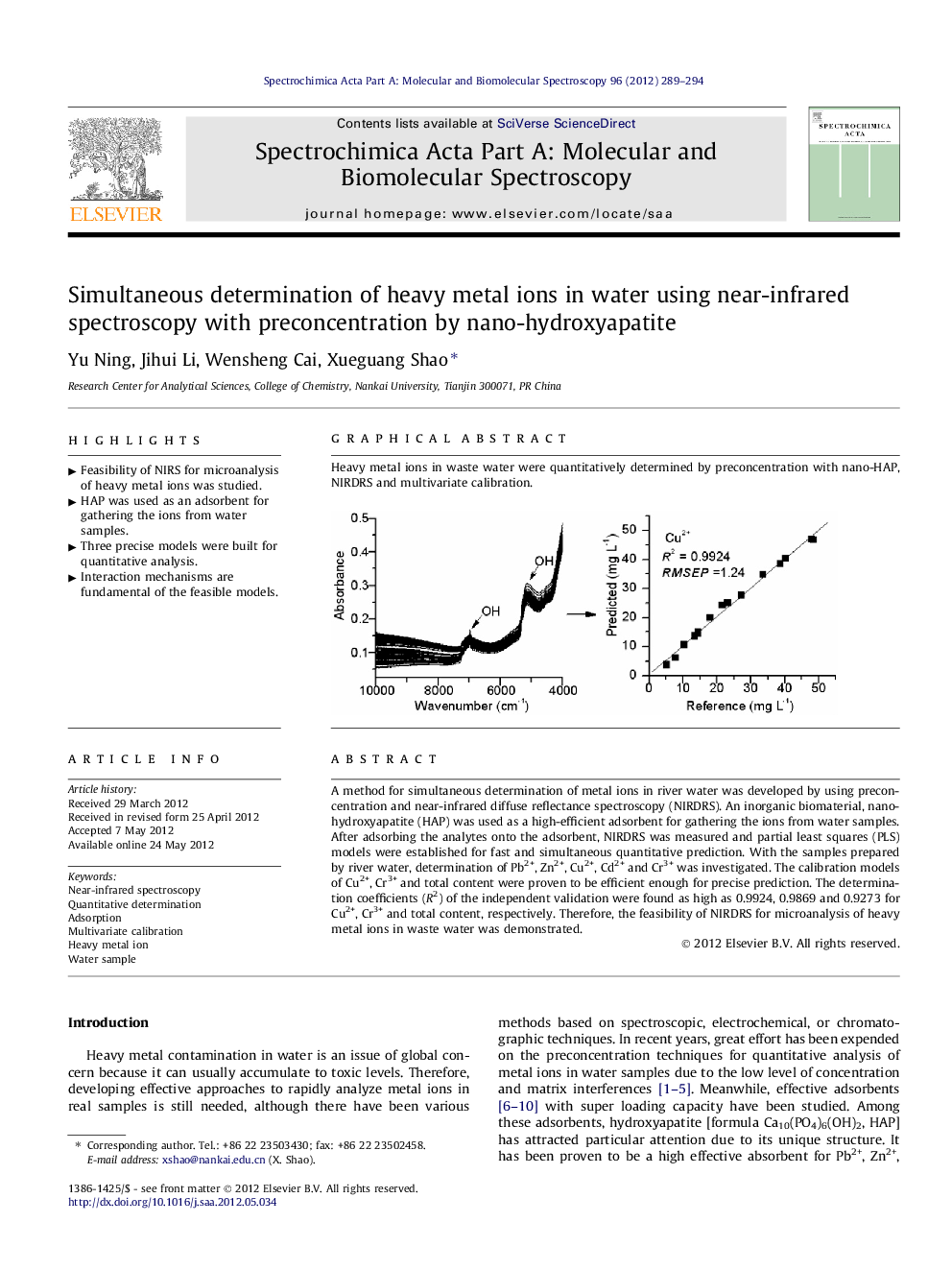
A method for simultaneous determination of metal ions in river water was developed by using preconcentration and near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (NIRDRS). An inorganic biomaterial, nano-hydroxyapatite (HAP) was used as a high-efficient adsorbent for gathering the ions from water samples. After adsorbing the analytes onto the adsorbent, NIRDRS was measured and partial least squares (PLS) models were established for fast and simultaneous quantitative prediction. With the samples prepared by river water, determination of Pb2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, Cd2+ and Cr3+ was investigated. The calibration models of Cu2+, Cr3+ and total content were proven to be efficient enough for precise prediction. The determination coefficients (R2) of the independent validation were found as high as 0.9924, 0.9869 and 0.9273 for Cu2+, Cr3+ and total content, respectively. Therefore, the feasibility of NIRDRS for microanalysis of heavy metal ions in waste water was demonstrated.
Graphical abstractHeavy metal ions in waste water were quantitatively determined by preconcentration with nano-HAP, NIRDRS and multivariate calibration.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Feasibility of NIRS for microanalysis of heavy metal ions was studied. ► HAP was used as an adsorbent for gathering the ions from water samples. ► Three precise models were built for quantitative analysis. ► Interaction mechanisms are fundamental of the feasible models.